- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Maintenance Practices Keep a Cooling Tower Circulation Pump Running Efficiently?
Cooling tower circulation pumps are a critical component of HVAC and industrial cooling systems, responsible for moving water through the tower to dissipate heat efficiently. Proper maintenance of these pumps ensures optimal performance, energy efficiency, and long operational life. Neglecting maintenance can lead to reduced flow rates, higher energy consumption, mechanical failures, and costly downtime. This article explores comprehensive maintenance practices that keep cooling tower circulation pumps running efficiently.
Understanding the Role of Cooling Tower Circulation Pumps
Cooling tower circulation pumps circulate water from the cooling tower basin to the heat exchangers and back, facilitating the removal of heat generated by industrial processes or HVAC systems. Their efficiency directly impacts the overall thermal performance of the system, energy usage, and the longevity of other components such as the tower fill, pipes, and heat exchangers.
Understanding the operational parameters of the pump, such as flow rate, head pressure, and motor load, is essential for establishing an effective maintenance schedule and identifying potential performance issues early.

Routine Inspection and Monitoring
Regular inspection is crucial for maintaining cooling tower circulation pumps. Key inspection tasks include:
- Checking for leaks in the pump casing, mechanical seals, and piping connections.
- Monitoring vibration levels to detect misalignment, bearing wear, or imbalance.
- Observing unusual noises that may indicate cavitation, worn bearings, or impeller damage.
- Inspecting the motor for overheating, unusual currents, or insulation deterioration.
- Verifying that gauges, flow meters, and pressure sensors are functioning correctly.
Early detection of these issues can prevent severe damage, reduce downtime, and maintain efficient operation.
Lubrication and Bearing Care
Bearings in cooling tower circulation pumps require proper lubrication to minimize friction and wear. The type of lubricant, frequency of application, and lubrication method vary depending on the pump model and operating conditions.
Over-lubrication can cause overheating and seal damage, while under-lubrication accelerates bearing wear. Many modern pumps feature sealed or grease-packed bearings that reduce maintenance frequency. Regularly check bearing temperature and vibration readings to ensure proper lubrication and alignment.
Mechanical Seal Maintenance
Mechanical seals prevent water from leaking along the pump shaft and protect the motor from water ingress. Over time, seals can wear due to friction, chemical attack, or improper installation. Maintenance practices include:
- Regular inspection for leaks and seal integrity.
- Cleaning seal faces to prevent debris buildup.
- Replacing seals before they fail to avoid damage to the pump shaft or motor.
- Ensuring proper alignment of the shaft to reduce seal stress.
Impeller Inspection and Cleaning
The pump impeller is the heart of a cooling tower circulation pump. Scaling, debris, or corrosion can reduce efficiency and increase energy consumption. Key maintenance practices include:
- Visual inspection for cracks, erosion, or cavitation damage.
- Cleaning to remove mineral deposits, algae, or biofilm that may accumulate in water circuits.
- Checking impeller clearance and alignment to prevent rubbing against the pump casing.
- Rebalancing or replacing impellers if performance degradation is detected.
Motor and Electrical System Maintenance
The motor driving the circulation pump must also be maintained for reliable operation. Recommended practices include:
- Inspecting electrical connections for looseness, corrosion, or insulation damage.
- Checking voltage, current, and power consumption to ensure the motor operates within specifications.
- Cleaning the motor housing and ventilation openings to prevent overheating.
- Verifying operation of overload protection devices and control systems.
Water Quality and Corrosion Prevention
Water quality directly affects pump performance and longevity. Poor water quality can cause scaling, corrosion, and biological fouling. Key practices include:
- Implementing proper water treatment to control pH, hardness, and microbial growth.
- Regularly flushing the system to remove accumulated sediments or debris.
- Using corrosion inhibitors or coatings on metallic pump components.
- Monitoring water chemistry and adjusting treatment as needed to prevent damage.
Vibration and Alignment Checks
Vibration and misalignment are common causes of premature pump failure. Maintenance procedures include:
- Measuring vibration levels regularly and comparing with manufacturer tolerances.
