- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
How Do Cutting Sewage Pumps Prevent Clogs and Improve Wastewater Handling?
Cutting sewage pumps are specialized wastewater pumps designed to handle liquids containing solids, fibrous materials, and debris without clogging. They combine a centrifugal pumping mechanism with cutting blades that shred large solids before they enter the pump, ensuring smooth flow and preventing blockages in piping systems.
These pumps are essential in municipal wastewater treatment, industrial effluent handling, and residential sewage systems. By reducing the size of solids in sewage, they protect downstream equipment, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall system reliability.
Structural Design and Components
Understanding the structure of a cutting sewage pump helps in selection, installation, and maintenance.
Pump Casing
The pump casing is typically made from cast iron, stainless steel, or high-strength alloys. It is designed to withstand abrasive fluids and prevent corrosion. The casing also houses the impeller and cutting assembly.
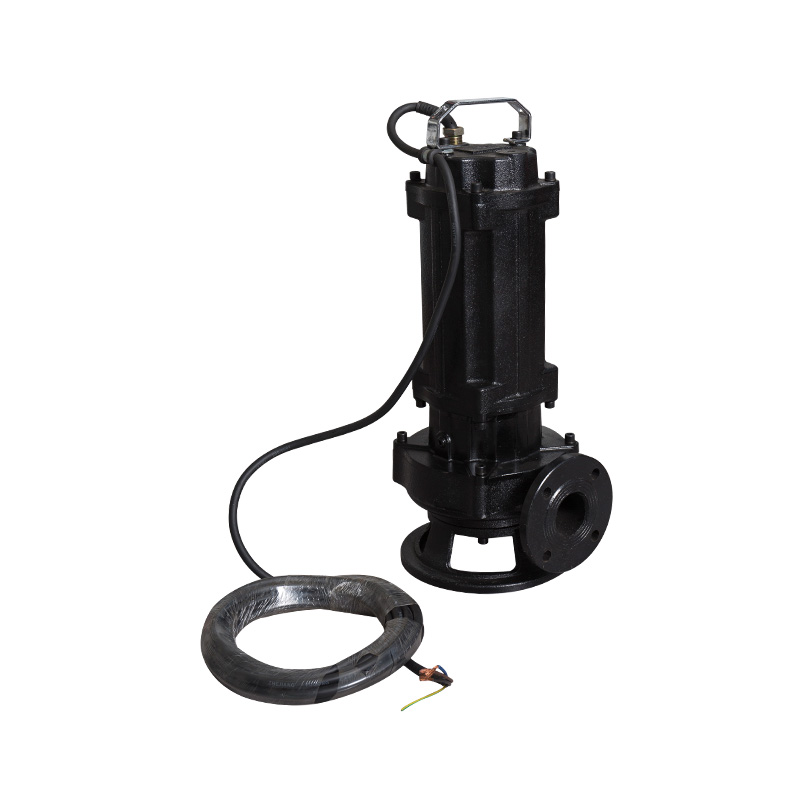

