- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Types of Sewage Pumps Are Most Suitable for Residential, Commercial, and Industrial Applications?
Sewage pumps are critical components in modern wastewater management systems. They are designed to transport wastewater and sewage from lower to higher elevations, overcoming gravity and ensuring efficient flow in both residential and industrial contexts. With increasing urbanization and industrial activity, selecting the right type of sewage pump for a particular application is essential for reliability, efficiency, and long-term performance.
This article explores the types of sewage pumps, their characteristics, and which applications—residential, commercial, or industrial—they are best suited for.
1. Understanding Sewage Pumps
Sewage pumps, sometimes referred to as wastewater pumps, are specialized pumps that handle liquids containing solids, fibers, or debris. Unlike standard water pumps, sewage pumps are engineered to:
- Handle solids without clogging
- Resist abrasion and corrosion
- Operate in submerged or dry environments
Sewage pumps are classified based on installation type, impeller design, and pumping capacity, allowing them to cater to different scales and types of wastewater management.
2. Main Types of Sewage Pumps
a. Submersible Sewage Pumps
Description:
Submersible sewage pumps are designed to operate fully submerged in wastewater or sewage. They consist of a sealed motor attached directly to the pump housing, which is placed within the liquid to be pumped.
Key Features:
- Submersible design: Eliminates the need for priming and reduces the risk of cavitation.
- Impeller types: Vortex, channel, or grinder impellers handle varying levels of solids and fibers.
- Sealed motor: Prevents water ingress, ensuring durability.
Best Applications:
- Residential: Suitable for basement sump pits, small sewage ejector systems, and residential wastewater systems.
- Commercial: Ideal for hotels, restaurants, and apartment complexes where wastewater may contain moderate solids.
- Industrial: Can handle moderate industrial wastewater but typically limited to systems with smaller solids or less abrasive materials.
Advantages:
- Space-saving design, quiet operation, and reduced installation complexity.
- Good for continuous operation in wet environments.
b. Grinder Sewage Pumps
Description:
Grinder pumps include a cutting mechanism that macerates solids and fibers, producing a uniform slurry that can be easily pumped through smaller diameter pipes.
Key Features:
- Integrated grinder mechanism: Reduces risk of clogging.
- Handles materials such as toilet paper, sanitary products, and fibrous waste.
- Often used in pressurized sewer systems where small-diameter piping is required.
Best Applications:
- Residential: Suitable for homes located far from main sewer lines, requiring pressurized waste transport.
- Commercial: Restaurants, office buildings, or facilities with high concentrations of solids.
- Industrial: Light industrial facilities where wastewater contains fibrous or stringy materials.
Advantages:
- Prevents blockages in pipelines, reducing maintenance.
- Enables efficient pumping over long distances with smaller pipes.
c. Non-Clog Sewage Pumps
Description:
Non-clog pumps, also known as vortex or channel impeller pumps, are designed to handle large solids and fibrous materials without clogging.
Key Features:
- Open impeller design: Allows large solids to pass through the pump without damage.
- Handles raw sewage, rags, and other debris effectively.
- Robust construction for frequent or continuous operation.
Best Applications:
- Residential: Less common, but suitable for larger multi-residential complexes or community septic systems.
- Commercial: Medium-sized commercial facilities like schools, hospitals, or commercial buildings with high wastewater flow.
- Industrial: Ideal for industrial wastewater with high solid content, including food processing or paper manufacturing plants.
Advantages:
- Reliable handling of high solids content.
- Reduces downtime due to clogs, improving system reliability.
