- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
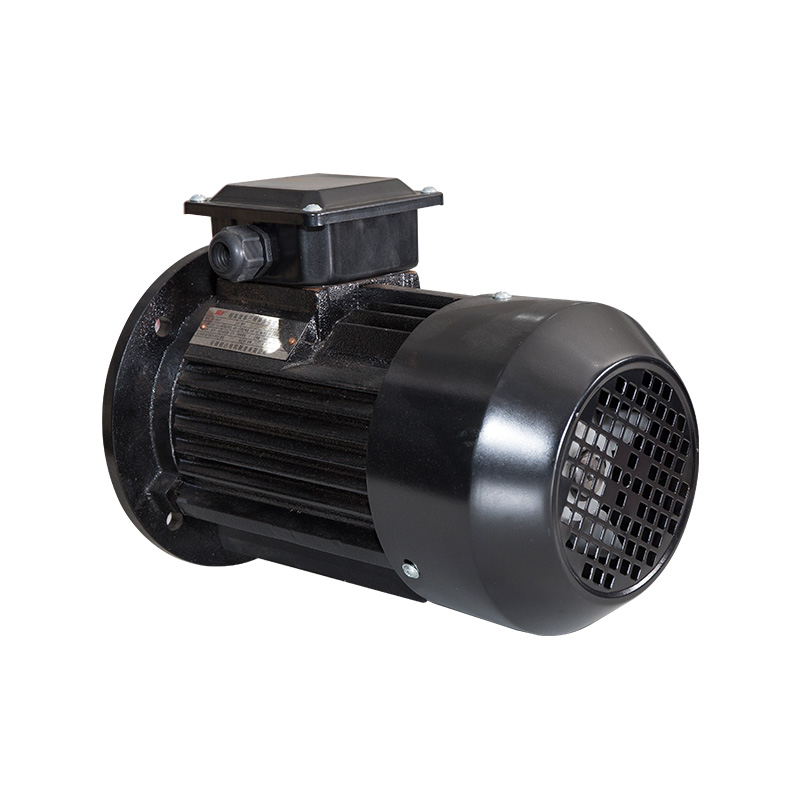
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Are the Common Applications of Vertical Motors Across Industries?
Vertical motors, also referred to as vertical shaft motors or vertically mounted electric motors, are a critical component in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. Unlike conventional horizontal motors, vertical motors are mounted with their shaft oriented vertically, allowing them to save space, facilitate direct coupling with certain equipment, and optimize energy efficiency in specialized systems. Their robust construction, high torque, and adaptability make them ideal for applications where space constraints, mechanical alignment, and high-performance requirements are essential.
This article explores the common applications of vertical motors across different industries, highlighting why they are chosen, their benefits, and key considerations for their implementation.
1. Understanding Vertical Motors
1.1 Construction and Features
Vertical motors generally share core components with traditional electric motors, including stator, rotor, bearings, and shaft, but their vertical orientation and mounting bring unique features:
- Vertical shaft orientation: Allows for direct connection to equipment like pumps, agitators, and conveyors without complex coupling.
- Compact footprint: Suitable for installations with limited horizontal space.
- High torque and efficiency: Optimized for applications requiring continuous operation and heavy loads.
- Enhanced cooling: Some designs allow for natural convection or forced air cooling aligned with vertical orientation.
These motors are available in AC and DC variants, with power ratings ranging from fractional horsepower to several hundred kilowatts, making them versatile for industrial, commercial, and municipal applications.

2. Water and Wastewater Industry
Vertical motors are extensively used in pumping applications, especially in municipal and industrial water systems.
2.1 Vertical Pumps
- Application: Vertical motors are often directly coupled with vertical pumps for water supply, irrigation, and wastewater treatment.
- Advantages: The vertical alignment minimizes the need for complex drive systems, reduces footprint, and allows the pump to be submerged or partially submerged in water reservoirs.
- Key Industries: Municipal water treatment plants, industrial cooling systems, agricultural irrigation systems.
2.2 Sewage and Slurry Pumps
- Application: Handling liquids with solids, such as wastewater, slurry, and chemical mixtures.
