- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
How Often Should a Sewage Pump Be Serviced or Replaced?
Introduction: Why Scheduled Care for Sewage Pumps Matters
Sewage pumps play a critical role in moving wastewater away from homes, commercial buildings, and municipal systems. Neglecting their maintenance can lead to backups, costly emergency repairs, health hazards, and premature replacement. This article explains practical service intervals, replacement triggers, and maintenance tasks tailored to different pump types and operating conditions so you can build a realistic lifecycle plan and reduce downtime.
Understanding Sewage Pump Types and How That Affects Service Frequency
Not all sewage pumps are the same — service intervals vary depending on whether you have a submersible pump, pedestal pump, grinder pump, or a municipal pump station. Each design presents different wear points (impellers, seals, bearings, motors) and different exposure to solids and abrasive particles. Knowing your pump type is the first step to setting a realistic maintenance schedule.
Residential submersible pumps
Submersible sewage pumps sit inside the wet well and handle raw sewage directly. Due to constant immersion and exposure to grit and solids, these pumps typically require inspection every 6 months, with a more thorough service annually. High-use homes or homes with frequent solids (e.g., three-plus bathrooms) should consider quarterly checks.
Pedestal (dry-pit) pumps
Pedestal pumps have the motor above the wet well and a long shaft to the impeller. Because the motor avoids immersion, electrical failure risk is lower, but shaft bearings and seals still wear. Inspect these pumps annually and service based on bearing condition and shaft alignment.
Grinder and macerator pumps
Grinder pumps macerate solids before pumping and are often used in low-pressure sewer systems or when toilets are connected to the pump. The cutting mechanisms and seals require closer attention; inspect quarterly and replace cutting components or seals at the first sign of dullness or leakage.
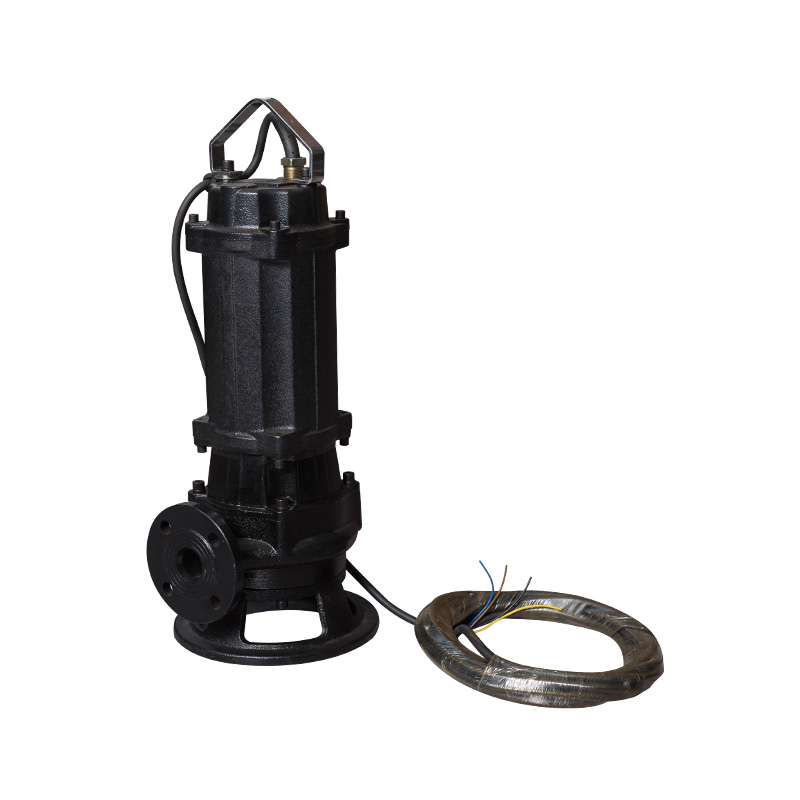

Recommended Service Intervals — Practical Schedule
Use these general guidelines as a starting point and adapt based on workload, environment, and pump performance history. Factors such as grit, grease, chemical exposure, and run-time hours can shorten recommended intervals.
| Pump Type | Routine Inspection | Preventive Service | Typical Replacement |
| Residential Submersible | Every 6 months | Annually | 7–12 years |
| Pedestal (Dry-Pit) | Annually | Every 1–2 years | 10–15 years |
| Grinder/Macerator | Quarterly | Every 6–12 months | 5–10 years |
| Municipal/High-Duty | Monthly | Every 3–6 months | 5–20 years (varies greatly) |
Key Maintenance Tasks for Each Service Visit
A well-structured service visit includes inspection, cleaning, basic repairs, and performance testing. Below is a practical checklist that technicians and facility managers can follow.