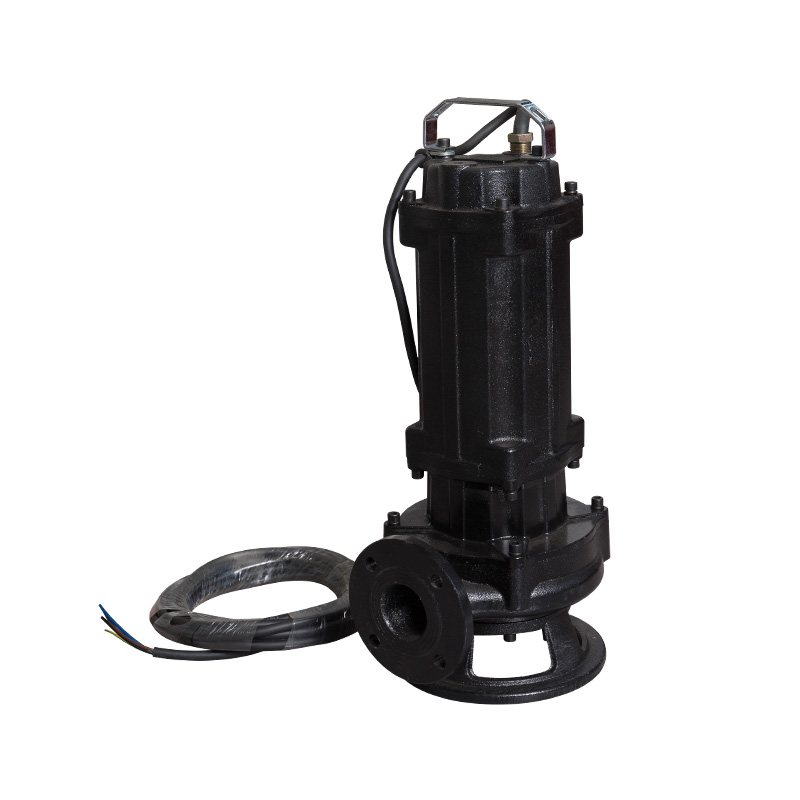

d. Dry-Pit Sewage Pumps
Description:
Dry-pit pumps are installed outside the liquid, with the pump intake submerged and the motor positioned above the liquid level. They are commonly used in large-scale wastewater treatment plants.
Key Features:
- Accessible motor for maintenance: Motor and pump can be serviced without entering the pit.
- Often coupled with vertical or horizontal pump shafts for large flows.
- Suitable for high-capacity pumping.
Best Applications:
- Commercial: Large hotels, shopping malls, or hospitals with high wastewater volume.
- Industrial: Municipal sewage systems, factories, or plants with large wastewater discharge.
- Residential: Rarely used in single-family homes due to size and installation requirements.
Advantages:
- Easy maintenance and inspection without pump removal.
- Handles large flows and high capacities, suitable for continuous operation.
e. Self-Priming Sewage Pumps
Description:
Self-priming pumps are designed to automatically remove air from the suction line, allowing them to start pumping without manual priming.
Key Features:
- Can be installed above or away from the liquid source.
- Often used in temporary or mobile sewage systems.
- Efficient for pumping wastewater containing small solids or light debris.
Best Applications:
- Residential: Temporary or portable sewage pumping systems.
- Commercial: Construction sites or facilities requiring flexible wastewater pumping.
- Industrial: Light-duty industrial wastewater handling where submersible installation is impractical.
Advantages:
- Flexibility in installation and location.
- Reduces downtime during startup by eliminating manual priming.
3. Factors Affecting Sewage Pump Selection
Selecting the right sewage pump for any application involves considering multiple factors:
- Type and Volume of Wastewater: High solid content requires non-clog or grinder pumps.
- Flow Rate and Head: Residential systems may need lower flow rates, while industrial systems require high-capacity pumps.
- Installation Environment: Submersible vs. dry-pit installation depends on available space and access.
- Maintenance Requirements: Accessibility and serviceability are critical, especially in commercial and industrial facilities.
- Power Supply: Single-phase motors are suitable for residential pumps, while three-phase motors are common in commercial and industrial pumps.
- Distance to Discharge Point: Long pipelines or elevated discharge points may require grinder pumps or high-capacity pumps.
4. Applications by Sector
a. Residential Applications
- Basement sewage ejector systems: Submersible or grinder pumps to lift wastewater to the main sewer line.
- Remote homes: Grinder pumps for pressurized waste systems.
- Small apartment complexes: Non-clog submersible pumps for multiple units.
b. Commercial Applications
- Restaurants and hotels: Submersible grinder pumps to handle food waste and fibrous materials.
