- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Are the Common Causes of Vibration in Pipeline Pumps and How to Fix Them?
Pipeline pumps are integral components in a wide variety of fluid transport systems. They are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, chemical processing, and HVAC systems, where they help transfer liquids and gases across pipelines. While pipeline pumps are designed for durability and efficiency, they can develop issues over time, with vibration being one of the most common. Vibration in pipeline pumps can lead to reduced operational efficiency, premature wear, and even catastrophic failure if not properly addressed. Understanding the common causes of vibration in pipeline pumps and knowing how to fix them is essential for maintaining smooth operation and ensuring the longevity of the system. This article explores the common causes of vibration in pipeline pumps and offers solutions for addressing these issues.
1. Imbalance in the Rotating Components
One of the most frequent causes of vibration in pipeline pumps is an imbalance in the rotating components, such as the impeller, rotor, or shaft. These components are critical for the movement of fluids through the system, and any imbalance can lead to excessive vibration.
Causes of Imbalance:
- Wear and Tear: Over time, components like the impeller and rotor may wear unevenly, leading to an imbalance in the pump.
- Manufacturing Defects: If the pump components were not precisely manufactured or balanced during production, the system may experience vibrations.
- Deposits and Build-Up: Sediment, debris, or scaling can accumulate on the rotating components, leading to imbalances.
How to Fix It:
- Regular Inspections: Perform regular inspections of rotating components to detect any wear or buildup. Cleaning the impeller and rotor surfaces can help prevent the accumulation of debris.
- Balancing the Pump: If an imbalance is detected, the pump should be shut down and the rotating components rebalanced. This can be done either by adding weights to the components or by removing material from the heavier side of the rotor.
- Replacing Worn Parts: If components are significantly worn or damaged, replace them with new, balanced parts to restore smooth operation.