- Visual inspection of the wet well and pump exterior for corrosion, buildup, or blockages.
- Check and clean impellers, cutting rings, and strainers to prevent clogging and loss of performance.
- Verify float switches, level sensors, and control panel indicators for correct operation and adjust setpoints if needed.
- Measure amp draw and compare to motor nameplate ratings to detect bearing wear, blockage, or electrical issues.
- Inspect seals, mechanical seals, and shaft coupling for leaks or wear; replace seals before catastrophic failure.
- Lubricate bearings and check gearbox oil level where applicable, following manufacturer torque and lubrication specs.
- Test backup systems: check standby pumps, check valves, alarms, and emergency power supplies.
When to Replace a Sewage Pump — Clear Replacement Triggers
Replacement is not only a function of age; several practical warning signs indicate replacement is necessary to avoid failures that lead to backups and safety issues. Monitor these red flags closely.
- Persistent loss of pumping capacity despite cleaning and repairs (reduced flow or head).
- Frequent tripping of motor overloads or rising amp draw indicating internal friction, bearing failure, or blocked impeller.
- Recurrent seal failures or leakage from the motor housing — a sign that corrosion or wear has compromised internal protection.
- Rusted or damaged structural components (lift chains, guide rails, brackets) that undermine safe extraction and serviceability.
- Motor winding issues, excessive vibration, or noise after corrective repairs — these often presage imminent motor failure.
Cost Factors and Budgeting for Service vs Replacement
Budgeting should consider routine labor and parts for preventive upkeep, emergency call-out costs, and capital expenses for replacement. Typical cost drivers include pump size and type, accessibility (wet-well confined space increases labor and safety costs), specialty parts (grinder blades, OEM seals), and control upgrades (level sensors, SCADA integration).
Rough cost ranges (illustrative)
Small residential submersible service visit: $150–$400. Grinder pump major service or rebuild: $400–$1,200. New residential pump replacement (installed): $800–$3,000. Large commercial or municipal replacements can range from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars depending on motor power, redundancy, and controls.
Practical Tips to Extend Pump Life
- Reduce ingress of fats, oils, and grease at the source; FOG causes clogging and increases maintenance frequency.
- Install and maintain coarse screens or grinders upstream to reduce large debris reaching the pump.
- Monitor run-hours and schedule parts replacement (seals, bearings) before end-of-life to avoid emergency downtime.
- Keep access points, guide rails, and lifting gear corrosion-free and serviced to minimize service time and hazards.
Conclusion: Balance Proactive Service with Practical Replacement Decisions
A disciplined maintenance schedule reduces unexpected failures and keeps total lifecycle costs manageable. Use type-specific inspection intervals, monitor performance metrics (flow, amp draw, vibration), and act on the replacement triggers listed above. When in doubt, consult manufacturer recommendations and keep a log of run-hours and service actions — that historical data is the most reliable guide for an evidence-based replacement timeline.