- Office buildings and schools: Non-clog or dry-pit pumps for moderate to high flows.
- Shopping malls and hospitals: High-capacity dry-pit pumps for continuous wastewater management.
c. Industrial Applications
- Food processing plants: Grinder and non-clog pumps to handle fibrous and solid waste.
- Municipal wastewater treatment: Dry-pit or submersible non-clog pumps for continuous operation.
- Manufacturing facilities: High-capacity pumps for chemical-laden or abrasive wastewater.
5. Advantages of Using the Right Type of Sewage Pump
- Reduced Clogging: Using grinder or non-clog pumps minimizes maintenance.
- Improved Efficiency: Selecting pumps according to capacity and flow reduces energy consumption.
- Enhanced Reliability: Proper pump selection ensures continuous wastewater handling.
- Longevity: Pumps designed for specific applications resist wear and corrosion, extending service life.
- Cost Savings: Reduces downtime, maintenance costs, and replacement frequency.
6. Maintenance Considerations
Proper maintenance ensures efficient and long-lasting operation:
- Regular Inspection: Check for wear, seals, and debris.
- Lubrication: Some pumps require motor and bearing lubrication.
- Cleaning Impellers and Grinder Blades: Prevent clogging and maintain efficiency.
- Electrical Checks: Ensure motor insulation and wiring are in good condition.
- Monitoring Performance: Flow rate and pressure should meet design specifications to avoid overload.
7. Conclusion
Sewage pumps play a critical role in residential, commercial, and industrial wastewater management. Choosing the right type depends on factors such as wastewater composition, flow rate, solids content, installation environment, and maintenance requirements.
- Residential systems benefit from submersible and grinder pumps for efficient handling of household sewage.
- Commercial applications require non-clog, submersible, and dry-pit pumps to manage moderate to high flows with mixed solids.
- Industrial facilities and municipal systems rely on high-capacity non-clog, dry-pit, or specialized grinder pumps to handle heavy, abrasive, or fibrous wastewater continuously.
By selecting the appropriate pump type, end-users can achieve reliable operation, reduced maintenance costs, and long-term performance, ensuring that wastewater is efficiently and safely transported in any application.
Related Products
-
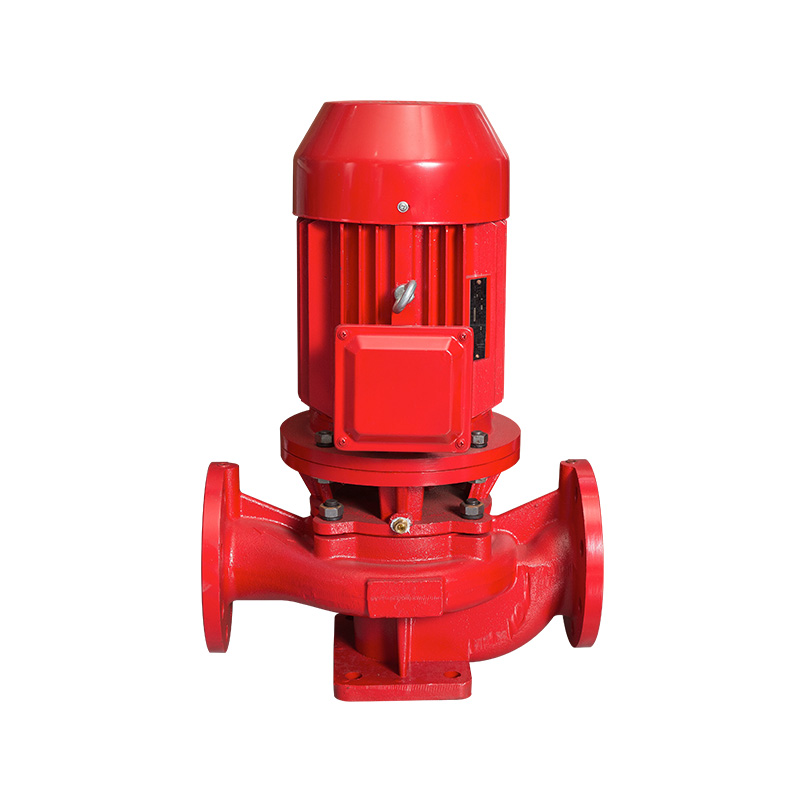

Vertical pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISG series single-stage single-suction vertical centrifugal pump is a ...