2. Misalignment of the Shaft
Another common cause of vibration in pipeline pumps is misalignment of the pump shaft. Misalignment occurs when the pump shaft is not correctly aligned with the motor shaft, leading to uneven force distribution and excessive vibration. This misalignment can result from poor installation practices or mechanical wear over time.
Causes of Misalignment:
- Improper Installation: When the pump and motor are not properly aligned during installation, it can cause the shafts to operate at an angle.
- Thermal Expansion: If the pump or motor experiences significant changes in temperature, the materials may expand or contract, causing misalignment.
- Foundation Issues: A weak or uneven foundation can cause the pump or motor to shift, leading to misalignment.
How to Fix It:
- Proper Installation: Ensure that both the pump and motor are installed according to the manufacturer’s specifications, with the shafts aligned correctly.
- Shaft Alignment Tools: Use precision shaft alignment tools, such as laser alignment devices, to accurately align the shafts and reduce vibration.
- Regular Monitoring: Conduct periodic alignment checks, particularly after any maintenance or adjustments to the pump or motor.
3. Cavitation
Cavitation occurs when the pressure of the fluid inside the pump drops below its vapor pressure, causing the formation of vapor bubbles. These bubbles implode when they reach higher pressure areas of the pump, creating shock waves that generate vibration and noise. Cavitation can cause serious damage to the pump components over time.
Causes of Cavitation:
- Low Inlet Pressure: If the pump is experiencing low inlet pressure due to restrictions or insufficient flow, cavitation is more likely to occur.
- High Pump Speed: Running the pump at higher speeds than it is designed for can create conditions conducive to cavitation.
- Improper Pump Selection: Choosing a pump that is too large or too small for the application can lead to cavitation due to excessive or insufficient flow rates.
How to Fix It:
- Increase Inlet Pressure: Ensure that the pump is supplied with sufficient inlet pressure. This can be done by using a larger pipe or reducing restrictions in the pipeline.
- Operating Speed Adjustment: Adjust the speed of the pump to ensure it operates within the recommended range for the specific application.
- Select the Right Pump: Choose a pump that is correctly sized for the flow rate and pressure requirements of the system to minimize the risk of cavitation.
- Use Anti-Cavitation Devices: Some pumps come equipped with anti-cavitation features such as diffuser vanes or cavitation-resistant impellers, which can help reduce cavitation.
4. Fluid Flow Problems
Inconsistent or turbulent fluid flow can also contribute to vibration in pipeline pumps. This can happen if the fluid flow is uneven, if there are large changes in the direction of flow, or if the pipeline is subject to obstructions or restrictions.
Causes of Fluid Flow Problems:
- Pipeline Restrictions: Obstructions, like debris, bends, or valves, can cause uneven fluid flow, leading to turbulence and vibrations within the pump.
- Suction and Discharge Pressure Imbalances: If the suction or discharge pressures are not balanced, it can cause the pump to work inefficiently, leading to vibrations.
- Flow Instability: Pulsations or fluctuations in the flow, caused by improper system design or fluctuating demand, can result in vibration.
How to Fix It:
- Clear Obstructions: Regularly inspect and clean the pipeline to remove any debris or sediment that may obstruct the flow.
- Reduce Flow Turbulence: Minimize sharp bends, reduce pipe diameter, and install straight sections of pipe before and after the pump to ensure smooth fluid flow.
- Install Pressure Control Valves: Use pressure relief or control valves to maintain consistent suction and discharge pressure.
- Flow Stabilizers: In cases of fluctuating flow rates, installing dampeners or flow stabilizers can help mitigate flow pulsations and reduce vibrations.
5. Bearing Failures
Bearings support the rotating components of the pump, and any issues with the bearings can lead to significant vibration. Bearing failures can result from inadequate lubrication, wear, contamination, or improper installation.
Causes of Bearing Failures:
- Insufficient Lubrication: If the bearings do not receive enough lubrication or the wrong type of lubricant is used, they can wear out quickly.
- Contamination: Dirt, moisture, or foreign particles entering the bearing housing can cause excessive friction and premature bearing failure.
- Overloading: Excessive loads or high-speed operations can strain the bearings, leading to vibrations and damage.
How to Fix It:
- Lubrication Maintenance: Ensure that the bearings are properly lubricated with the appropriate lubricant. Regularly check the lubrication levels and replace old or degraded lubricant.
- Protect the Bearings: Install seals or filters to prevent contaminants from entering the bearing housing.
- Bearings Inspection: Perform routine inspections of the bearings for signs of wear, and replace them as necessary to prevent vibration and potential failure.
6. Excessive Pump Speed
Running a pump at speeds higher than its design specifications can cause various problems, including excessive vibration. High speeds can increase the centrifugal forces acting on the components, leading to imbalance, wear, and vibration.
Causes of Excessive Pump Speed:
- Incorrect Motor Speed: A mismatch between the motor and pump speed can cause the pump to operate at higher speeds than intended.
- Speed Control Failure: Malfunctions in speed control devices, such as variable frequency drives (VFDs), can result in the motor running at an excessively high speed.
How to Fix It:
- Match Motor and Pump Specifications: Ensure that the motor speed is correctly matched to the pump’s design specifications to avoid over-speeding.
- Use VFDs with Proper Settings: Install and maintain variable frequency drives (VFDs) to ensure that the pump operates at the correct speed for the application.
Conclusion
Vibration in pipeline pumps is a common issue that can lead to inefficiency, reduced performance, and, in some cases, catastrophic failure if not properly addressed. Understanding the causes of vibration, such as imbalance in rotating components, misalignment, cavitation, fluid flow problems, bearing failures, and excessive pump speed, is the first step in diagnosing and resolving these issues. Regular inspection, maintenance, and proper installation practices can significantly reduce the likelihood of vibration problems and extend the lifespan of pipeline pumps. By implementing corrective measures and adhering to best practices, operators can ensure smooth and efficient operation of pipeline pumps, reducing downtime and minimizing repair costs.
Related Products
-

TD high efficiency and energy saving circulating pump pump shaft
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
The pump shaft is the component that connects the motor to the impelle...
See Details -

