- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Factors Affect the Longevity of a Cooling Tower Circulation Pump?
The longevity of a cooling tower circulation pump is crucial for the efficient and reliable operation of cooling systems in various industrial applications. These pumps are integral to maintaining the flow of water through cooling towers, which is essential for heat dissipation in HVAC systems, power plants, and other industrial facilities. Understanding the factors that affect the lifespan of a cooling tower circulation pump can help operators prevent costly breakdowns, ensure optimal performance, and extend the pump’s operational life. In this article, we explore the various elements that influence the longevity of these vital pumps and provide practical insights for maximizing their lifespan.
Key Factors That Affect the Longevity of Cooling Tower Circulation Pumps
Several factors contribute to the longevity of cooling tower circulation pumps, from the operating conditions and maintenance practices to the design and materials used in their construction. Below, we explore these factors in detail to provide a comprehensive understanding of how each one impacts the pump's durability and performance over time.
Operating Conditions
The operating conditions in which a cooling tower circulation pump functions play a significant role in determining its lifespan. Pumps that operate under harsh conditions are subject to higher wear and tear, leading to a reduced service life. Factors like water quality, temperature, and the nature of the substances circulating through the pump all influence its durability.
- Water Quality: The presence of corrosive agents, suspended solids, and biological growth can lead to premature wear. Water with high levels of minerals can cause scaling, while water with high acidity can accelerate corrosion.
- Temperature: The temperature of the water being pumped can also impact pump longevity. Extremely high or low temperatures can stress the pump's components, leading to wear or failure. High temperatures, in particular, can cause seals and gaskets to degrade faster.
- Flow Conditions: Excessive flow rates or inconsistent water flow can result in cavitation, where vapor bubbles form and collapse within the pump. This phenomenon can cause severe damage to internal components, reducing the lifespan of the pump.

Maintenance Practices
Proper and regular maintenance is one of the most important factors influencing the longevity of a cooling tower circulation pump. Neglecting routine maintenance tasks can lead to reduced efficiency, increased wear, and ultimately a shortened lifespan for the pump. Some critical maintenance practices include:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically checking the pump for signs of wear, leaks, or damage can prevent minor issues from escalating into major failures. Inspections should cover seals, bearings, shafts, and other critical components.
- Cleaning: Pump components such as impellers and casings should be cleaned regularly to remove debris, scale, and biological buildup. This helps maintain efficient pump operation and prevents corrosion or blockages that could damage the pump.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication of moving parts such as bearings and shafts reduces friction, minimizes wear, and helps maintain smooth operation. Inadequate lubrication can cause parts to overheat and fail prematurely.
- Monitoring: Using monitoring tools such as vibration sensors, temperature sensors, and pressure gauges can provide early warnings of potential issues, allowing for corrective action before a failure occurs.
Design and Material Quality
The design and materials used in the construction of the cooling tower circulation pump significantly influence its durability. High-quality materials that resist corrosion and abrasion can extend the life of the pump, while poor-quality components may result in premature failure.
- Corrosion Resistance: Pumps that are made from materials that resist corrosion, such as stainless steel or high-grade alloys, are better equipped to handle exposure to water and chemicals over time. Corrosion-resistant coatings or linings can also be used to protect vulnerable parts.
- Wear Resistance: The internal components, particularly the impeller and bearings, should be constructed from materials that can withstand abrasive particles in the circulating water. Pumps that handle dirty or contaminated water should be equipped with robust materials to prevent erosion and failure.
- Seal Integrity: The seals in the pump help maintain pressure and prevent leaks. Seals that are designed to withstand high pressures and resist chemical degradation are essential for maintaining long-term pump performance.
Pump Sizing and System Design
Proper pump sizing and system design are essential to ensuring that the circulation pump operates within its optimal range. A pump that is either undersized or oversized for the application may experience increased stress, leading to higher rates of wear and failure.
- Oversized Pumps: Using a pump with excessive capacity can lead to inefficient operation, increased energy consumption, and excessive wear on the pump's components due to higher operating speeds.