See Details -
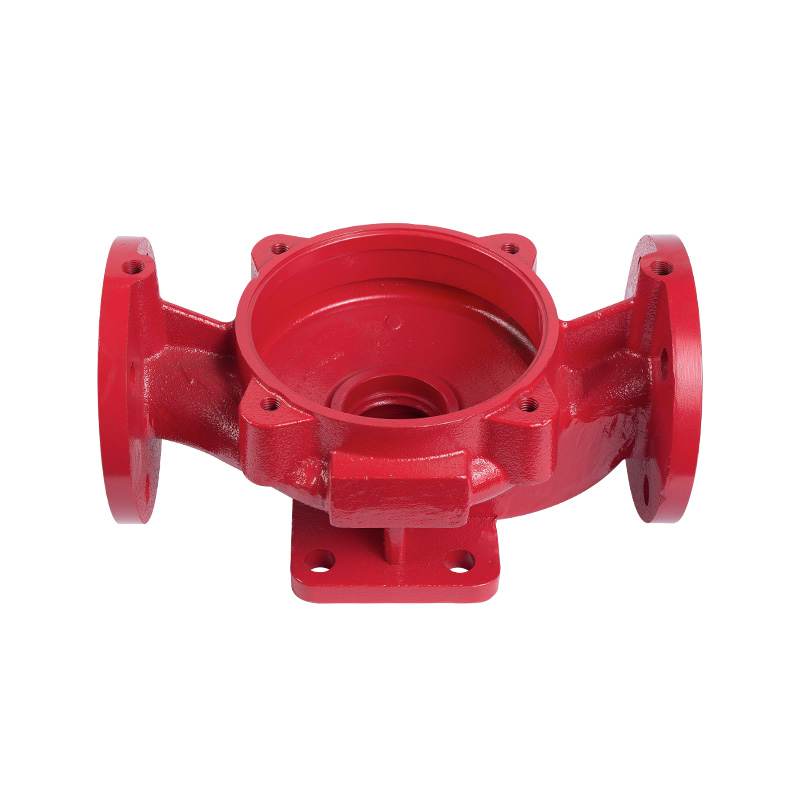

Vertical pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -
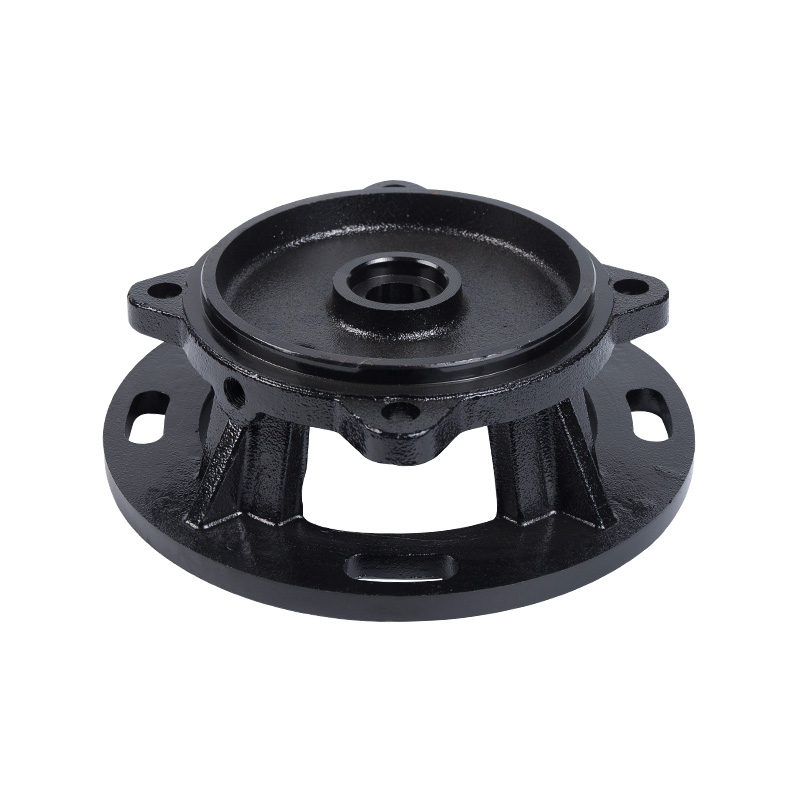

Pipe pump cover
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump cover is used to tighten and seal. The pump cover ensures tha...