Pipeline pump B14 pump cover
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pipeline pump B14 pump cover is a specific type of pump cover for ...
See Details -
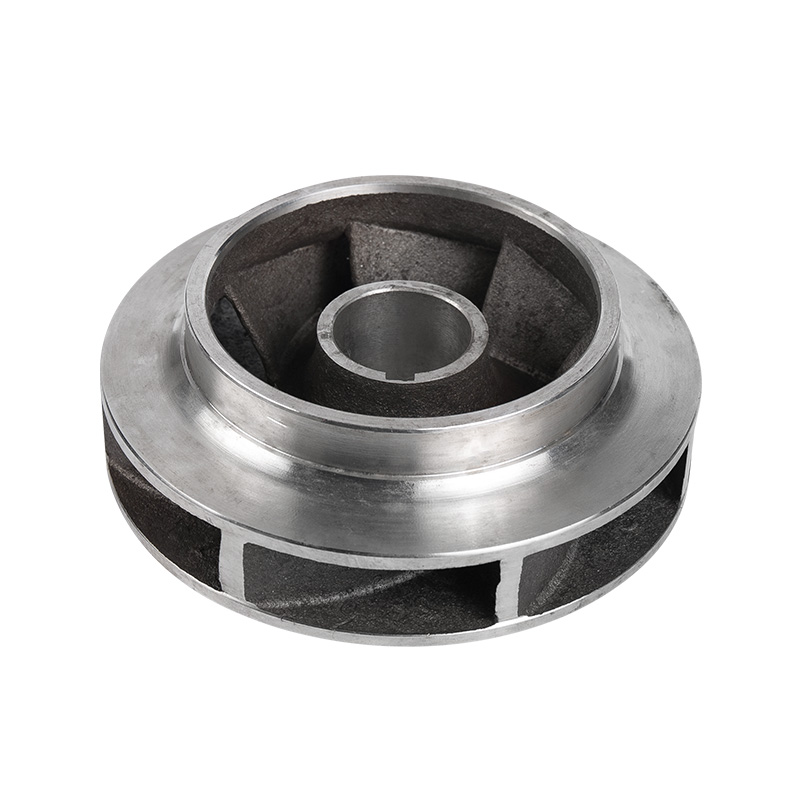

Pipe pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impeller material is stainless steel, it is not easy t...
See Details -
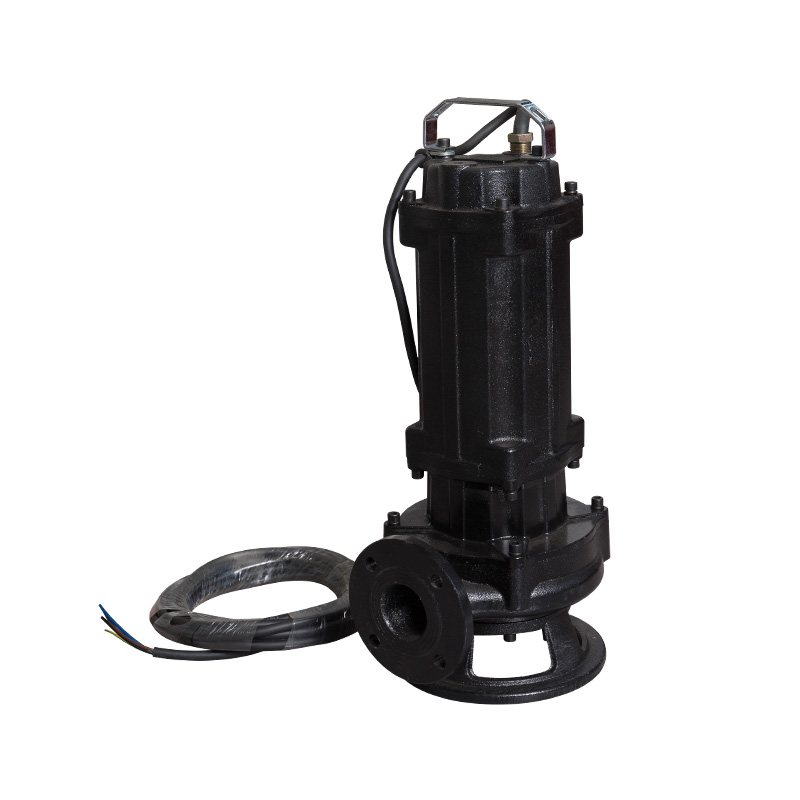