- Undersized Pumps: A pump that is too small for the required load will need to work harder to meet the system’s demands. This can lead to overheating, cavitation, and eventual failure if the pump is not properly sized for the flow rate and pressure requirements of the system.
- System Compatibility: The design of the entire cooling system, including piping, valves, and controls, must be compatible with the pump’s specifications. Incompatible systems can lead to pressure fluctuations, cavitation, and other issues that affect pump performance and longevity.
Environmental Factors
External environmental factors can also impact the lifespan of a cooling tower circulation pump. Factors such as ambient temperature, humidity, and exposure to harsh chemicals or pollutants can accelerate wear and degradation of pump components.
- Temperature Extremes: Cooling towers are often located in outdoor environments, and extreme temperatures can impact pump performance. Freezing conditions can cause water inside the pump to expand, leading to cracks and structural damage. Similarly, very high temperatures can degrade seals and lubricants.
- Corrosive Environments: Cooling towers often operate in environments where chemicals such as chlorine, scale inhibitors, and other additives are present. Pumps exposed to these substances without proper chemical resistance can experience faster corrosion and material breakdown.
- Pollutants: Dust, debris, and other contaminants in the environment can enter the pump and cause blockages or abrasions that reduce efficiency and shorten its lifespan.
Conclusion
The longevity of a cooling tower circulation pump depends on several factors, including operating conditions, maintenance practices, material quality, proper sizing, and environmental influences. By understanding and addressing these factors, operators can significantly extend the service life of their pumps, improving efficiency, reducing maintenance costs, and ensuring the reliable operation of cooling systems. Regular inspections, routine maintenance, and careful system design are key to preventing premature pump failure and ensuring optimal performance over the long term.
Related Products
-

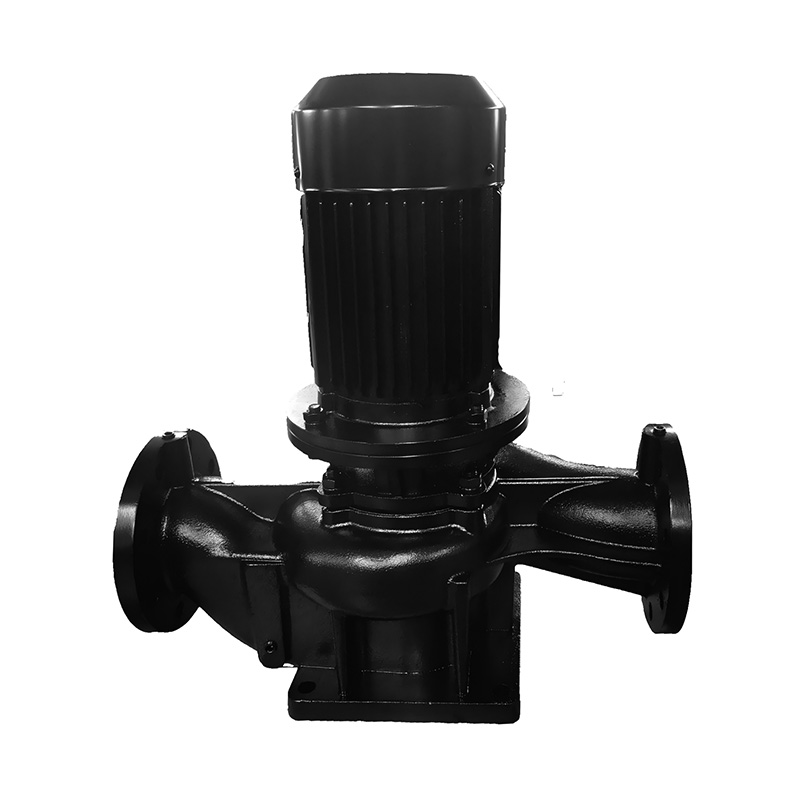
Horizontal pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISW series single-stage single-suction horizontal centrifugal pumps ar...