Impeller and Cutting Mechanism
The impeller moves fluid efficiently while integrated cutting blades shred fibrous or solid materials. The number, shape, and arrangement of cutting edges determine the cutting efficiency and particle size reduction.
Motor and Drive
Cutting sewage pumps use electric motors or diesel engines, depending on application. Motors are usually protected against moisture and overheating, and can be submersible or dry-mounted. Drive mechanisms may include direct-coupled or belt-driven systems.
Seals and Bearings
Mechanical seals and bearings ensure leak-free operation and long service life. Bearings are lubricated either by oil or grease, depending on the pump design, and must withstand high axial and radial loads caused by solids.
Performance Characteristics
Cutting sewage pumps are selected based on performance specifications to match the application.
Flow Rate and Head
Flow rate depends on impeller design, pump diameter, and motor speed. Head represents the pressure the pump can generate to move liquid through piping systems. Balancing flow rate and head ensures energy-efficient operation and prevents cavitation.
Cutting Capacity
Cutting capacity defines the size and type of solids the pump can handle. High-capacity pumps can shred fibrous materials, plastics, and sanitary waste, reducing the risk of clogs in downstream pipelines.
Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Efficiency depends on impeller design, motor type, and flow conditions. Optimized cutting sewage pumps consume less energy while maintaining effective pumping performance. Selection of a properly sized pump reduces operational costs.
Applications of Cutting Sewage Pumps
Cutting sewage pumps are widely used wherever sewage contains solids or fibrous material that may obstruct regular pumps.
Municipal Wastewater Treatment
These pumps are installed at lift stations, sewage collection points, and treatment plants. By shredding solids, they reduce maintenance on downstream pumps, prevent clogging in piping, and improve overall treatment efficiency.
Industrial Effluent Handling
Industries such as food processing, pulp and paper, and textile manufacturing generate effluents with fibrous and solid waste. Cutting sewage pumps efficiently process this wastewater, preventing pump failures and reducing downtime.
Residential and Commercial Sewage Systems
In apartment complexes, hotels, and commercial buildings, these pumps ensure reliable sewage transfer and minimize blockages caused by sanitary products, hair, and kitchen waste.
Maintenance and Operational Tips
Proper maintenance extends the life of cutting sewage pumps and ensures uninterrupted operation.
- Regularly inspect cutting blades for wear or damage and replace if necessary
- Check seals and bearings for leaks and lubricate according to manufacturer guidelines
- Monitor motor current and temperature to prevent overloads and overheating
- Keep the pump inlet clear of large debris that may bypass the cutting mechanism
Comparison of Pump Types for Sewage Handling
| Feature | Standard Centrifugal Pump | Cutting Sewage Pump |
| Solids Handling | Limited | High, with shredding capability |
| Maintenance | Moderate, may clog | Lower, prevents clogs |
| Application | Clean water or minor solids | Wastewater with solids, fibrous material |
| Durability | Moderate | High, abrasion-resistant materials |
Tips for Selecting the Right Cutting Sewage Pump
- Assess solids size, fibrous content, and flow rate requirements for your application
- Choose a motor type (submersible or dry-mounted) based on installation constraints
- Consider blade design and material for maximum cutting efficiency and longevity
- Evaluate maintenance needs, spare parts availability, and manufacturer support
Conclusion
Cutting sewage pumps are critical components in modern wastewater management, preventing clogs and ensuring reliable transfer of solids-laden liquids. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance optimize performance, extend service life, and reduce operational costs.
By understanding the pump’s design, cutting mechanism, and performance characteristics, engineers and operators can ensure efficient sewage handling across municipal, industrial, and residential applications, minimizing downtime and maintenance challenges.
Related Products
-
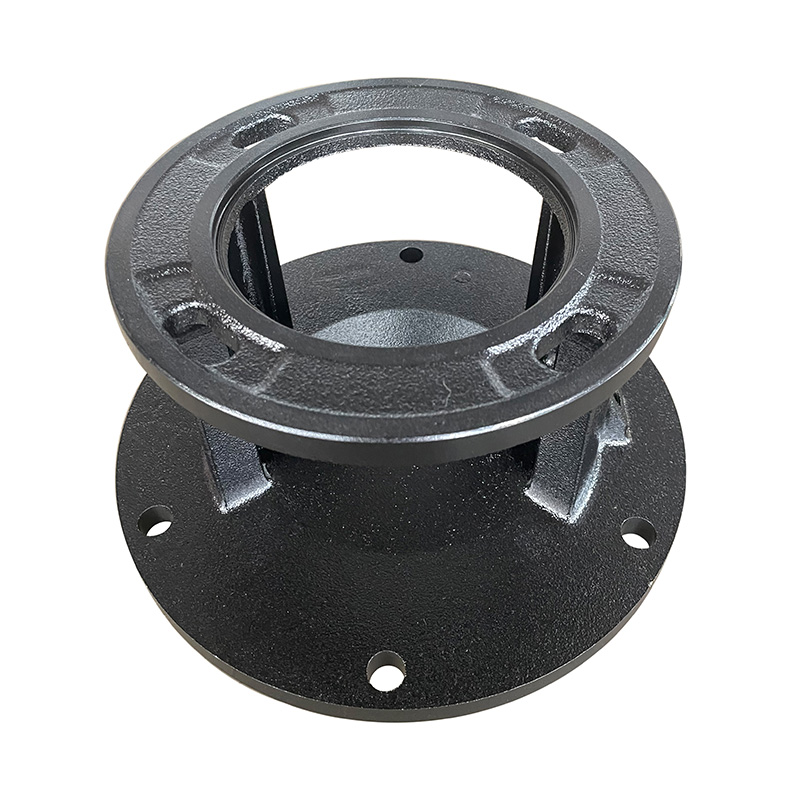

