- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Maintenance Practices Ensure Long-Term Reliability of Pipeline Pumps?
Introduction: The Importance of Pipeline Pump Maintenance
Pipeline pumps are critical components in industrial, municipal, and commercial fluid transport systems. Proper maintenance ensures reliable performance, minimizes downtime, and extends the pump’s operational life. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced efficiency, costly repairs, and even catastrophic failures. This article explores the key maintenance practices that guarantee long-term reliability of pipeline pumps.
Regular Inspection and Monitoring
Routine inspections are the first line of defense against pump failure. Regular monitoring allows early detection of potential issues, such as leaks, unusual vibrations, or temperature anomalies. Operators should implement a structured inspection schedule, which includes checking bearings, seals, couplings, and alignment.
Visual Inspection
Visual inspections help identify leaks, corrosion, or physical damage to the pump and pipeline. Inspecting the pump casing, inlet and outlet connections, and support structures ensures that minor issues are addressed before they escalate.
Vibration and Noise Monitoring
Excessive vibration or unusual noise can indicate misalignment, worn bearings, or cavitation. Using vibration sensors and regular acoustic monitoring allows maintenance teams to detect issues early, reducing the risk of sudden failures and ensuring smooth operation.
Lubrication and Bearing Care
Proper lubrication is essential for the longevity of bearings and rotating components. Over-lubrication can cause overheating, while under-lubrication leads to excessive wear. Maintenance schedules should specify lubrication types, quantities, and intervals based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and operating conditions.
Bearing Inspection and Replacement
Bearings should be periodically inspected for signs of wear, vibration, or temperature increase. Replacing bearings at the correct interval prevents sudden breakdowns and avoids collateral damage to other pump components.

Seal Maintenance and Leakage Prevention
Seals prevent fluid leakage and protect the pump’s internal components from contamination. Mechanical seals require regular inspection for wear, cracks, or misalignment. Replacing worn seals promptly avoids fluid loss, environmental hazards, and damage to bearings and shafts.
Packing and Gland Maintenance
For pumps using packing glands, proper adjustment and lubrication are necessary to maintain tight sealing without excessive friction. Over-tightened packing increases energy consumption and wear, while loose packing leads to leakage.
Alignment and Coupling Checks
Misalignment between the pump and motor can cause vibration, excessive wear, and reduced efficiency. Regularly checking shaft alignment and coupling integrity ensures smooth power transmission and minimizes mechanical stress. Laser alignment tools or dial indicators are recommended for precise adjustments.
Coupling Inspection
Flexible and rigid couplings should be inspected for wear, cracks, or loosening. Damaged couplings can cause misalignment, vibration, and premature failure of connected components.
Fluid Quality and Filtration
The quality of the fluid being pumped significantly affects pump life. Contaminated fluids can cause erosion, corrosion, and clogging. Installing appropriate filters, strainers, or separators reduces the entry of particulates and prolongs the pump’s operational life.
Water and Chemical Treatment
For water or chemical pumping applications, monitoring pH, hardness, and chemical composition helps prevent scaling, corrosion, and chemical damage. Proper treatment ensures that internal components remain in optimal condition.
Pump Operation and Load Management
Operating the pump within its designed flow and pressure range prevents overloading and excessive wear. Avoiding frequent starts and stops, or prolonged operation under low-flow conditions, helps maintain efficiency and reduces mechanical stress.
Monitoring Flow and Pressure
Installing flow meters and pressure sensors allows continuous monitoring of operating conditions. Deviations from normal parameters can indicate blockage, cavitation, or pump deterioration, prompting timely intervention.
Scheduled Maintenance and Record-Keeping
Structured maintenance schedules and detailed records are essential for long-term reliability. Documenting inspections, repairs, lubrication, and replacements helps identify recurring issues, plan predictive maintenance, and ensure compliance with manufacturer recommendations.
Predictive and Preventive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance uses condition monitoring data, such as vibration analysis or thermal imaging, to forecast potential failures. Preventive maintenance involves routine servicing based on operational hours or time intervals. Combining both approaches maximizes uptime and minimizes unexpected failures.
Conclusion: Ensuring Long-Term Pump Reliability
Maintaining pipeline pumps requires a holistic approach, including regular inspection, proper lubrication, seal and bearing care, alignment checks, fluid quality monitoring, and structured maintenance schedules. Implementing these practices not only ensures long-term reliability but also reduces operational costs, enhances efficiency, and prevents costly downtime. By prioritizing maintenance, operators can maximize the performance and lifespan of pipeline pumps across industrial and commercial applications.
Related Products
-