Related Products
-
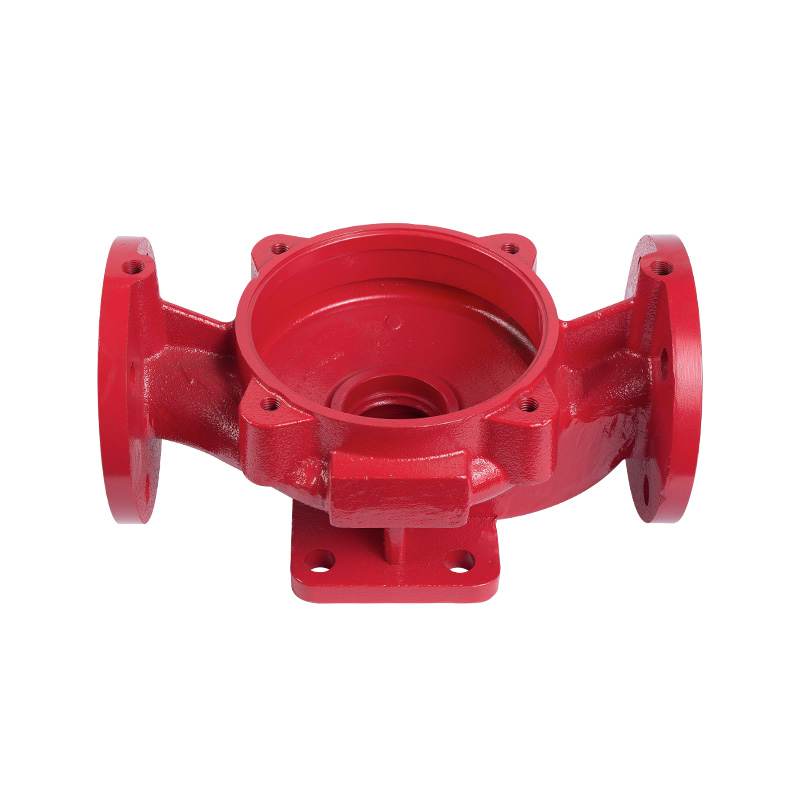

Vertical pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -
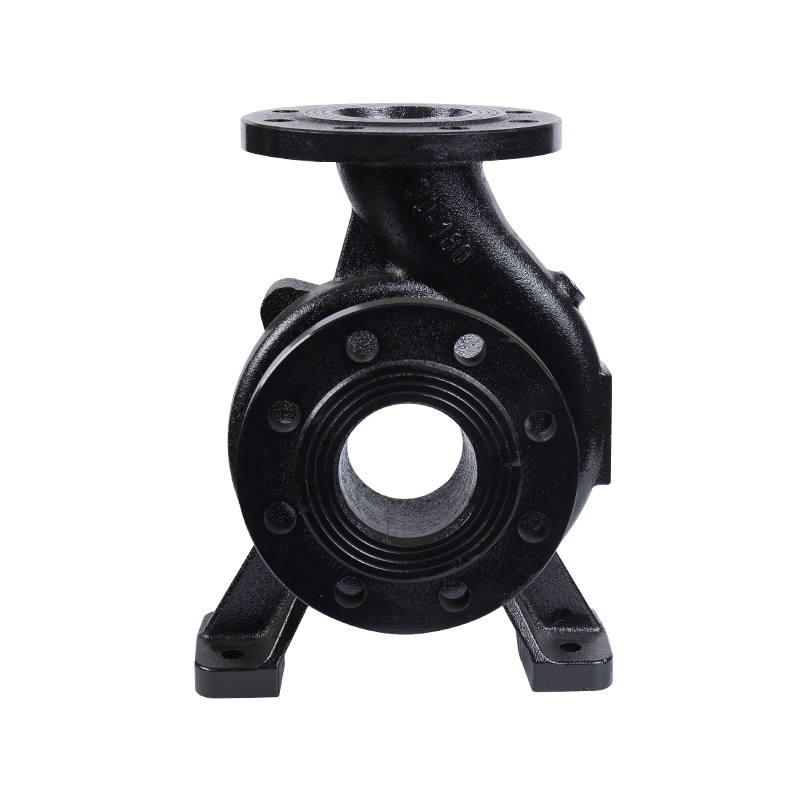

Horizontal pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -
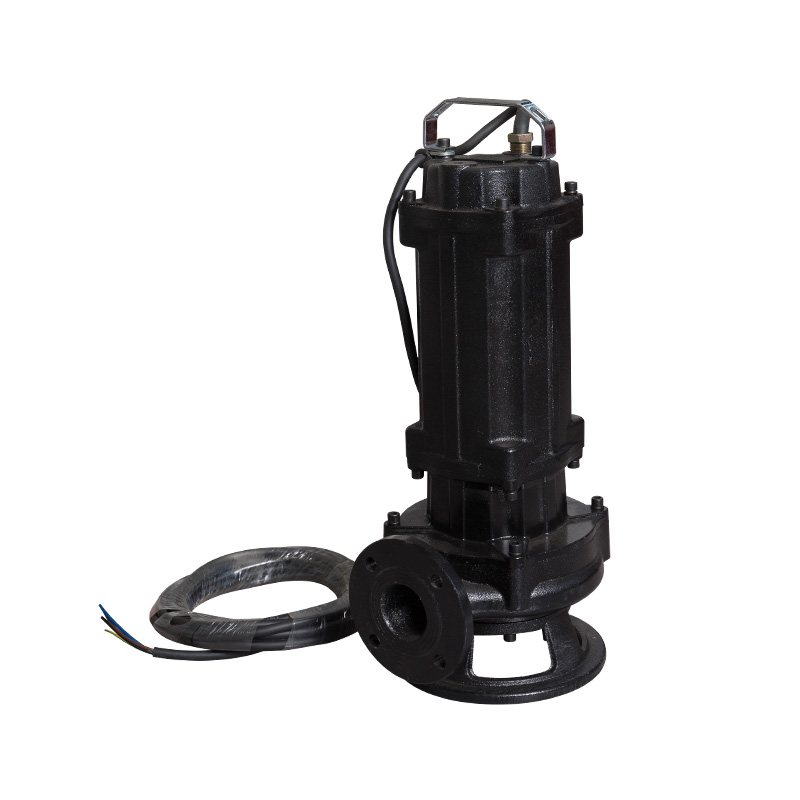

Cutting sewage pump