See Details -

Pipeline pump B14 pump cover
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pipeline pump B14 pump cover is a specific type of pump cover for ...
See Details -

Cutting sewage pump
Cat:Sewage Pump
Cutting sewage pump is a kind of sewage pump, also called cutting pump...
See Details -
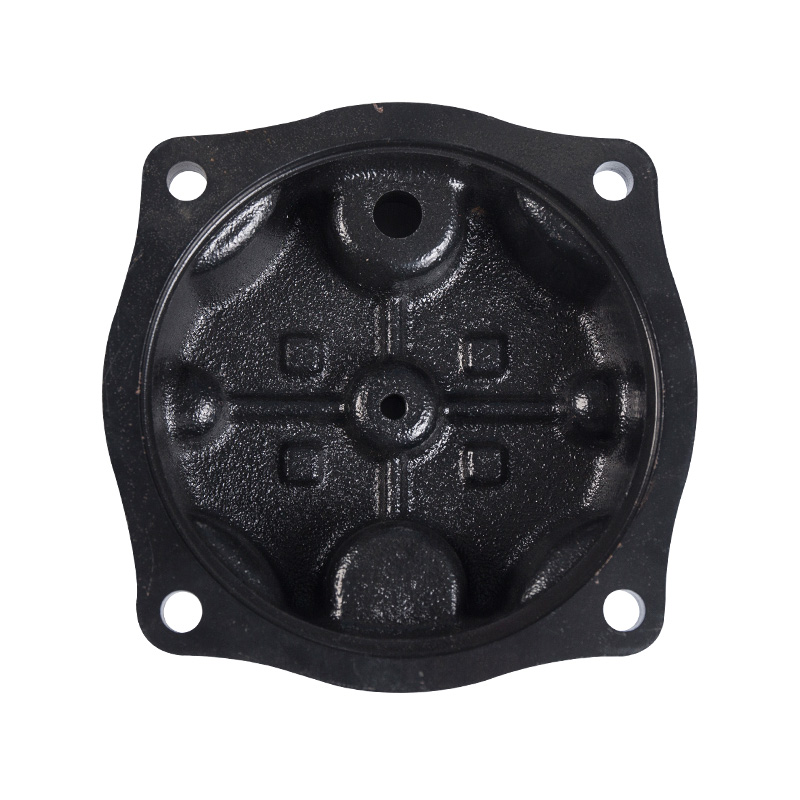

Sewage pump hanging cover
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Installed on the upper part of the sewage pump unit, it is used for li...