- Advantages: Robust vertical motor designs can handle harsh conditions, including exposure to moisture, chemicals, and abrasive materials.
- Benefit: Direct coupling ensures high efficiency and reduces maintenance caused by misalignment in horizontal configurations.
3. Chemical and Process Industries
Vertical motors are commonly deployed in mixing, agitation, and material handling processes in chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries.
3.1 Agitators and Mixers
- Application: Vertical motors drive agitators in tanks, reactors, and blending vessels.
- Advantages: Vertical orientation allows the motor to be mounted directly above the tank, transmitting torque efficiently without the need for additional shafts or pulleys.
- Benefits: Reduces energy loss, minimizes mechanical complexity, and ensures precise mixing.
3.2 Centrifugal Separators
- Application: Separators used for chemical clarification or oil-water separation often employ vertical motors to spin the rotor.
- Advantages: Compact vertical design integrates easily with industrial processes and improves system balance.
- Benefit: Ensures high-speed operation and consistent separation performance.
4. HVAC and Air Handling Systems
Vertical motors are widely used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems for fans, blowers, and compressors.
4.1 Vertical Shaft Fans and Blowers
- Application: Large industrial fans and blowers in air handling units, cooling towers, and ventilation systems.
- Advantages: The vertical motor drives the fan shaft directly, optimizing space in mechanical rooms where horizontal mounting is not feasible.
- Benefits: Reduced coupling components, improved energy efficiency, and simplified maintenance.
4.2 Compressors and Chillers
- Application: Driving vertical centrifugal or screw compressors used in industrial chillers and refrigeration systems.
- Advantages: Vertical configuration allows for compact, high-speed design with fewer vibration issues.
- Benefit: Reliable, continuous operation in demanding environments.
5. Material Handling and Conveying Systems
In industries like mining, cement, and food processing, vertical motors are employed in conveyors, bucket elevators, and screw conveyors.
5.1 Vertical Bucket Elevators
- Application: Moving bulk materials vertically in grain silos, cement plants, or chemical storage facilities.
- Advantages: Vertical motors reduce the need for extended horizontal space and allow direct coupling to elevator shafts.
- Benefit: Efficient energy transfer, minimal mechanical loss, and reduced maintenance.
5.2 Screw Conveyors and Feeders
- Application: Transporting powder, granules, or liquids through vertically oriented screw mechanisms.
- Advantages: Direct vertical drive ensures uniform torque and reduces belt or gear complications.
- Benefit: Reliable and precise control of material flow in automated systems.
6. Marine and Offshore Applications
Vertical motors are also used in marine and offshore platforms, where space constraints and environmental conditions dictate the choice of motor orientation.
6.1 Ballast and Bilge Pumps
- Application: Vertical motors drive submersible or semi-submersible pumps to manage water ingress and ballast systems.
- Advantages: Vertical orientation allows for direct coupling to pumps in tight engine rooms.
- Benefits: High reliability and corrosion resistance, essential in harsh marine environments.
6.2 Deck Machinery
- Application: Winches, cranes, and lifting equipment on ships may use vertical motors for torque transmission in confined spaces.
- Benefits: Compact design, robust construction, and precise control.
7. Renewable Energy and Power Generation
Vertical motors have applications in power plants and renewable energy systems, particularly in handling fluids or mechanical drives.
7.1 Hydro Turbine Systems
- Application: Vertical motors may be used in auxiliary systems such as lubrication pumps, cooling water pumps, and control actuators.
- Advantages: Direct vertical drive simplifies alignment with vertical shafts in turbine assemblies.
- Benefit: Efficient and low-maintenance operation in high-performance energy environments.
7.2 Wind Turbine Auxiliary Drives
- Application: Vertical motors can be used in yaw systems or pitch adjustment mechanisms.
- Advantages: High torque in a compact vertical configuration allows for precise blade positioning.
- Benefit: Enhanced control and reduced mechanical complexity.
8. Food and Beverage Industry
Vertical motors are commonly employed in mixers, pumps, and processing equipment in food production.