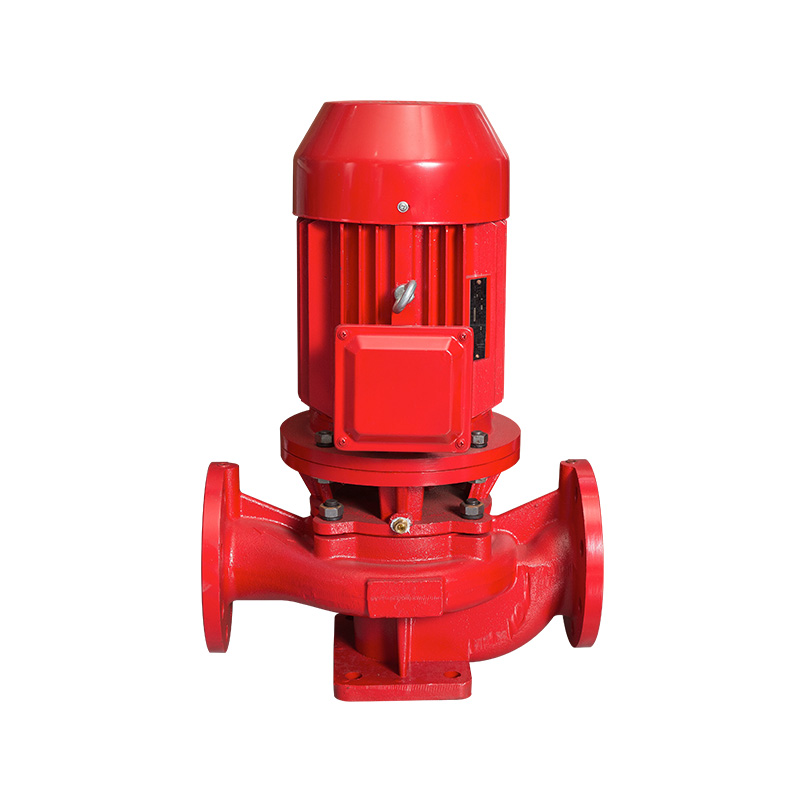
Vertical pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISG series single-stage single-suction vertical centrifugal pump is a ...
See Details -
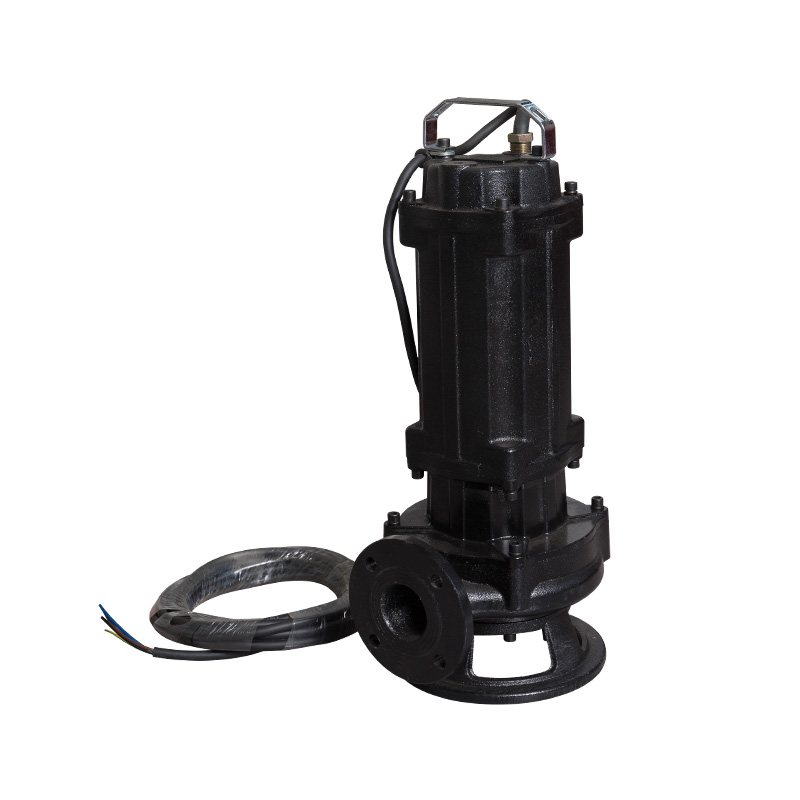