See Details -

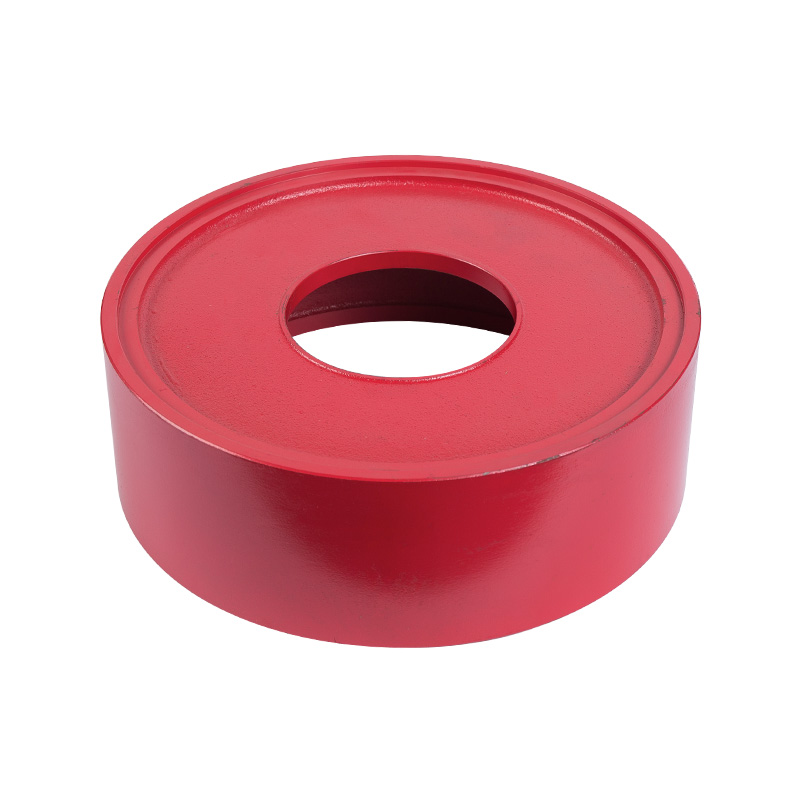
Sewage pump tank
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The oil in the oil chamber, in addition to lubricating the mechanical ...
See Details -

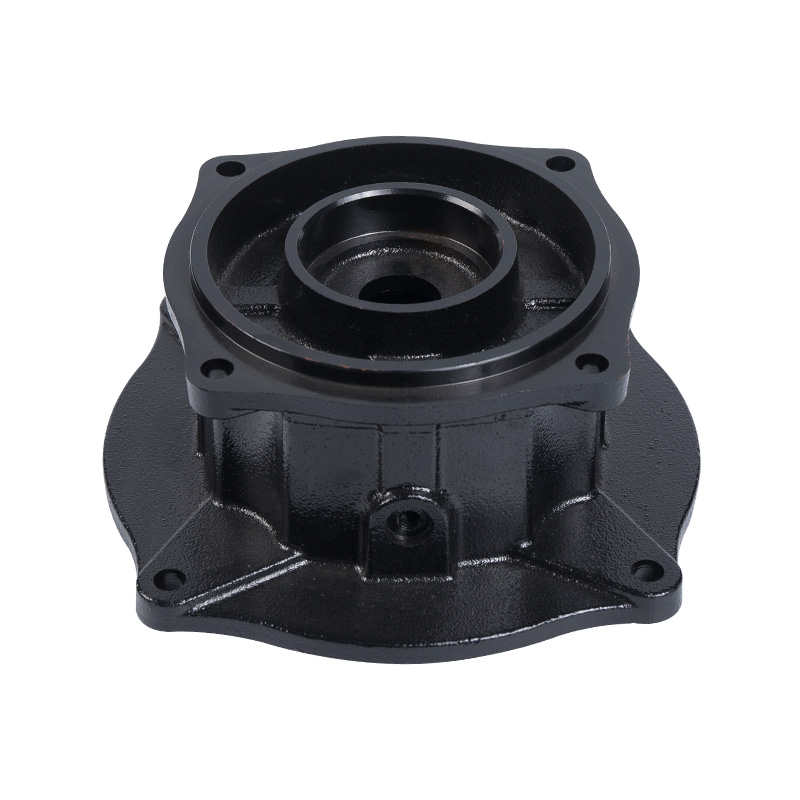
LG multi-stage pump middle section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The middle section is the main part of the pump body, responsible for ...