8.1 Mixing and Blending
- Application: Driving agitators in vats, tanks, and fermenters.
- Advantages: Vertical mounting allows direct drive to agitator shafts, improving hygiene and reducing contamination risk.
- Benefits: Consistent mixing, energy efficiency, and ease of cleaning.
8.2 Pumps for Liquid Handling
- Application: Handling beverages, syrups, or semi-viscous liquids.
- Advantages: Vertical motors with sealed construction resist moisture and cleaning fluids.
- Benefit: Reliable, sanitary operation in food processing environments.
9. Key Advantages of Vertical Motors Across Industries
- Space-Saving Design: Ideal for installations where horizontal space is limited.
- Direct Coupling: Reduces energy loss, mechanical components, and maintenance.
- High Torque: Efficiently drives heavy loads and high-resistance systems.
- Versatility: Applicable in pumps, mixers, conveyors, fans, compressors, and lifting systems.
- Durability: Designed for continuous operation in harsh conditions.
- Improved Alignment: Reduces vibration and mechanical wear compared to misaligned horizontal drives.
10. Considerations for Implementation
When selecting vertical motors for industrial applications, several factors should be considered:
- Power Rating: Ensure the motor can handle the required load continuously.
- Speed and Torque: Match motor characteristics with the application’s operational requirements.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider moisture, temperature, and corrosive exposure.
- Mounting and Alignment: Proper installation ensures minimal mechanical stress and optimal performance.
- Maintenance Access: Ensure vertical motors are installed for safe and easy maintenance.
Choosing the right motor enhances operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and ensures longevity.
Conclusion
Vertical motors are essential in a wide array of industries due to their space-saving design, high torque, and ability to directly drive vertically aligned equipment. They are prevalent in water and wastewater systems, chemical processing, HVAC, material handling, marine operations, renewable energy, and food and beverage production.
Their compact vertical configuration simplifies mechanical alignment, improves energy efficiency, and minimizes maintenance compared to horizontal motor arrangements. Whether driving pumps, mixers, fans, conveyors, or auxiliary equipment, vertical motors provide reliable and efficient solutions across industrial and commercial applications.
Understanding their applications, advantages, and implementation considerations is critical for engineers, operators, and plant managers seeking to optimize performance, reduce downtime, and ensure safe, continuous operation across diverse industrial environments.
Related Products
-
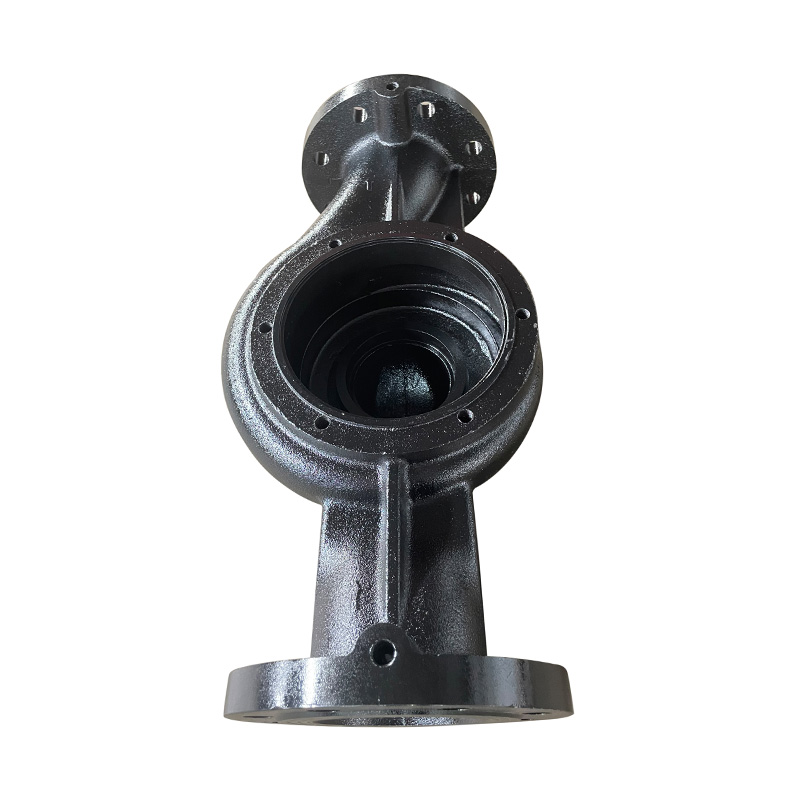

Vertical TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump body
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
Vertical TD Energy Efficient Circulating Pump Pump Body is the shell o...