Cat:Sewage Pump
Cutting sewage pump is a kind of sewage pump, also called cutting pump...
See Details -
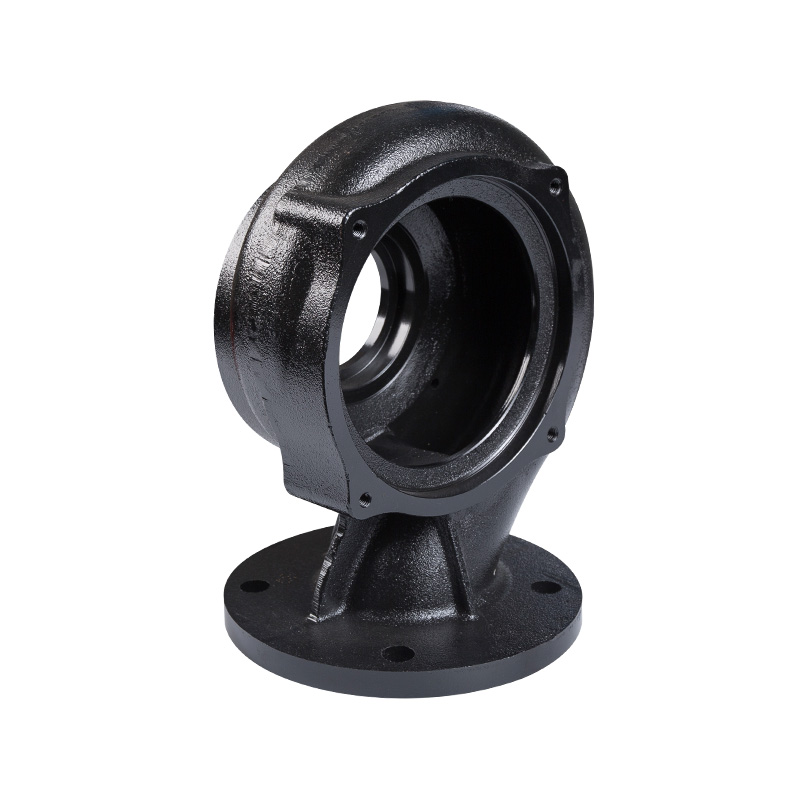

Sewage pump body
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The pump body is the outer shell of the sewage pump, with the function...