TD high-efficiency energy-saving circulation pump vertical base
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
A vertical base is a pedestal used to support and secure a vertical TD...
See Details -
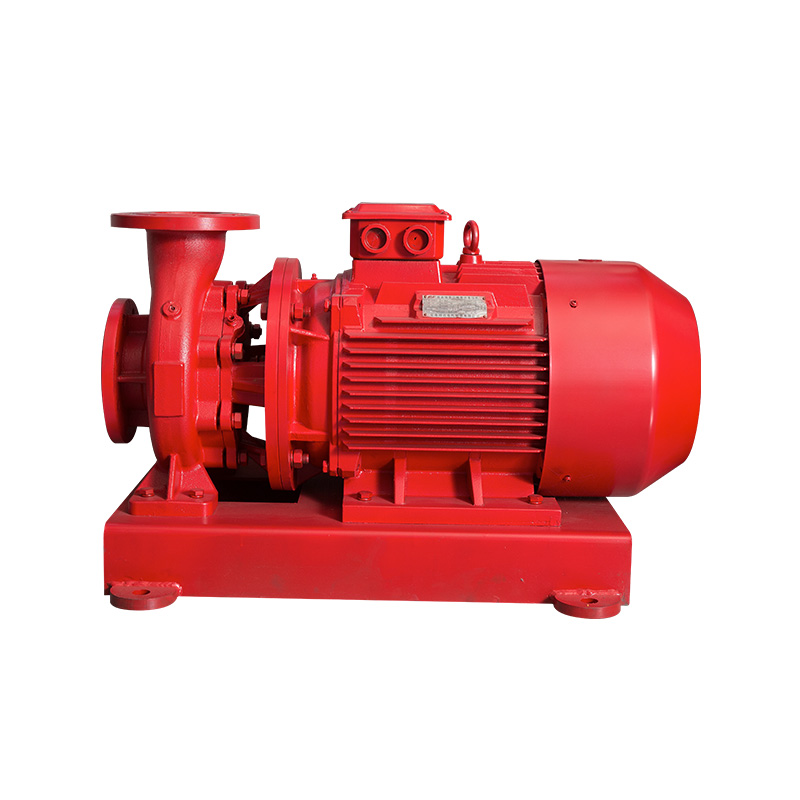

Horizontal pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISW series single-stage single-suction horizontal centrifugal pumps ar...
See Details -
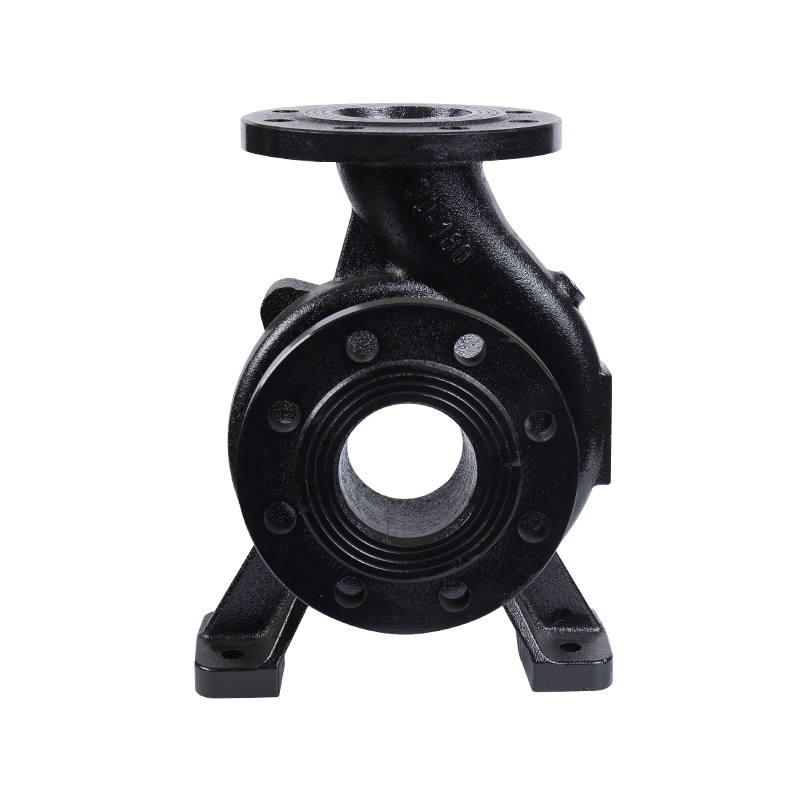

Horizontal pipeline pump body
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump body consists of two main parts: suction chamber and pressure...
See Details -