See Details -
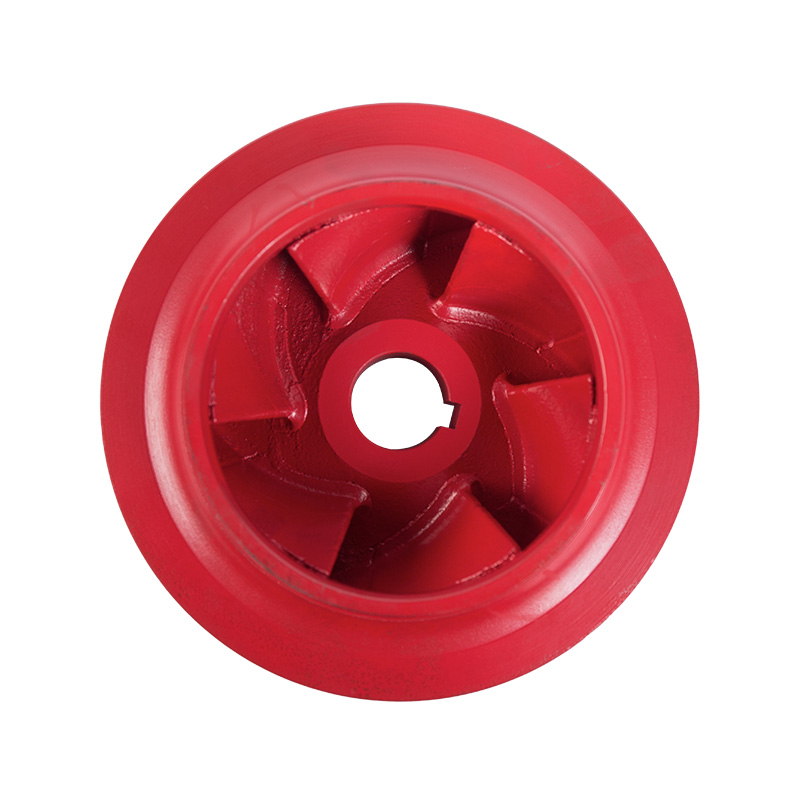

Pipeline pump cast iron impeller
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The impeller refers to both the disc with moving blades, which is an i...
See Details -
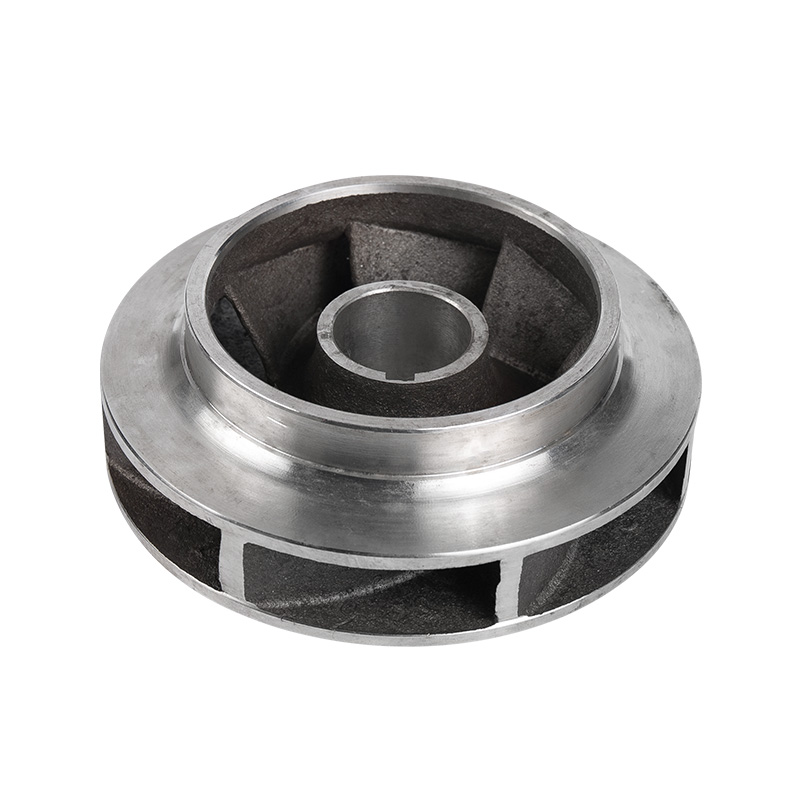

Pipe pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impeller material is stainless steel, it is not easy t...