Cutting sewage pump
Cat:Sewage Pump
Cutting sewage pump is a kind of sewage pump, also called cutting pump...
See Details -
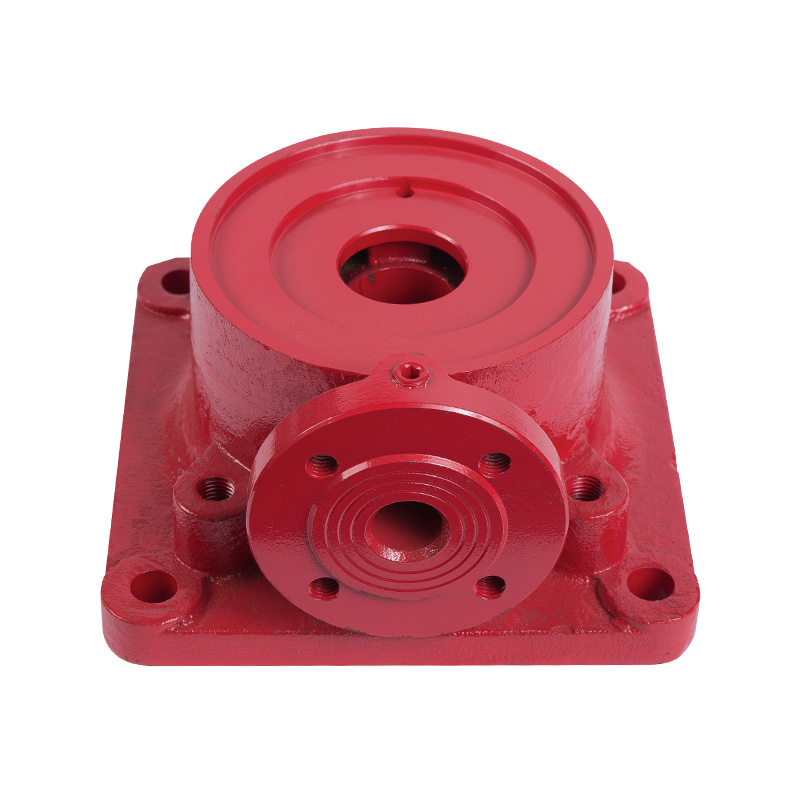

LG multi-stage pump water inlet section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The inlet section is the inlet portion of the pump and is responsible ...
See Details -
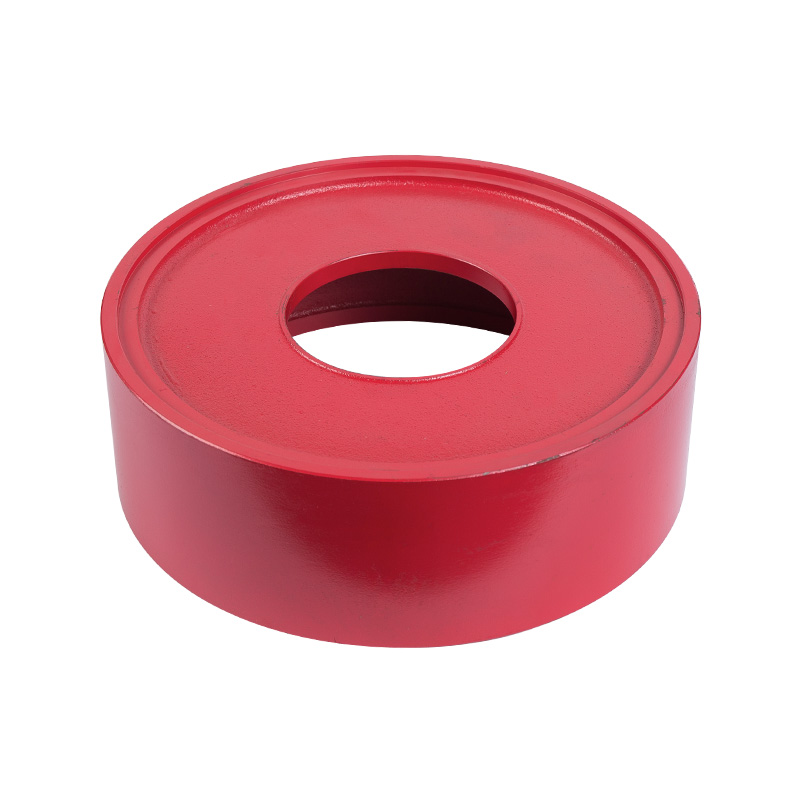