- Realigning the pump and motor shafts if misalignment is detected.
- Balancing rotating components to reduce excessive vibration.
- Using vibration monitoring sensors to detect early mechanical issues.
Scheduled Overhauls and Component Replacement
Periodic overhauls ensure the pump continues to operate efficiently. Maintenance activities during overhauls include:
- Replacing worn bearings, seals, and gaskets.
- Inspecting and refurbishing impellers, shafts, and casings.
- Checking and testing the motor, controls, and lubrication systems.
- Documenting performance data and maintenance history for future reference.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
Maintaining a cooling tower circulation pump not only ensures reliability but also improves energy efficiency. Properly maintained pumps operate closer to their design specifications, reducing unnecessary energy consumption. Practices include:
- Monitoring motor load and adjusting speed controls as necessary.
- Ensuring impellers and bearings are free from wear or obstructions.
- Reducing leaks and pressure drops in the piping system.
- Integrating variable frequency drives (VFDs) for precise flow control.
Conclusion: Maximizing Pump Lifespan and Efficiency
Implementing a comprehensive maintenance program for cooling tower circulation pumps is essential for reliable operation, energy efficiency, and cost savings. Regular inspections, proper lubrication, seal and impeller care, motor maintenance, water quality management, and vibration monitoring all contribute to maximizing pump lifespan.
By following these best practices, facilities managers and engineers can reduce downtime, maintain consistent cooling performance, and extend the operational life of their cooling tower systems, ensuring that both energy consumption and maintenance costs remain under control.
Related Products
-

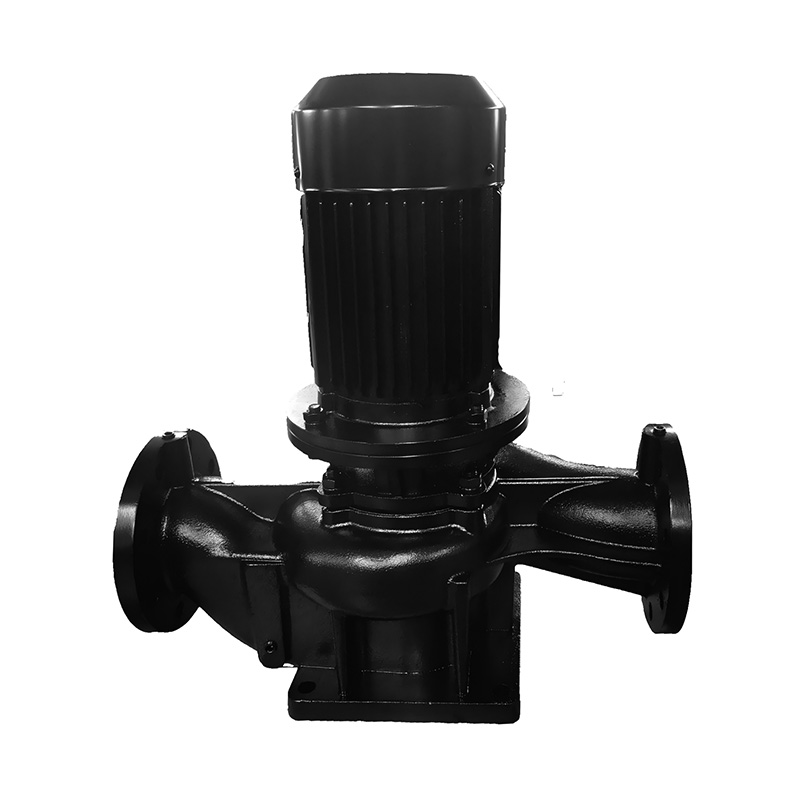
Vertical TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
The TD type single-stage pipeline circulation pump is a green, environ...