See Details -
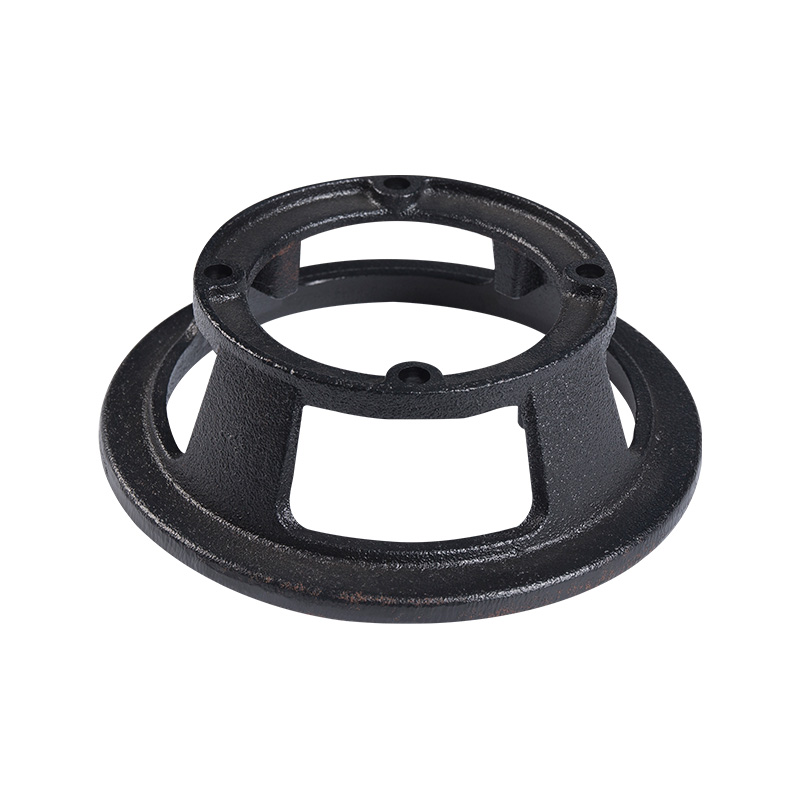

Sewage pump foot plate
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Components mounted on the bottom of the sewage pump unit to support th...