See Details -
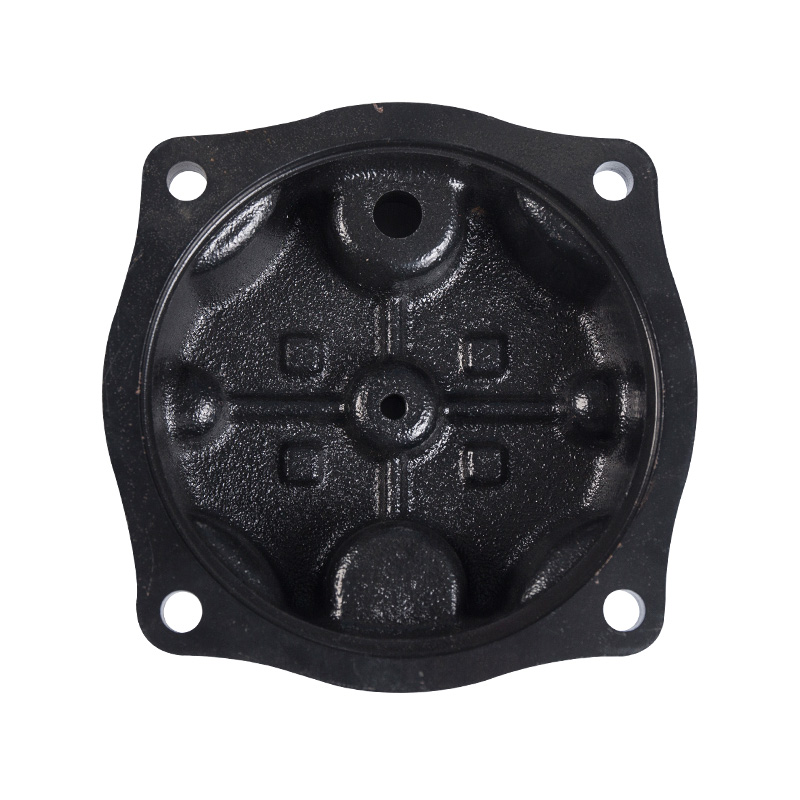

Sewage pump hanging cover
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Installed on the upper part of the sewage pump unit, it is used for li...
See Details -
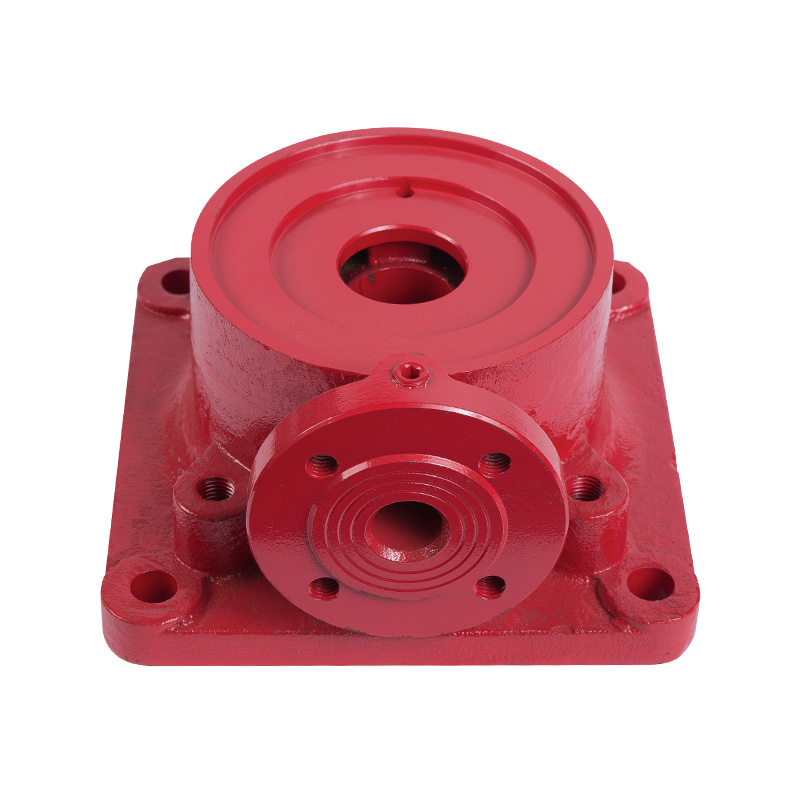

LG multi-stage pump water inlet section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The inlet section is the inlet portion of the pump and is responsible ...
