- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Why high-performance electric motors are the key to improving industrial efficiency and sustainability?
In today’s fast-paced industrial world, efficiency and reliability are key to maintaining competitive advantage. At the heart of nearly every modern machine or system lies the electric motor—an indispensable component for driving machines across a range of applications. From manufacturing and transportation to energy generation and automation, electric motors are essential for driving progress and productivity.
These motors operate on the principles of electromagnetism, where electric current passing through a conductor (such as a wire) generates a magnetic field that interacts with magnets or other electromagnetic fields to produce rotational motion.
Key Benefits of Electric Motors
1. Energy Efficiency
Electric motors are highly efficient compared to other types of power sources, such as internal combustion engines. Their design minimizes energy loss, and they typically operate at a much higher efficiency, making them ideal for companies looking to cut down on energy consumption and operational costs.
For businesses looking to optimize energy usage and reduce utility expenses, investing in energy-efficient electric motors is a wise decision. Many modern electric motors come equipped with variable frequency drives (VFDs), which allow for precise control over speed and torque, resulting in additional energy savings.
2. Low Maintenance and Durability
Electric motors are known for their longevity and low maintenance requirements. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors have fewer moving parts, which reduces the chances of wear and tear. As a result, they require minimal maintenance, saving companies time and money on repairs and servicing.
Additionally, these motors are built to withstand harsh environments, offering durability and reliability even in demanding conditions. Many electric motors are designed to operate for tens of thousands of hours before any significant maintenance is required.
3. Environmentally Friendly
Electric motors are a more environmentally friendly option compared to fossil-fuel-powered machinery. They produce little to no direct emissions, making them a cleaner choice for industries looking to reduce their carbon footprint and comply with environmental regulations. Moreover, electric motors can be powered by renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, further enhancing their eco-friendliness.
By switching to electric motors, companies can not only meet sustainability goals but also contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
4. Versatility and Adaptability
Electric motors come in various types and sizes, making them adaptable to a wide range of applications. From small motors that power household appliances to large motors used in industrial machinery, there is an electric motor suitable for virtually any task. Their flexibility allows them to be used in diverse sectors such as manufacturing, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), agriculture, and transportation.
Electric motors can also be easily integrated into automation systems, where they provide precise control over movements and operations, improving the overall efficiency and productivity of industrial processes.
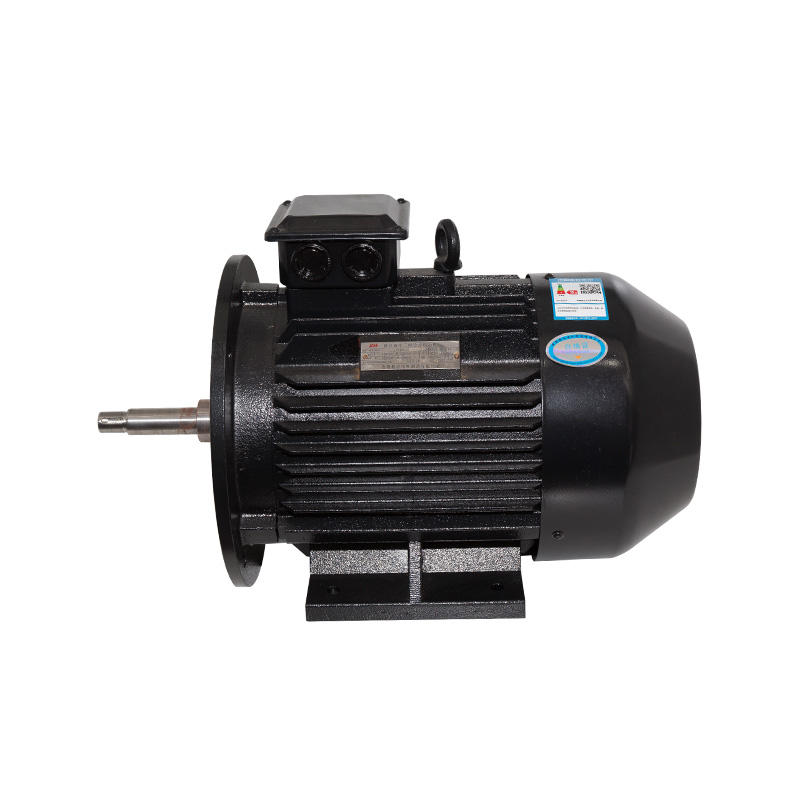