Cutting sewage pump
Cat:Sewage Pump
Cutting sewage pump is a kind of sewage pump, also called cutting pump...
See Details -
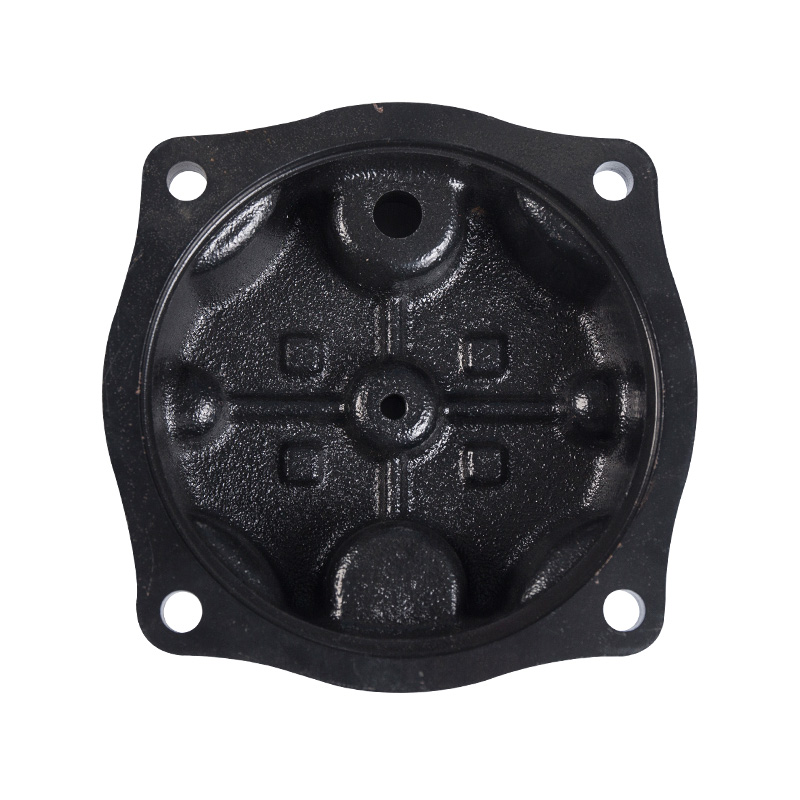

Sewage pump hanging cover
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Installed on the upper part of the sewage pump unit, it is used for li...
See Details -
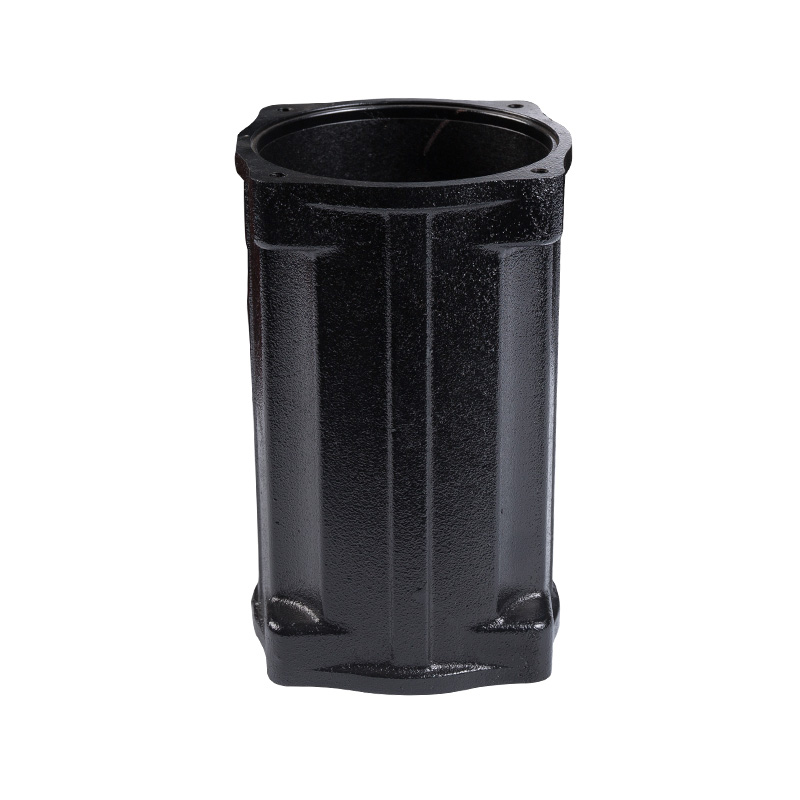