See Details -
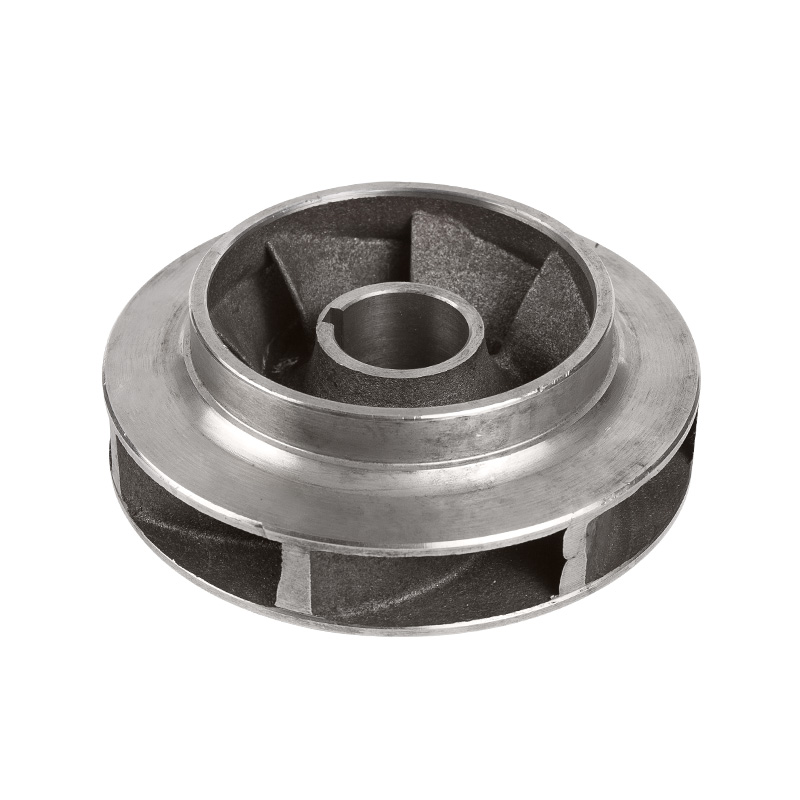

LG multi-stage pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impellers are impellers made of stainless steel materi...
See Details -
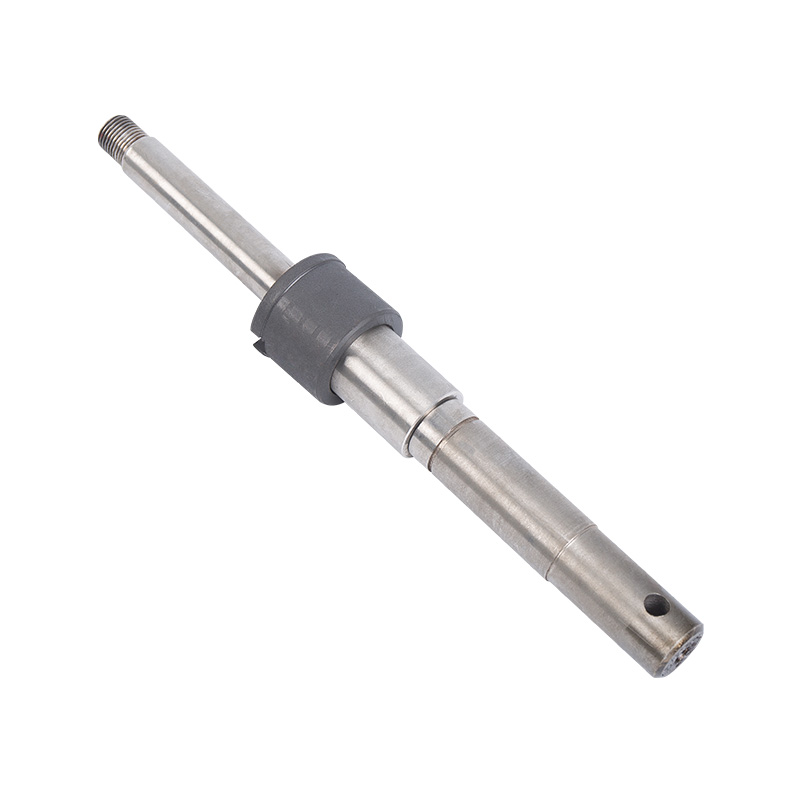

LG multi-stage pump shaft
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The pump shaft is the key component to bear the rotational force and t...