See Details -
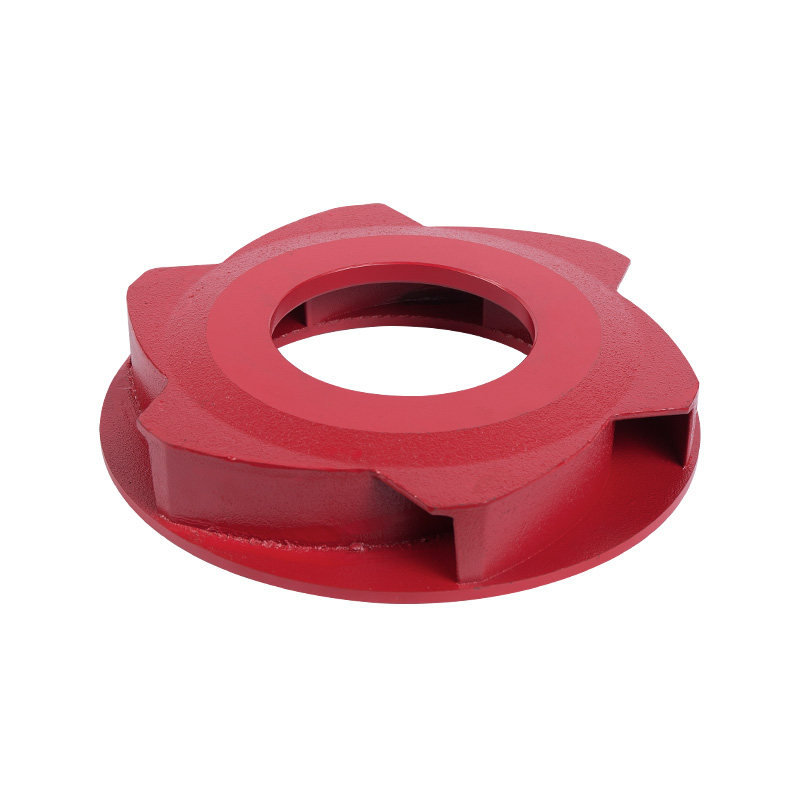

LG multistage pump cast iron impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Cast iron impeller is one of the key components of the pump, which pre...
See Details -
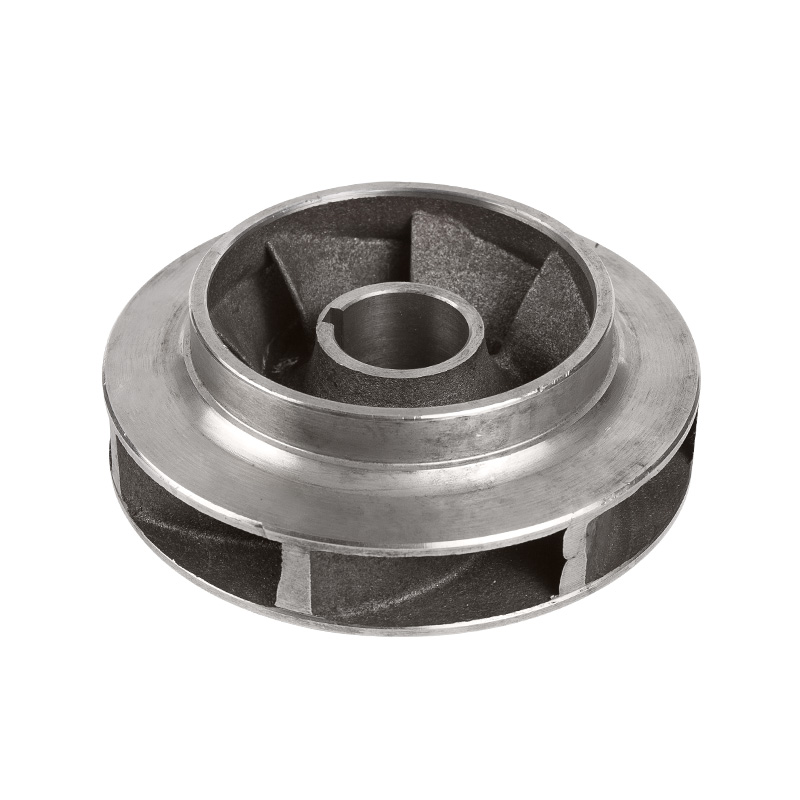

LG multi-stage pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impellers are impellers made of stainless steel materi...