Sewage pump casing
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The casing of the sewage pump unit plays a role in protecting the inte...
See Details -
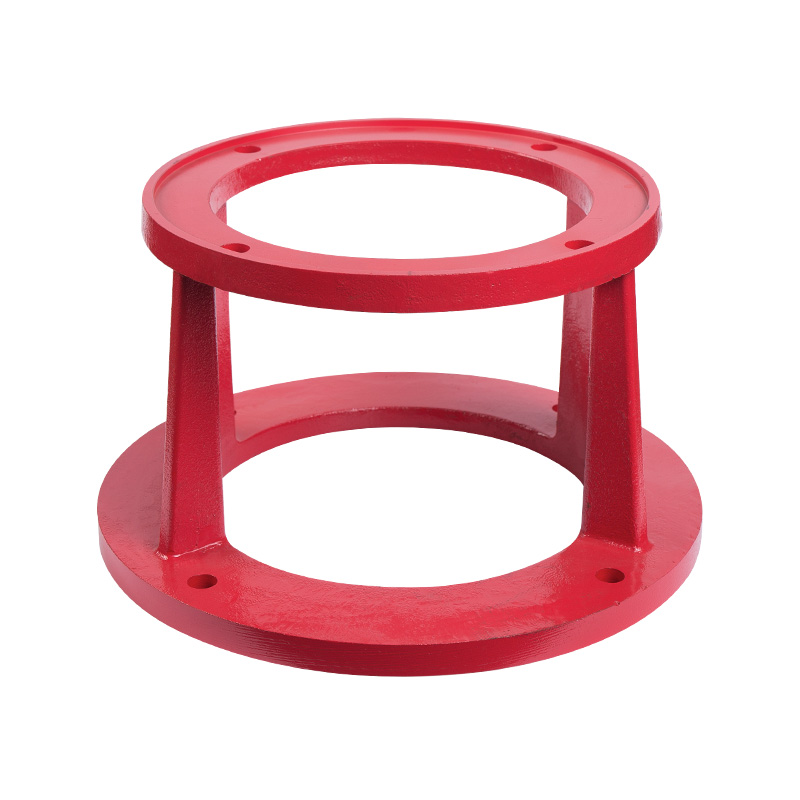

LG multi-stage pump motor bracket
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Motor bracket is a support part used to fix the motor and connect the ...
See Details -
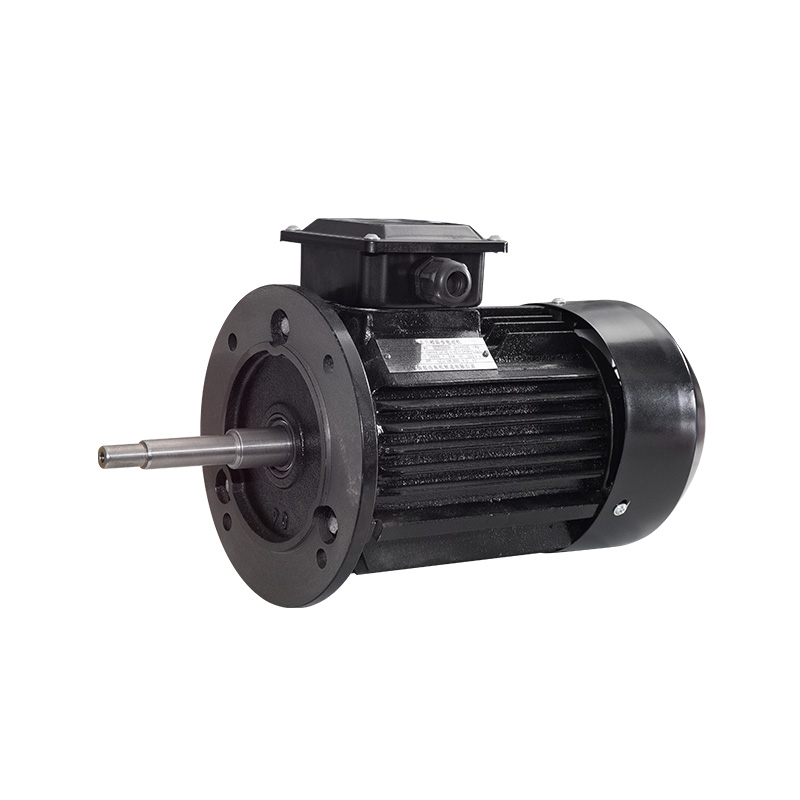