See Details -
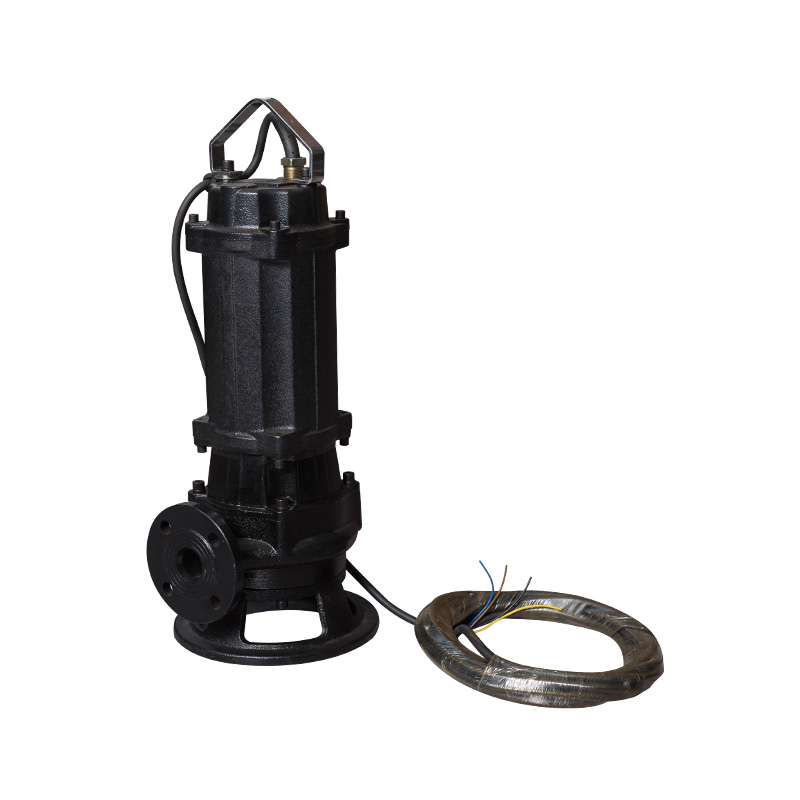

Ordinary sewage pump
Cat:Sewage Pump
1. Our WQ-type general sewage pump adopts a large flow channel anti-cl...
See Details -
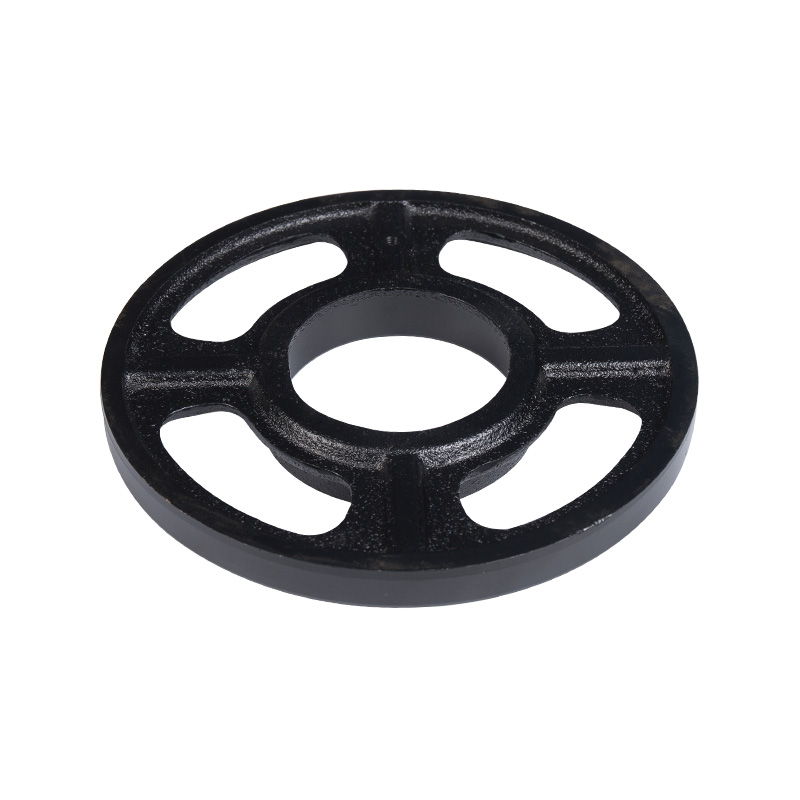

Sewage pump bearing seat
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Installed inside the sewage pump unit, they support the rotor part of ...