Pipeline pump B14 pump cover
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pipeline pump B14 pump cover is a specific type of pump cover for ...
See Details -
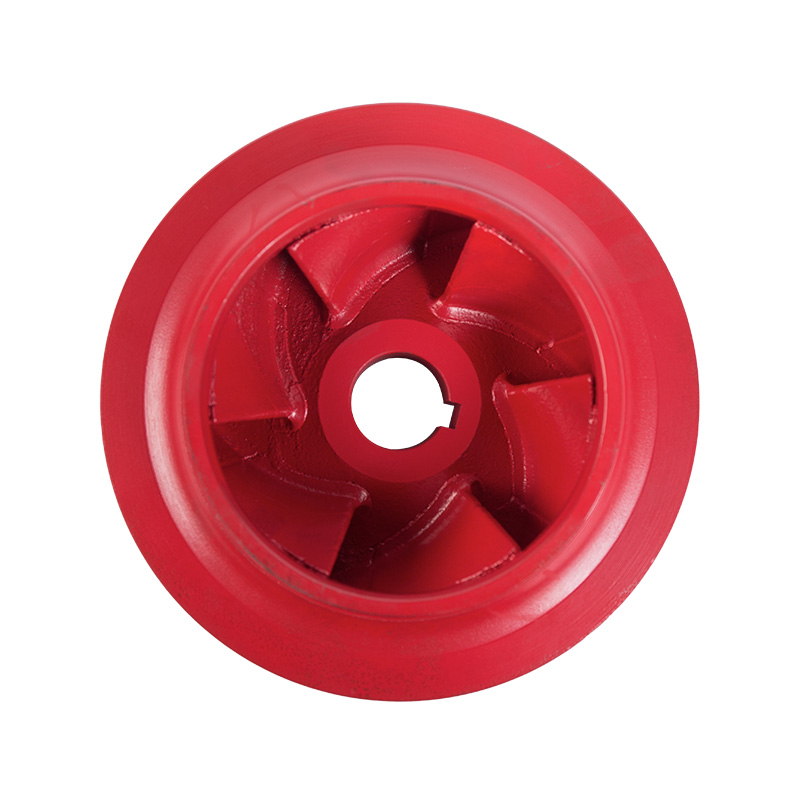

Pipeline pump cast iron impeller
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The impeller refers to both the disc with moving blades, which is an i...
See Details -
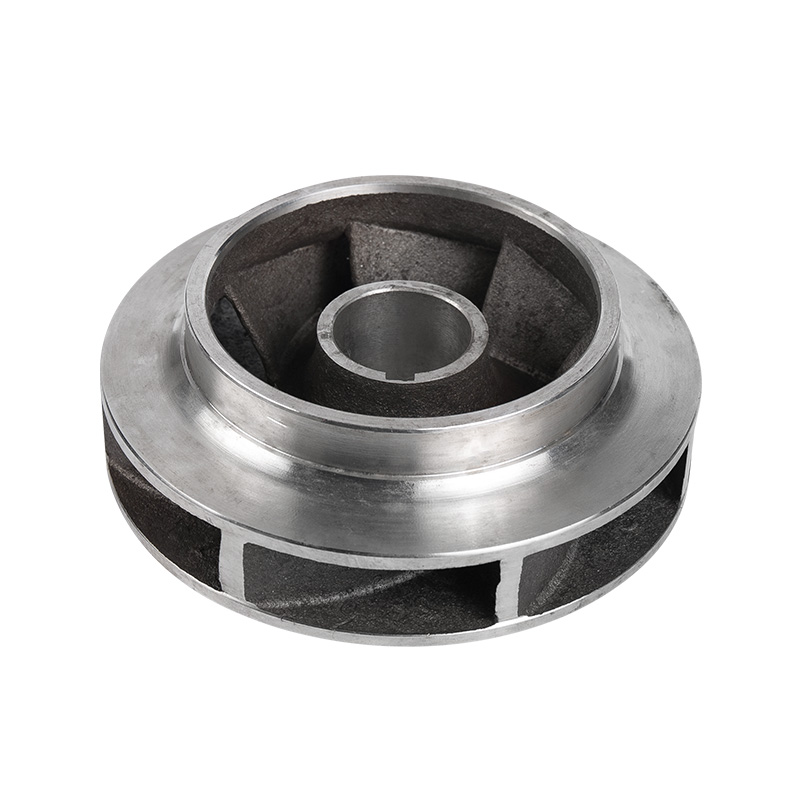