See Details -
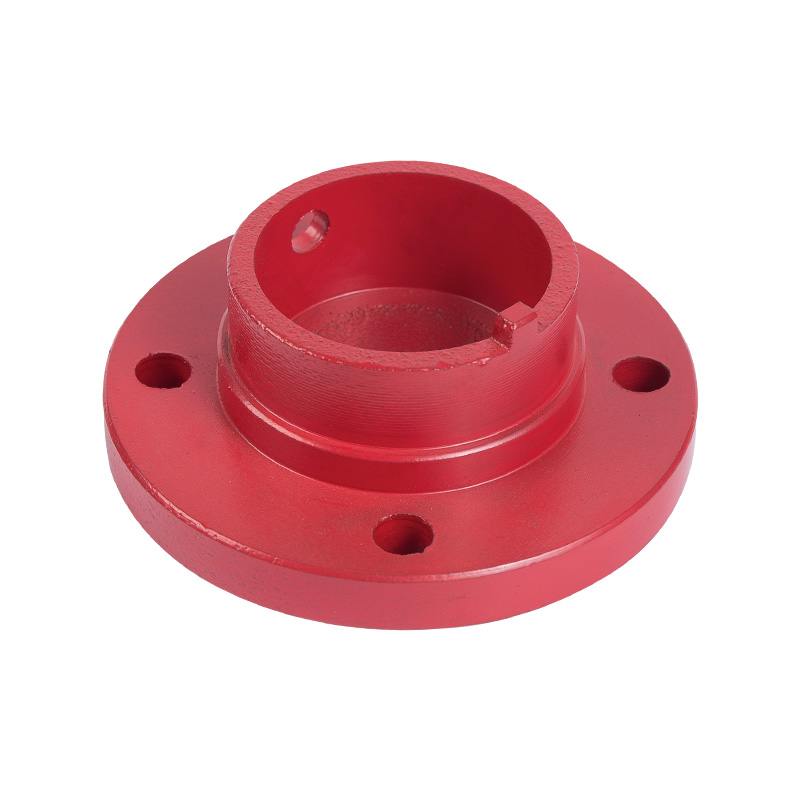

LG multi-stage pump water bearing gland
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Water bearing gland is the gland for fixing the water bearing, which s...
See Details -
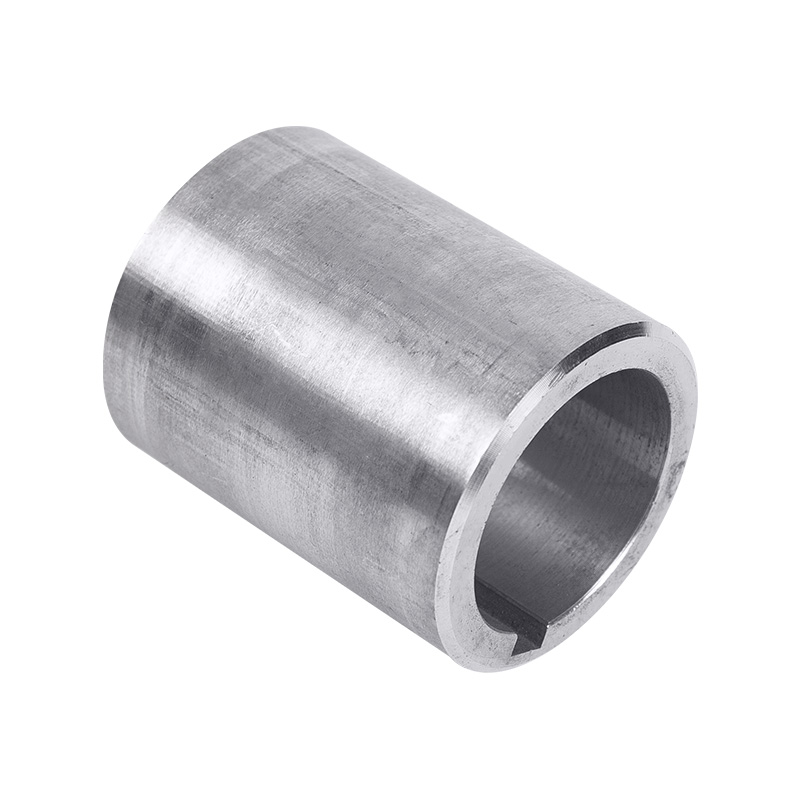

LG multi-stage pump spacer sleeve
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Spacer sleeve is a ring-shaped part installed between the impellers of...