See Details -
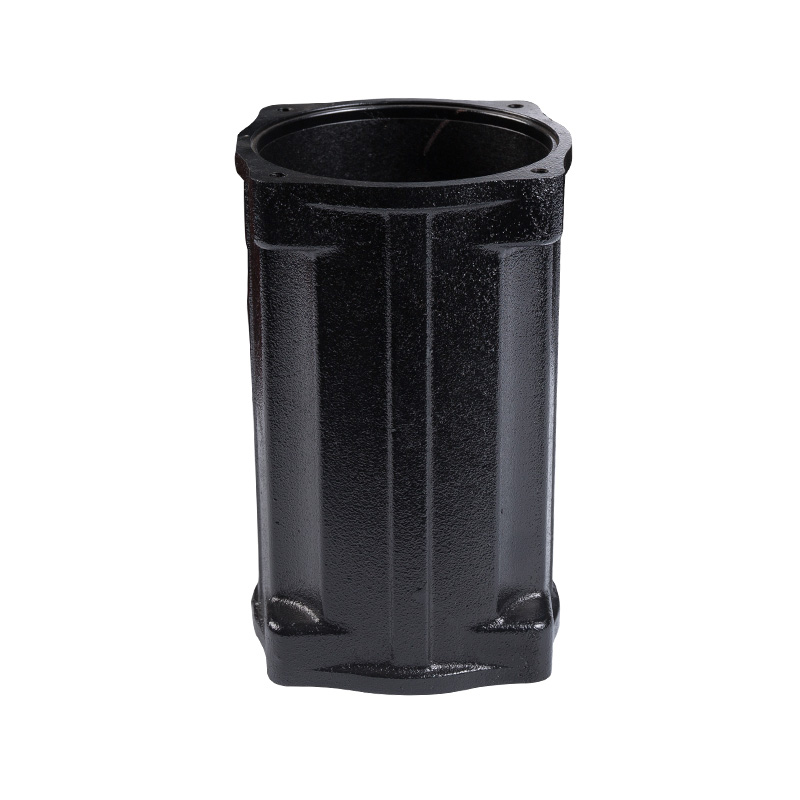

Sewage pump casing
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The casing of the sewage pump unit plays a role in protecting the inte...
See Details -
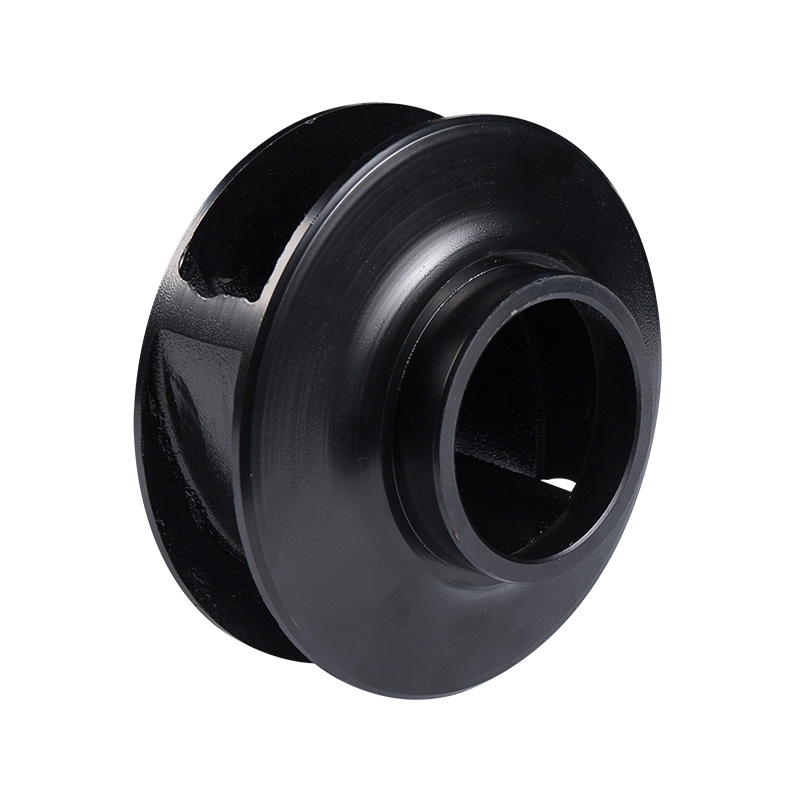

Sewage pump cast iron impeller
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The impeller is the core component of a sewage pump, responsible for r...