See Details -
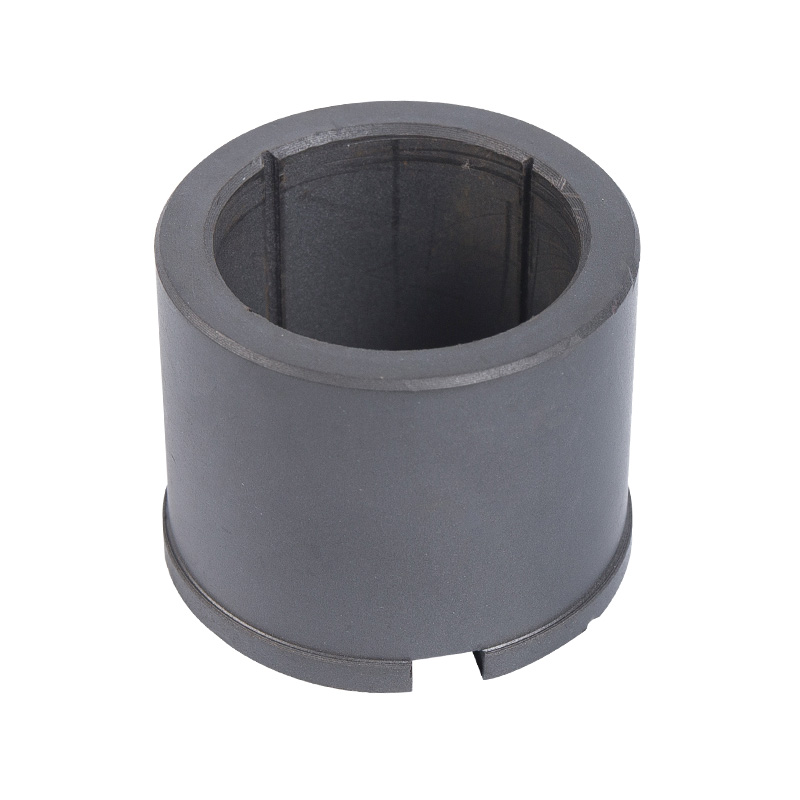

LG multi-stage pump water bearing
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Water bearings are a special type of bearings commonly used in multi-s...
See Details -
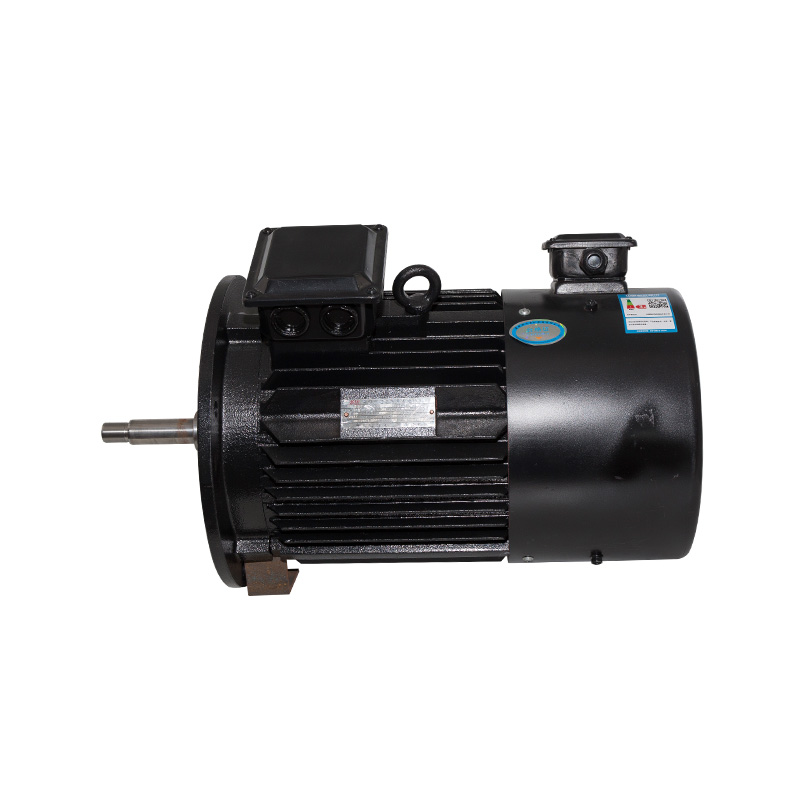

B14/B5 Vertical inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
A type of adjustable speed motor that can control the speed of the mot...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