See Details -
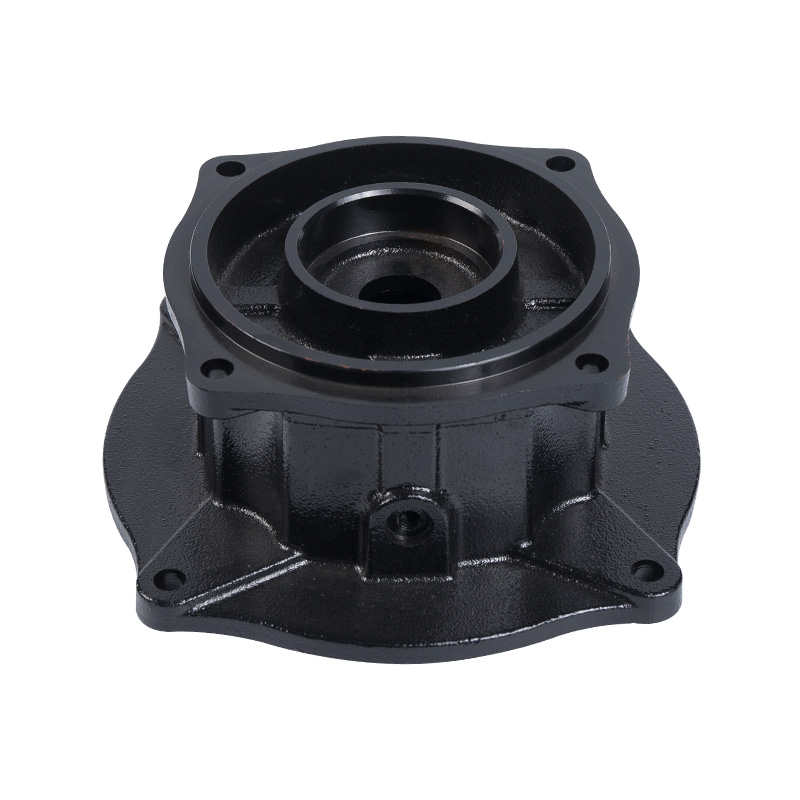

Sewage pump tank
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The oil in the oil chamber, in addition to lubricating the mechanical ...
See Details -
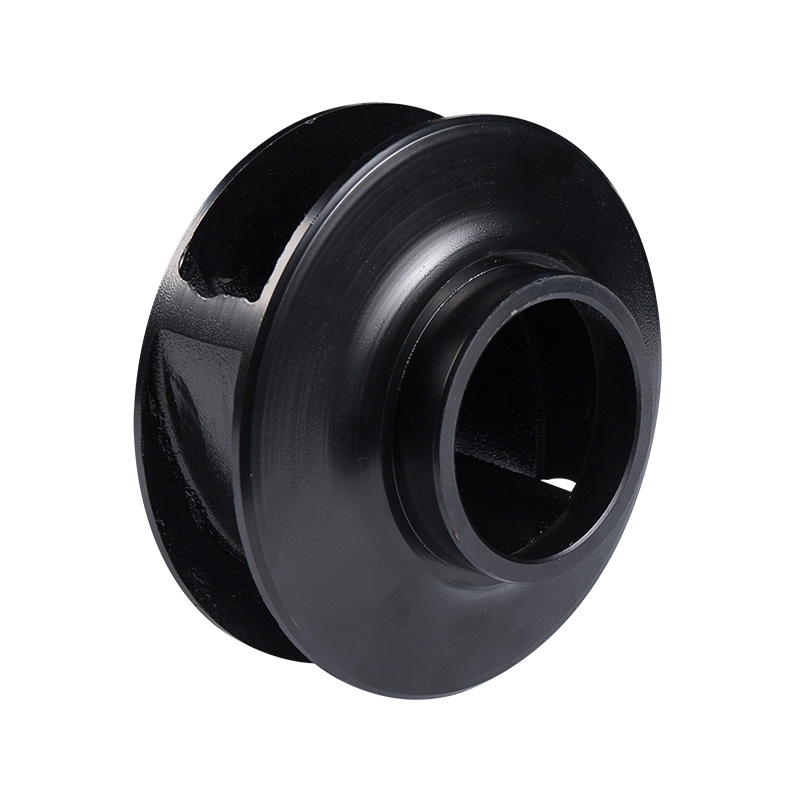

Sewage pump cast iron impeller
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The impeller is the core component of a sewage pump, responsible for r...