LG multi-stage pump middle section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The middle section is the main part of the pump body, responsible for ...
See Details -
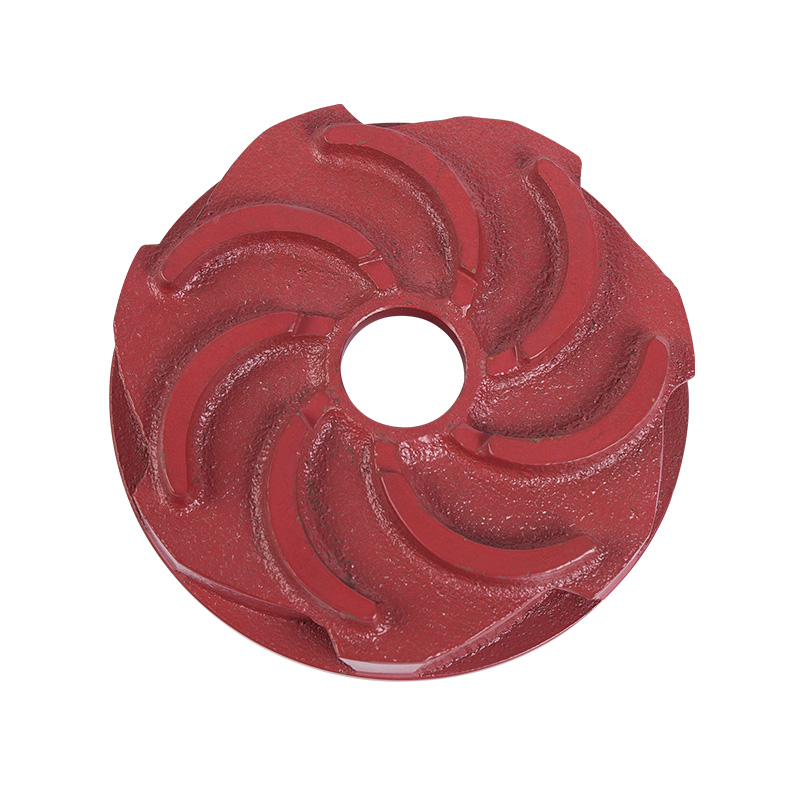

LG multi-stage pump guide vane
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
A guide vane is a guiding device located at the impeller inlet that gu...
See Details -
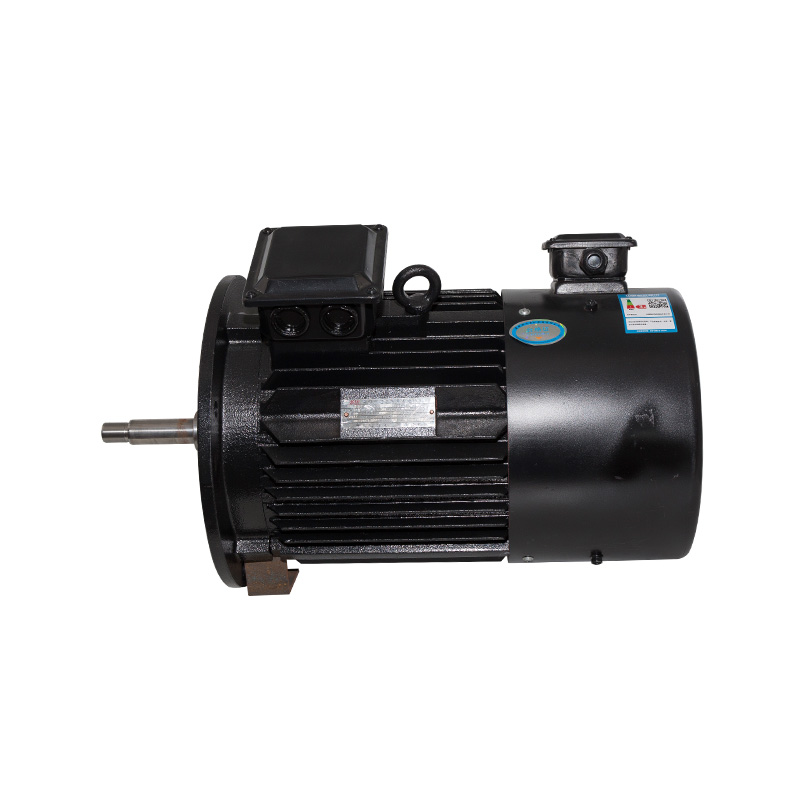