See Details -
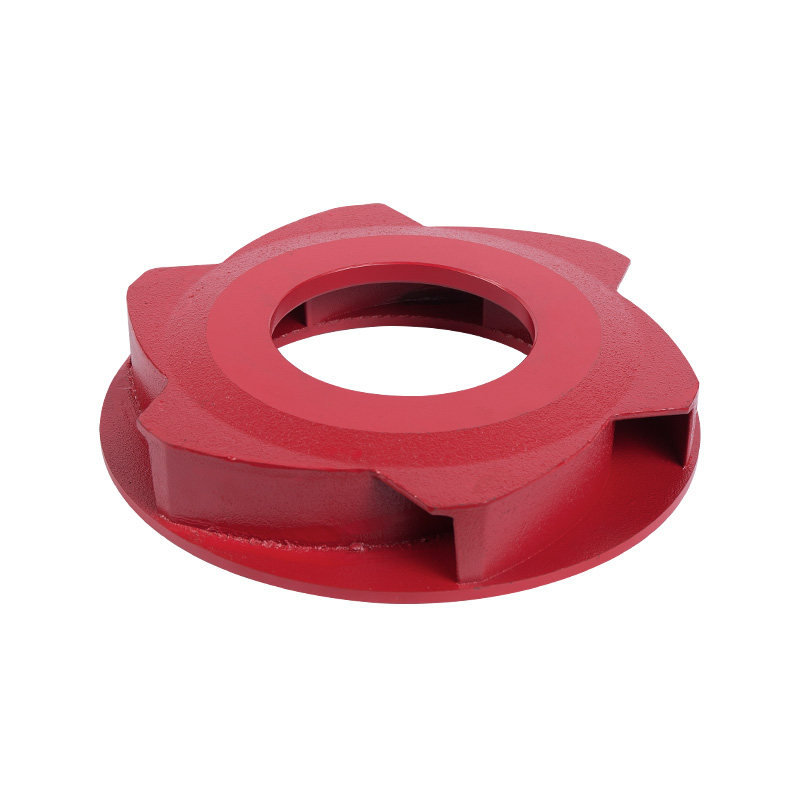

LG multistage pump cast iron impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Cast iron impeller is one of the key components of the pump, which pre...
See Details -
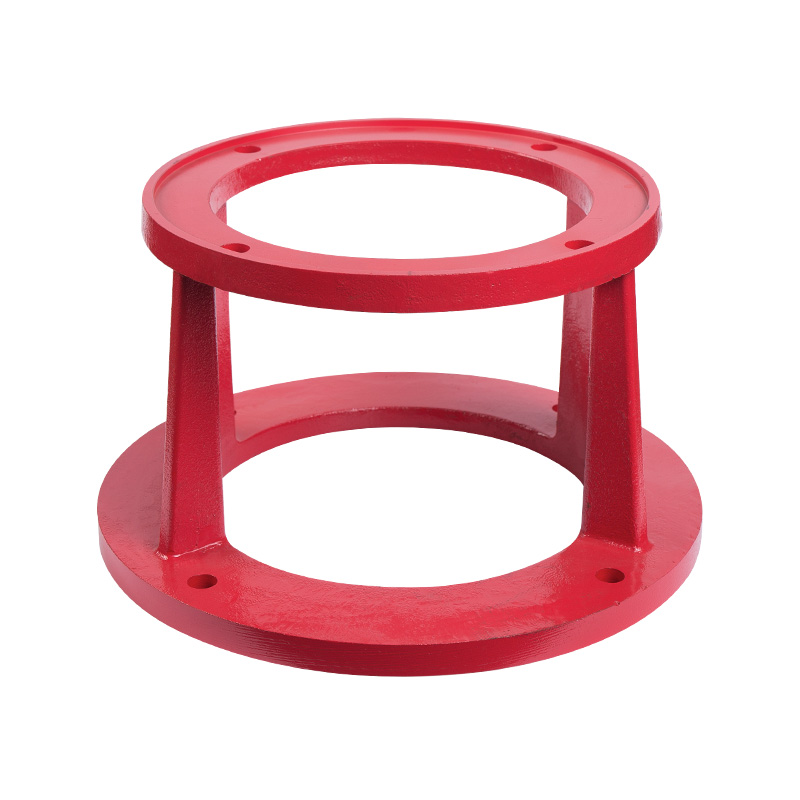

LG multi-stage pump motor bracket
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Motor bracket is a support part used to fix the motor and connect the ...