Pipe pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impeller material is stainless steel, it is not easy t...
See Details -
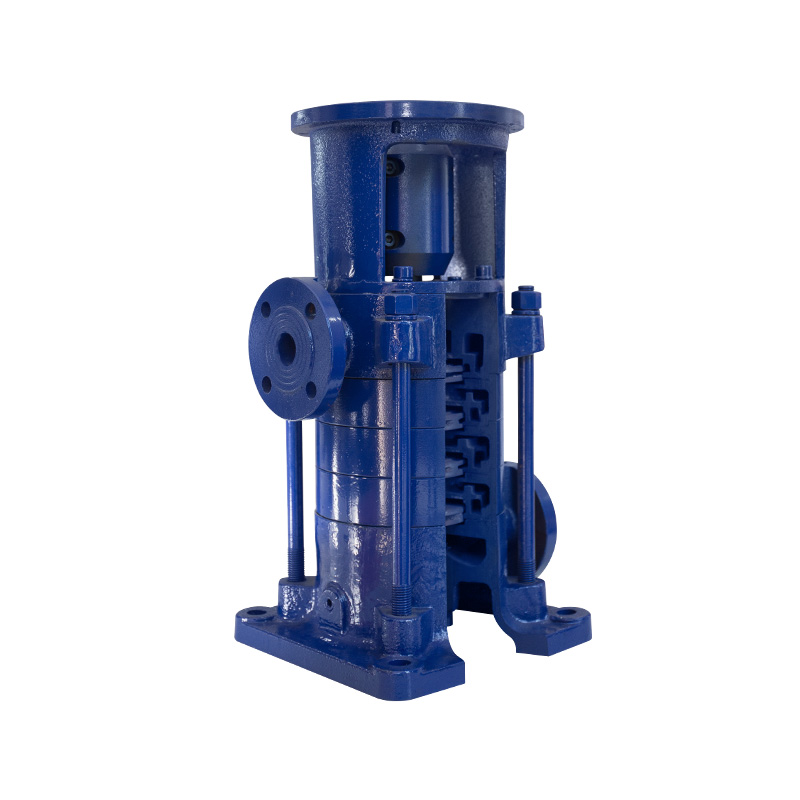

LG multi-stage pump 150 series
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump
Operating conditions 1. It can convey clear water or non-corrosive med...
See Details -
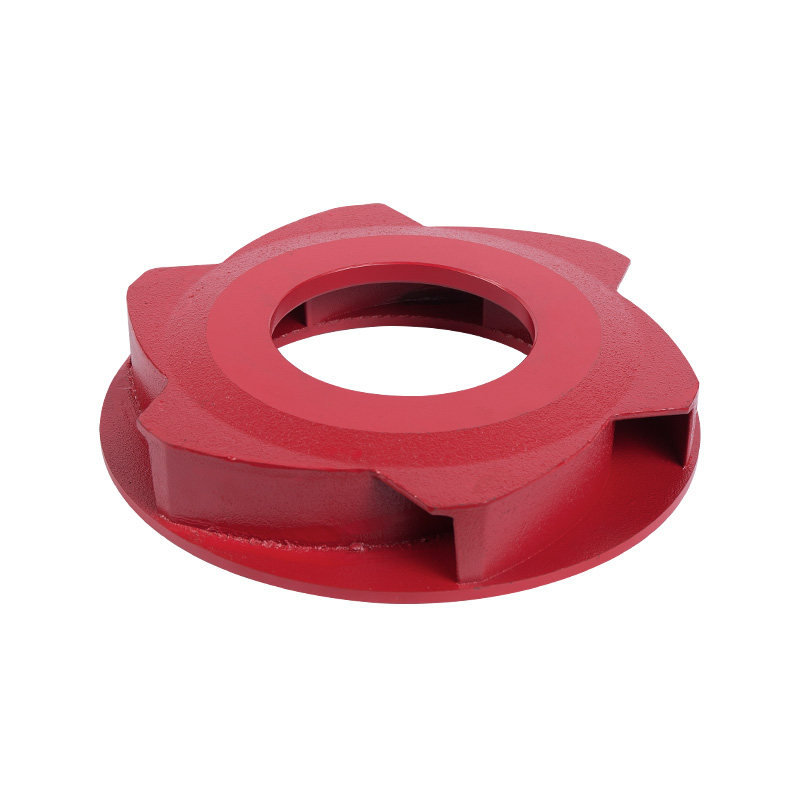