B14/B5 Vertical inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
A type of adjustable speed motor that can control the speed of the mot...
See Details -
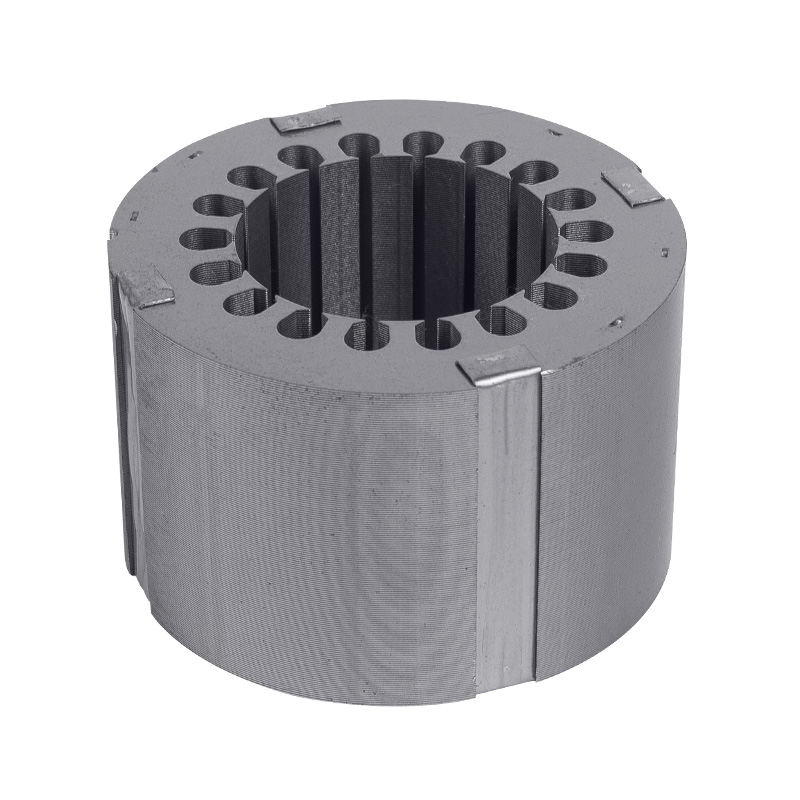

Motor core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A common motor structure, the stator is fixed by the iron core structu...
See Details -
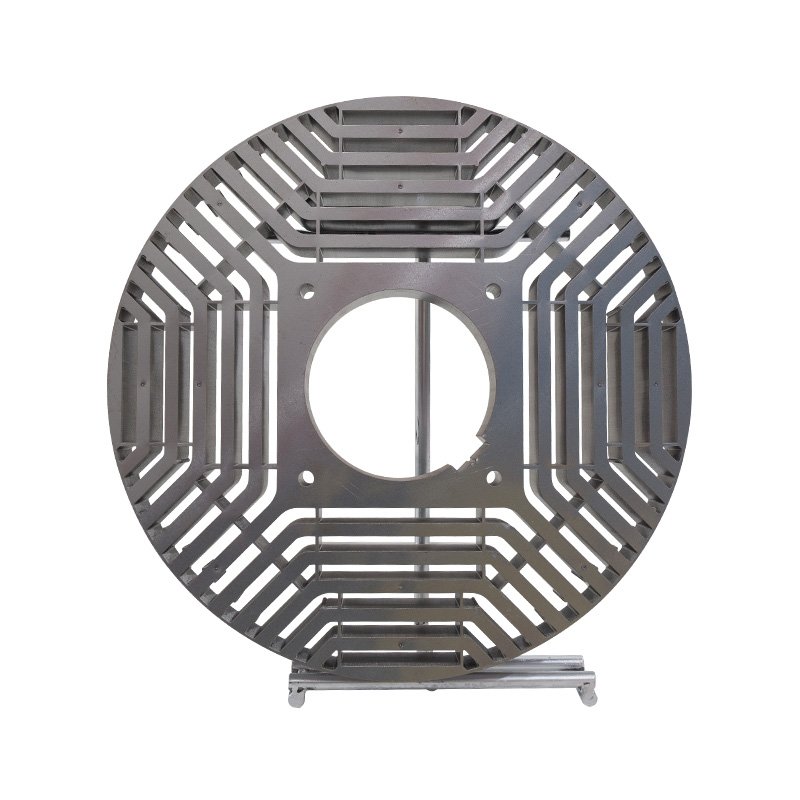