See Details -
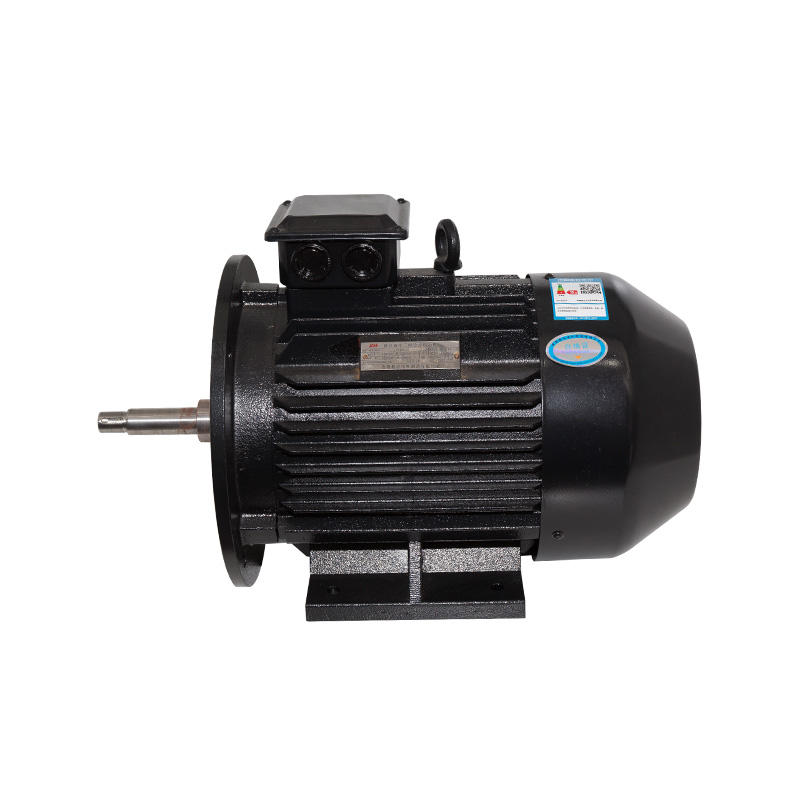

Horizontal motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -
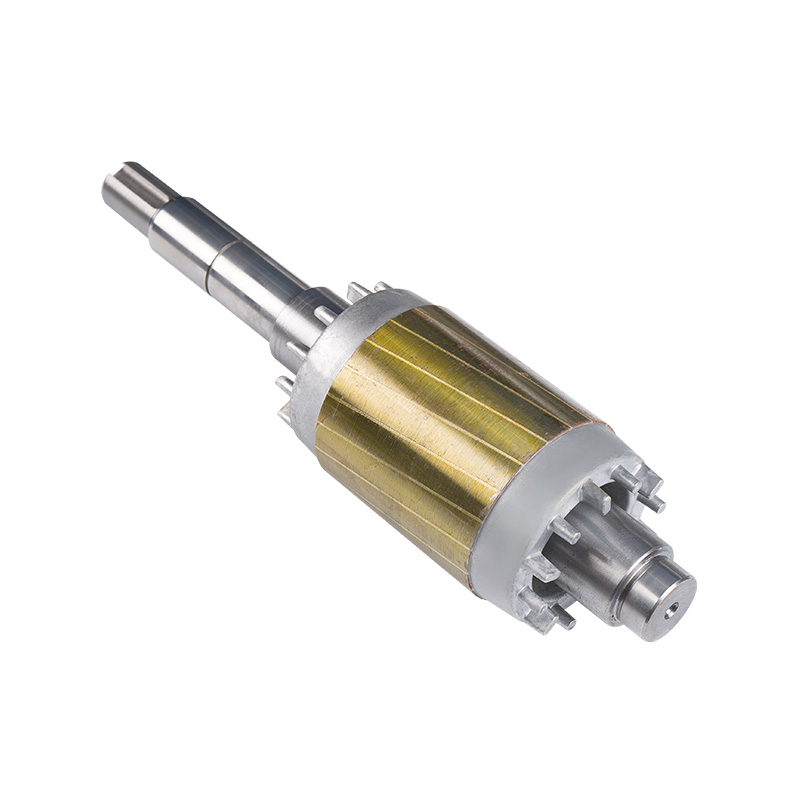

Finished rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
The rotor of a motor refers to the rotating part, which contains the r...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