See Details -
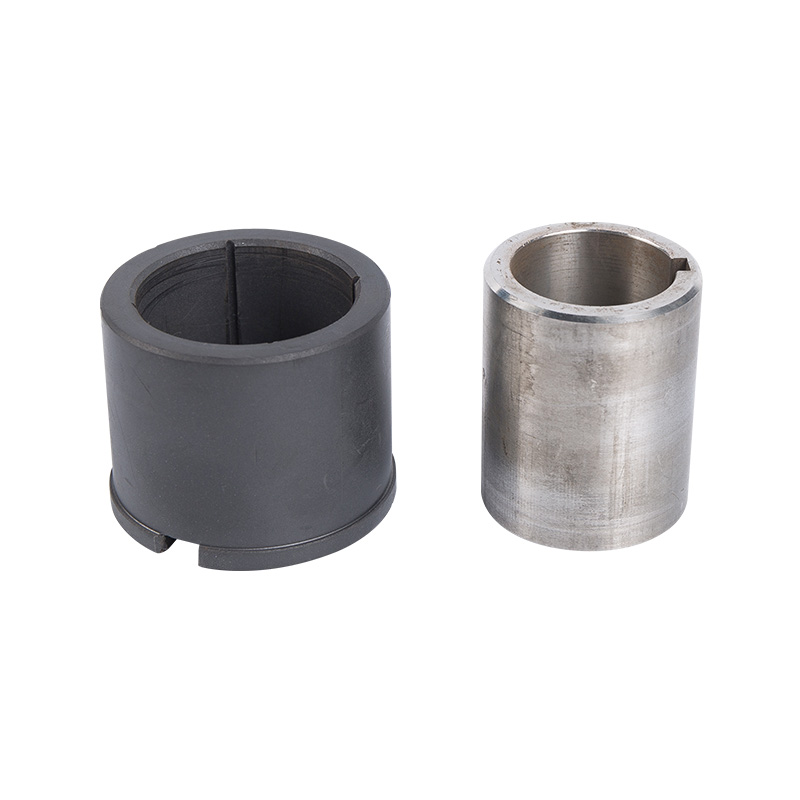

Stainless steel LG multi-stage pump bearing sleeve
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless Steel Bearing Sleeves are bearing sleeves made of stainless ...