Permanent magnet core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A type of rotor core that uses a permanent magnet material to achieve ...
See Details -
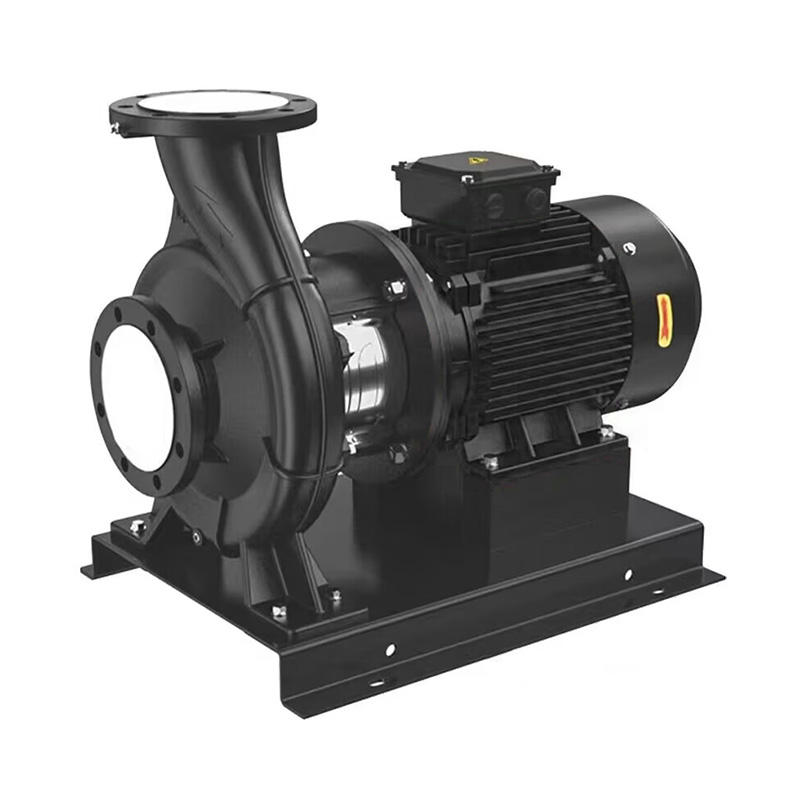

TD horizontal high-efficiency energy-saving circulation pump
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
1.TD horizontal high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump is ...
See Details -
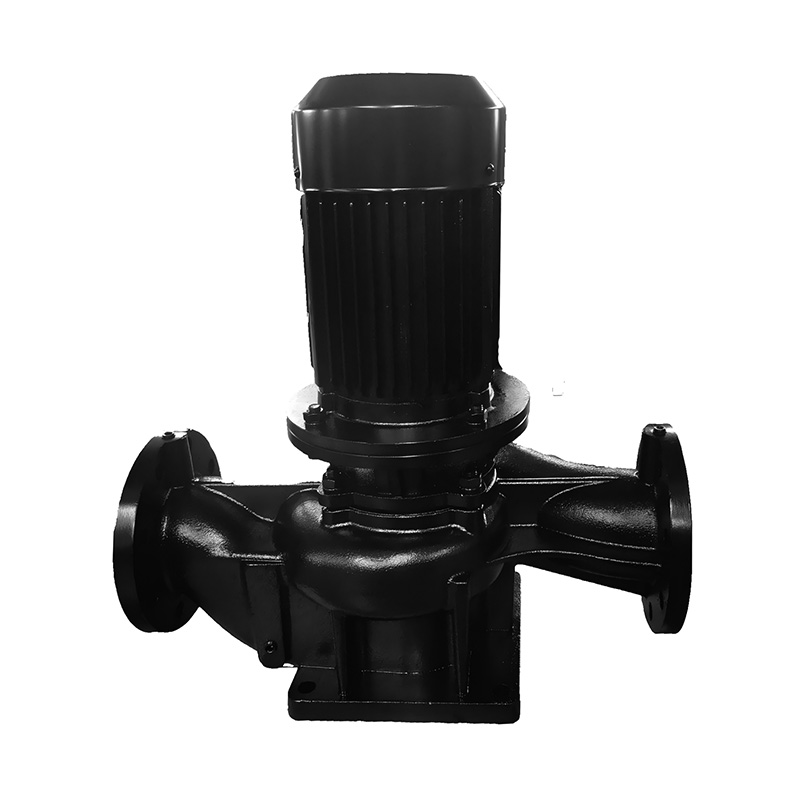

Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