See Details -
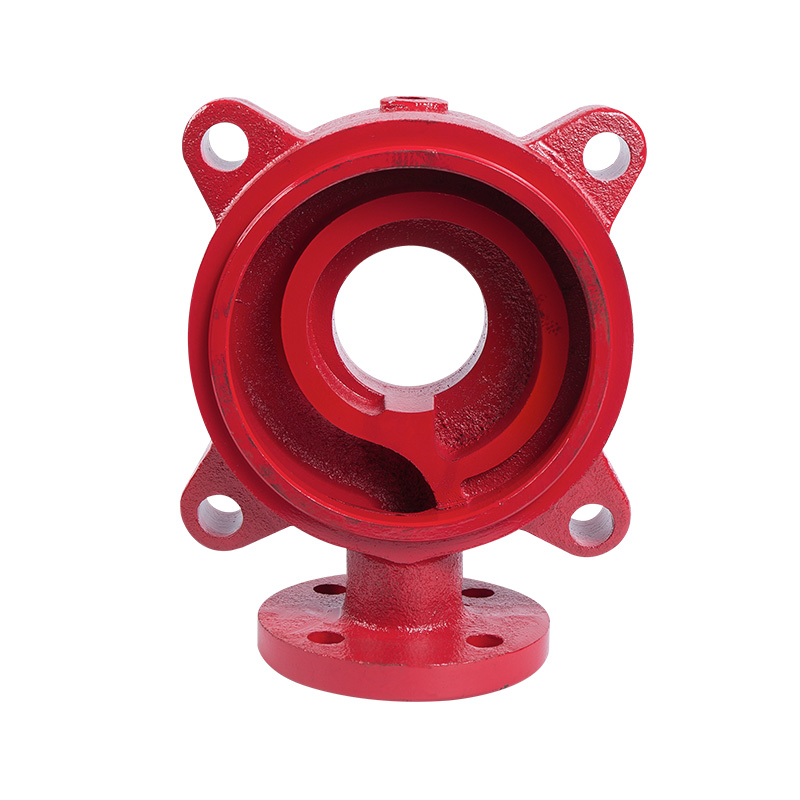

LG multi-stage pump water outlet section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The outlet section is the outlet part of the pump, which is responsibl...
See Details -
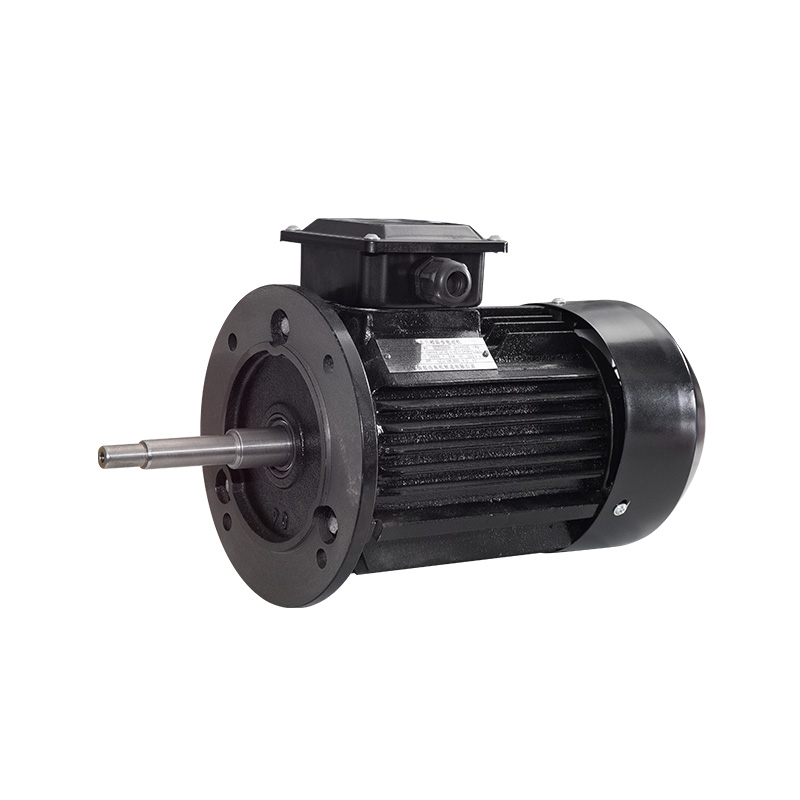

Vertical motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
A conventional fixed-speed motor whose operating speed is usually cons...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