Vertical motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
A conventional fixed-speed motor whose operating speed is usually cons...
See Details -
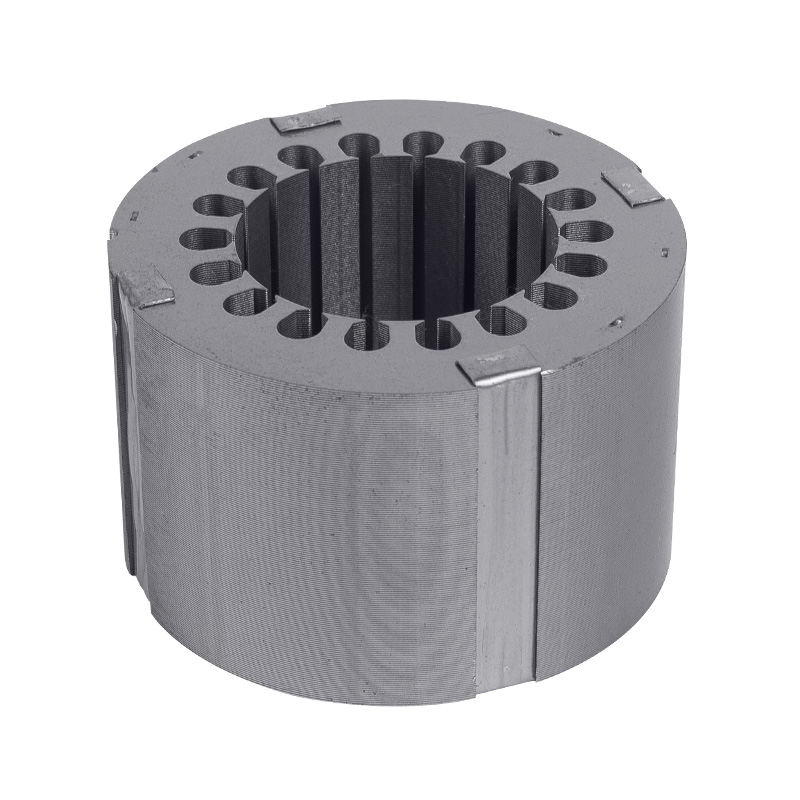

Motor core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A common motor structure, the stator is fixed by the iron core structu...
See Details -
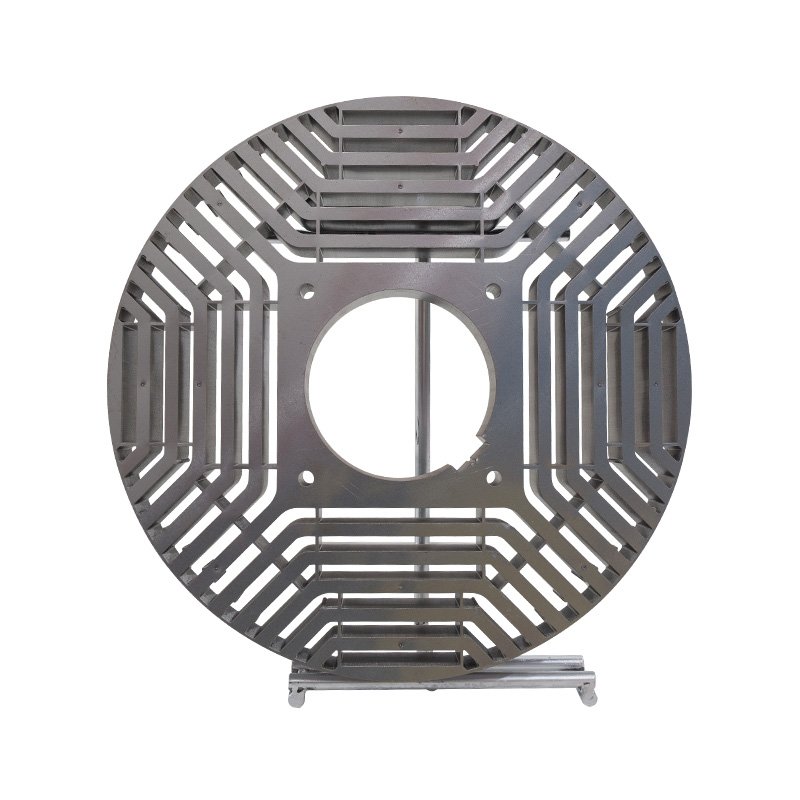

Permanent magnet core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A type of rotor core that uses a permanent magnet material to achieve ...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