See Details -
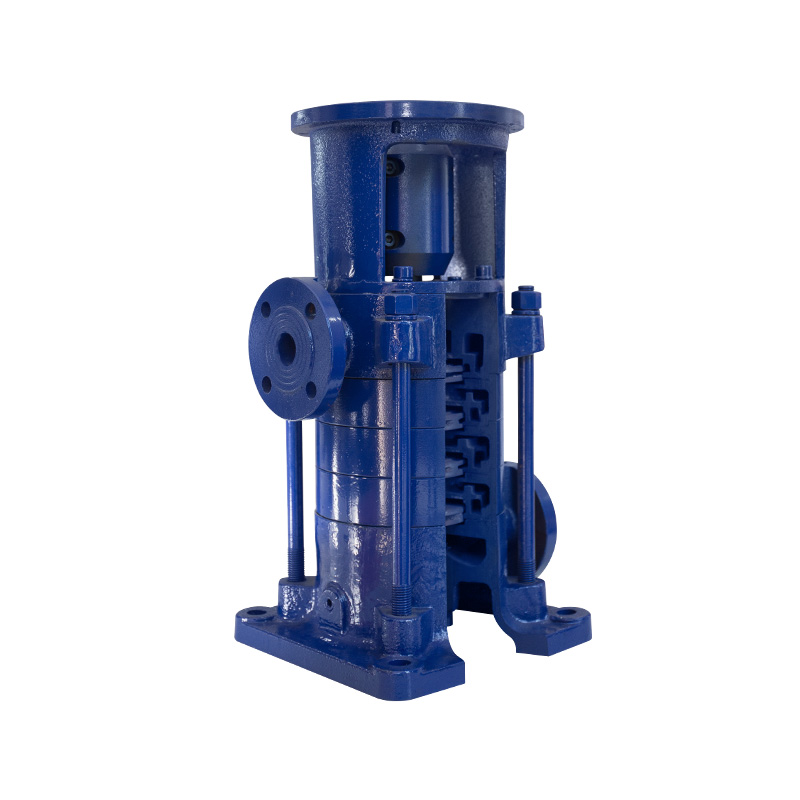

LG multi-stage pump 150 series
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump
Operating conditions 1. It can convey clear water or non-corrosive med...