See Details -
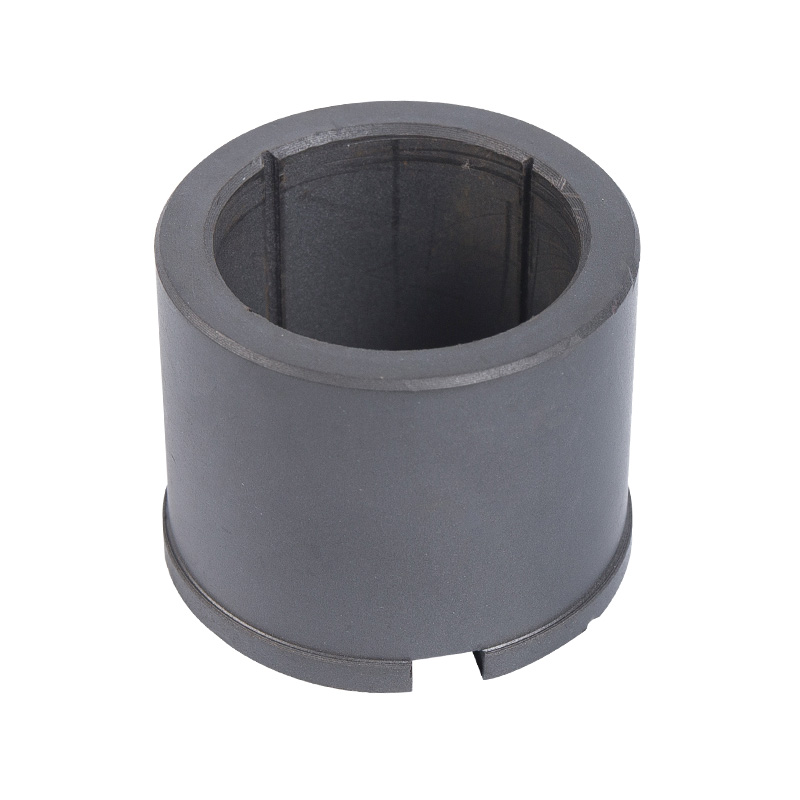

LG multi-stage pump water bearing
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Water bearings are a special type of bearings commonly used in multi-s...
See Details -
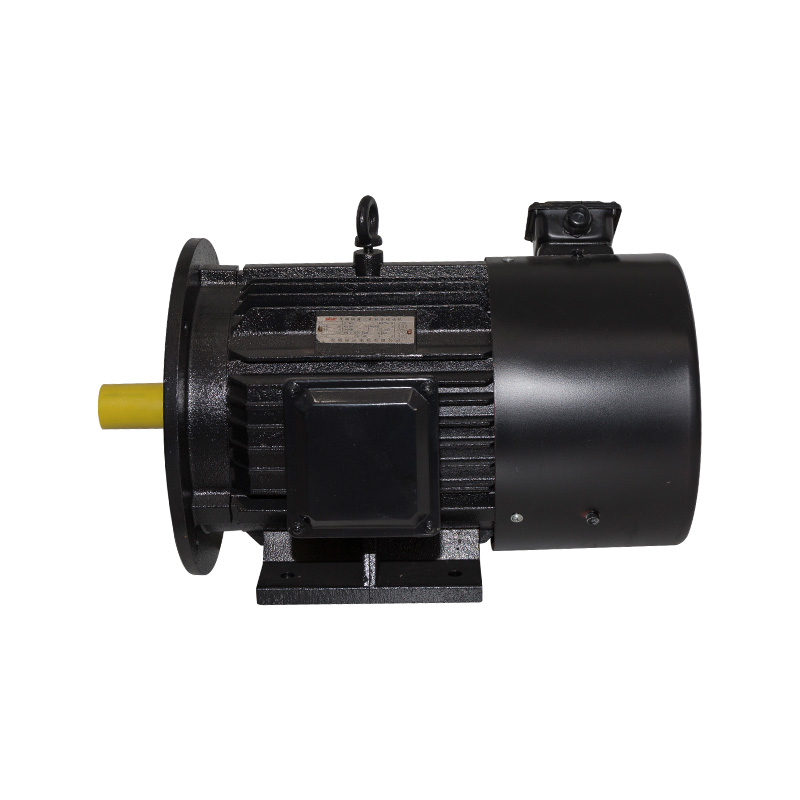

B3/B35 Horizontal inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -
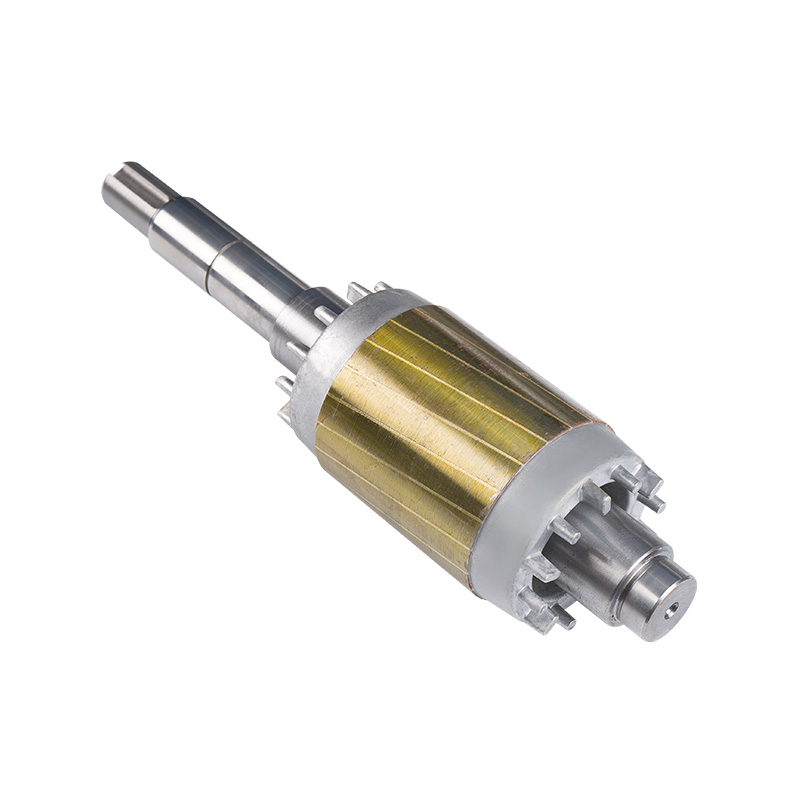

Finished rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
The rotor of a motor refers to the rotating part, which contains the r...
See Details -

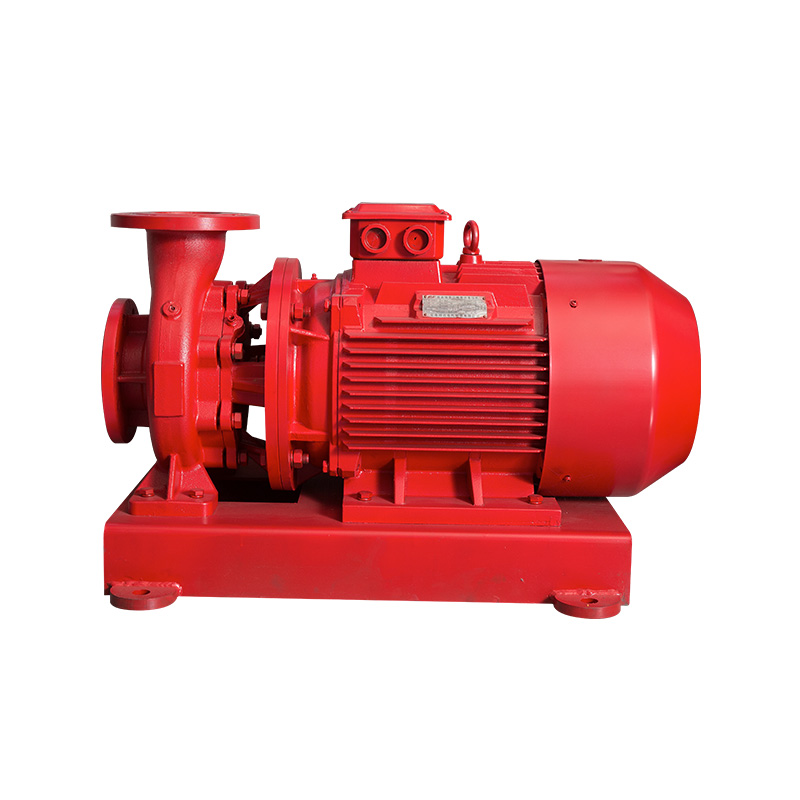
Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