LG multistage pump cast iron impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Cast iron impeller is one of the key components of the pump, which pre...
See Details -
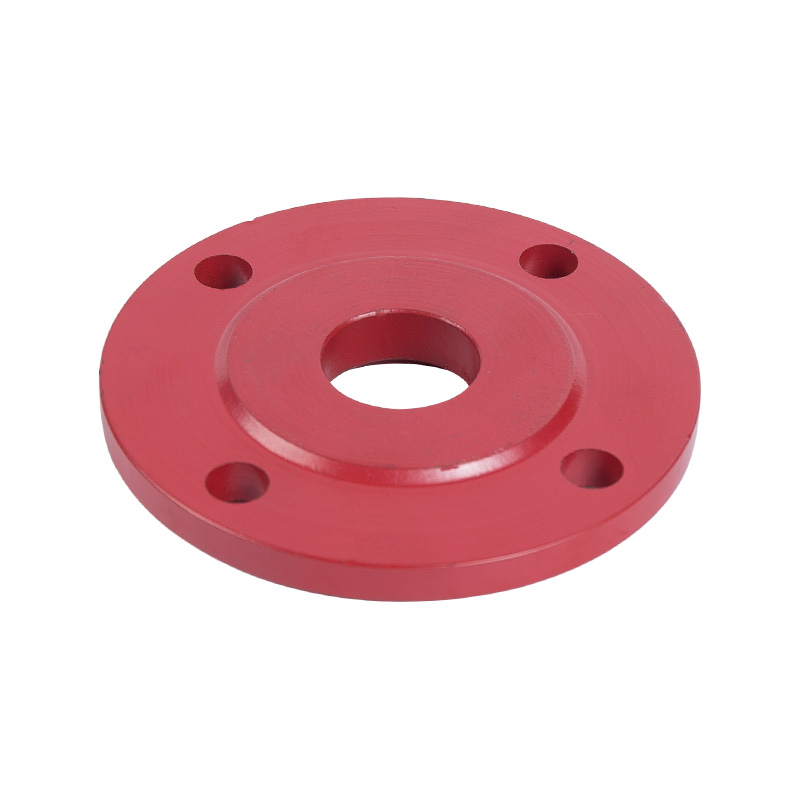

LG multi-stage pump seal gland
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The machine seal gland is a component that encloses the machine seal u...
See Details -
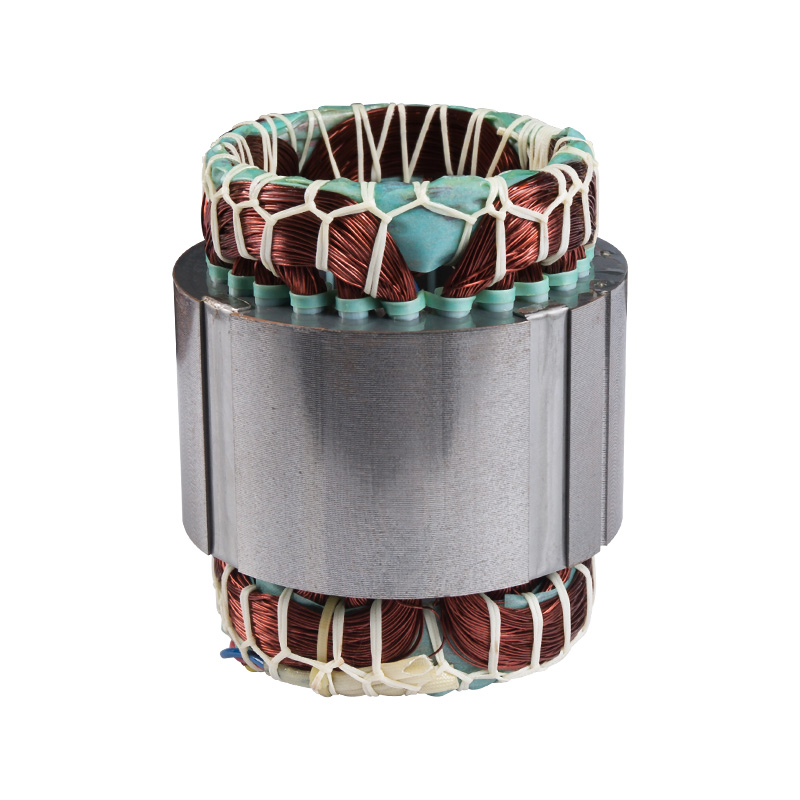

Finished stator
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
The stator of a motor refers to the fixed part which contains the stat...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