See Details -
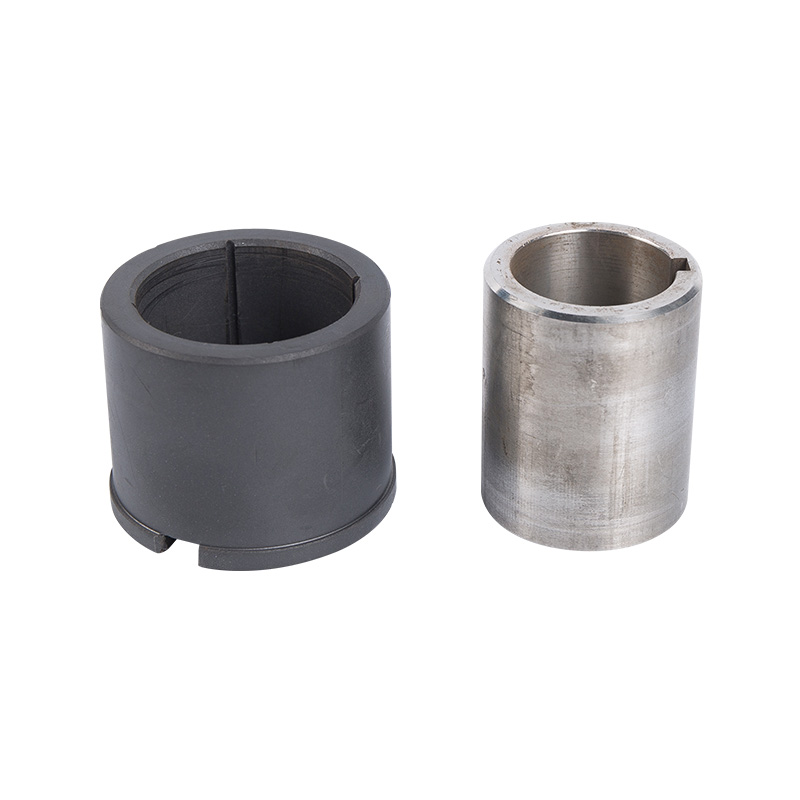

Stainless steel LG multi-stage pump bearing sleeve
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless Steel Bearing Sleeves are bearing sleeves made of stainless ...
See Details -
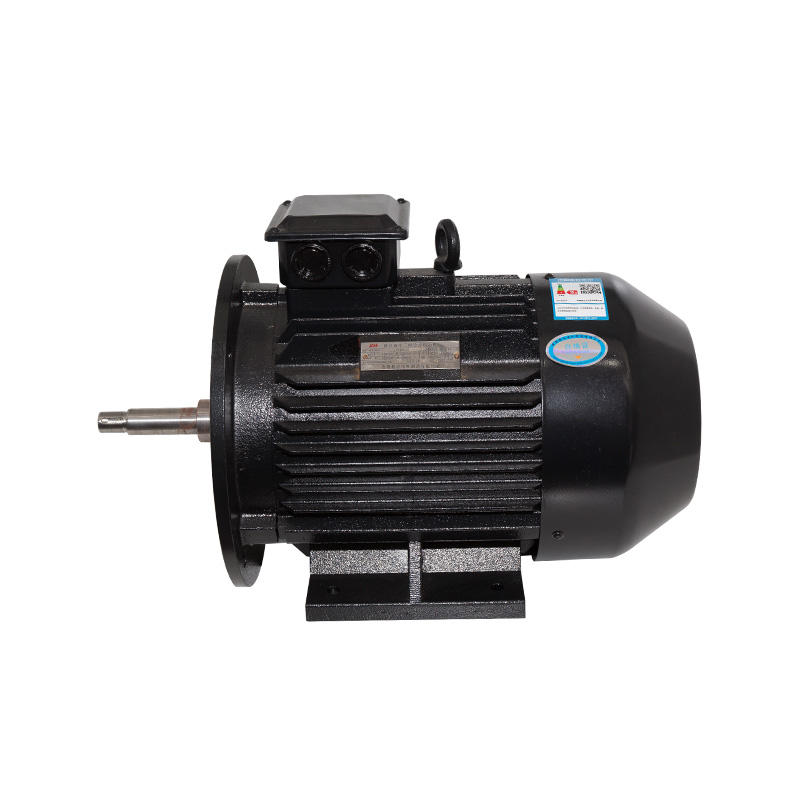

Horizontal motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -
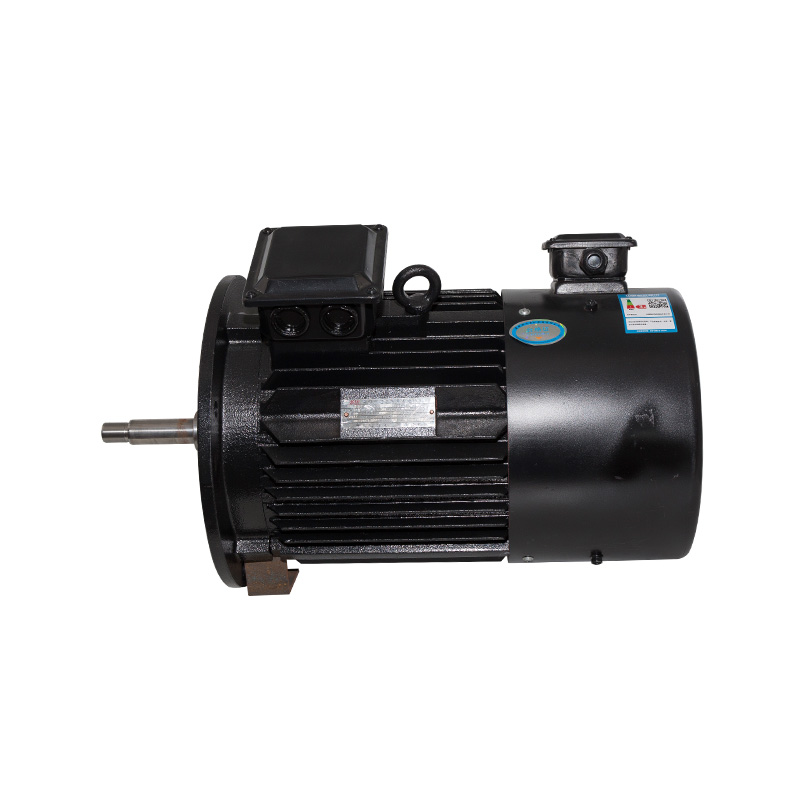

B14/B5 Vertical inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
A type of adjustable speed motor that can control the speed of the mot...
See Details -

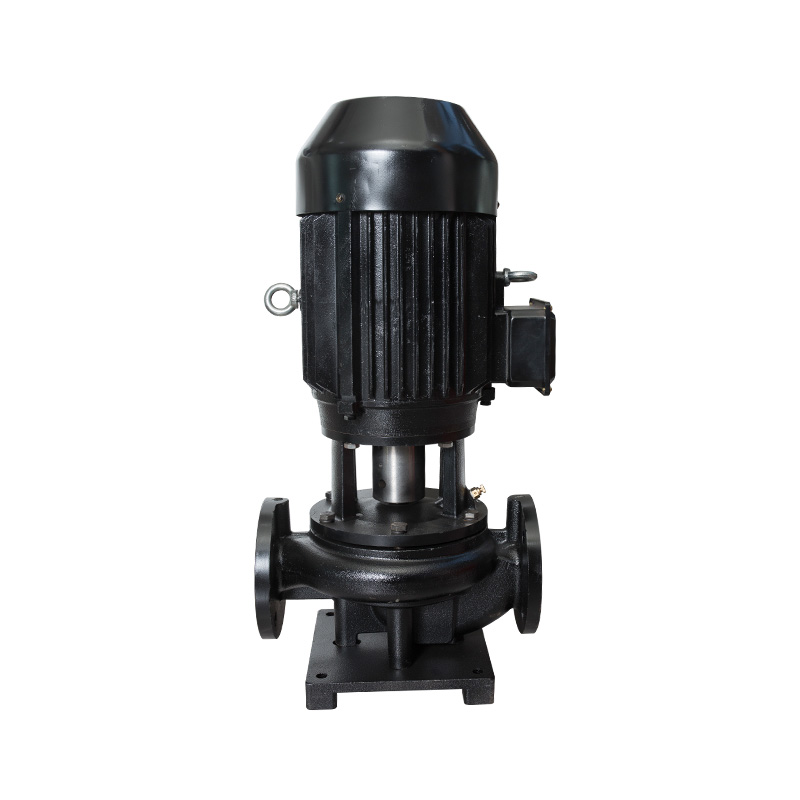
Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