Types of Electric Motors
Electric motors come in different designs, each with specific features that suit various applications:
1. AC Motors (Alternating Current Motors)
AC motors are the most commonly used type of electric motor in industrial and commercial settings. They operate on alternating current, which means the direction of the current periodically reverses. AC motors are popular for their simplicity, robustness, and ability to be easily connected to the power grid.
These motors come in two main types:
Induction Motors: These are the most widely used AC motors due to their cost-effectiveness and reliability.
Synchronous Motors: Used in applications requiring precise speed control.
2. DC Motors (Direct Current Motors)
DC motors operate on direct current, where the flow of electricity is unidirectional. They are known for their excellent speed control and high torque capabilities. DC motors are commonly used in electric vehicles, robotics, and variable-speed drives, where precision and adaptability are required.
3. Stepper Motors
Stepper motors are a type of DC motor that move in precis applications that require exact positioning, such as 3D printers, CNC machines, and camera systems. Their ability to rotate in small, precise increments makes them invaluable for industries where accuracy is crucial.
Applications of Electric Motors
The applications of electric motors are vast and varied, spanning nearly every industry. Below are just a few examples:
1. Manufacturing
Electric motors power machinery such as conveyor belts, mixers, and packaging equipment in factories. Their efficiency and reliability ensure smooth production processes, reducing downtime and maximizing output.
2. Transportation
In the transportation sector, electric motors are found in electric vehicles (EVs), buses, and trains. With the growing demand for sustainable and eco-friendly transportation options, electric motors are playing a pivotal role in the shift towards electric mobility.
3. HVAC Systems
Electric motors are essential components in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. They power fans, compressors, and pumps, ensuring optimal climate control in commercial and residential buildings.
4. Agriculture
In agriculture, electric motors are used to power irrigation systems, feeding equipment, and processing machinery. They provide a cost-effective and reliable solution for farmers and agricultural operations.
Electric motors are a cornerstone of modern industry, offering energy-efficient, low-maintenance, and environmentally friendly solutions for a wide variety of applications. Their adaptability, reliability, and precise control make them an indispensable tool in manufacturing, transportation, and beyond.
Related Products
-
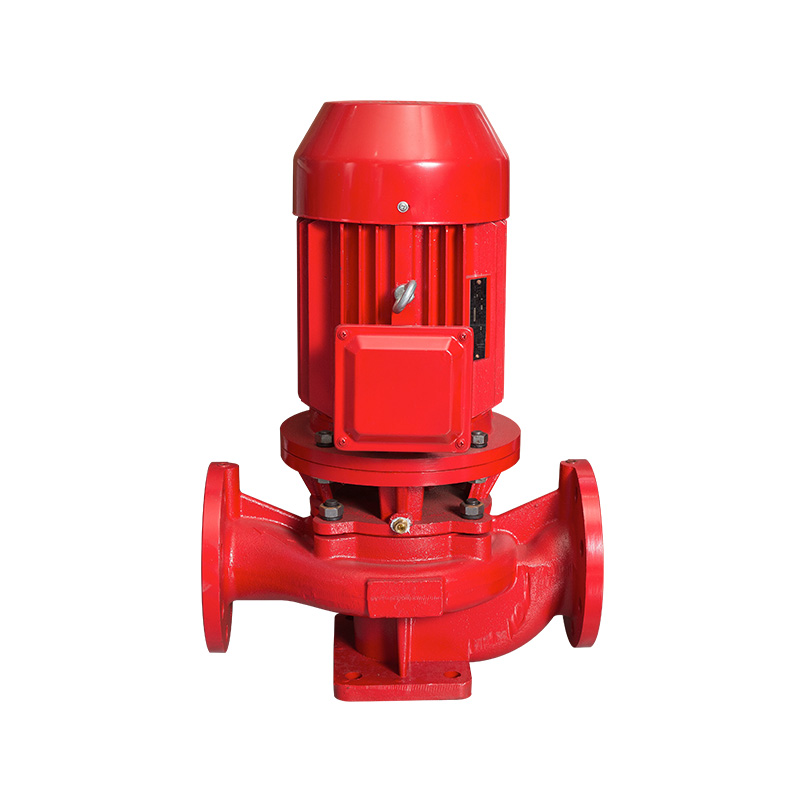

Vertical pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISG series single-stage single-suction vertical centrifugal pump is a ...
See Details -
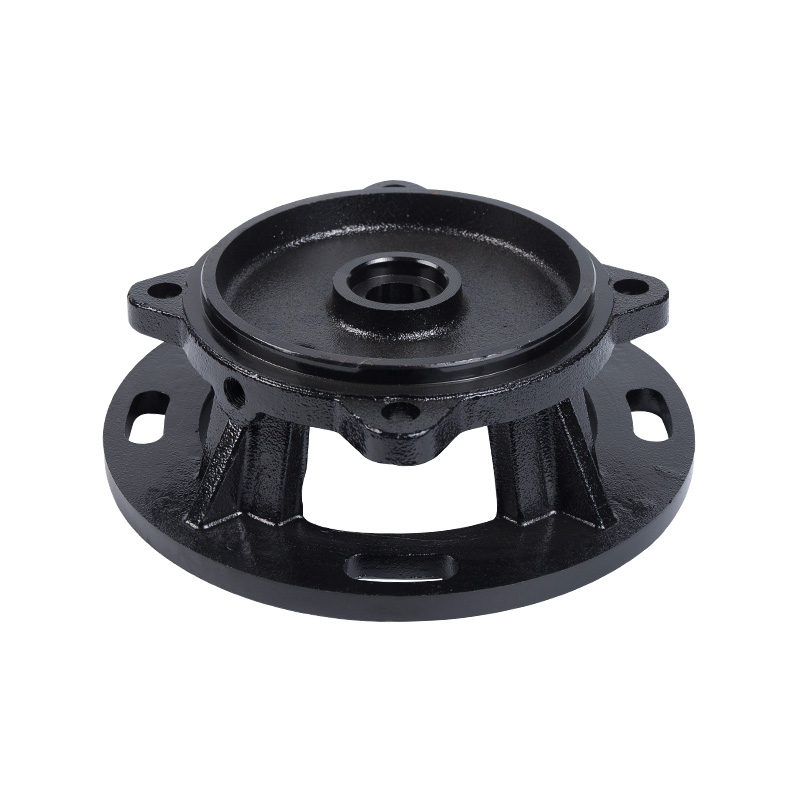

Pipe pump cover
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump cover is used to tighten and seal. The pump cover ensures tha...
See Details -
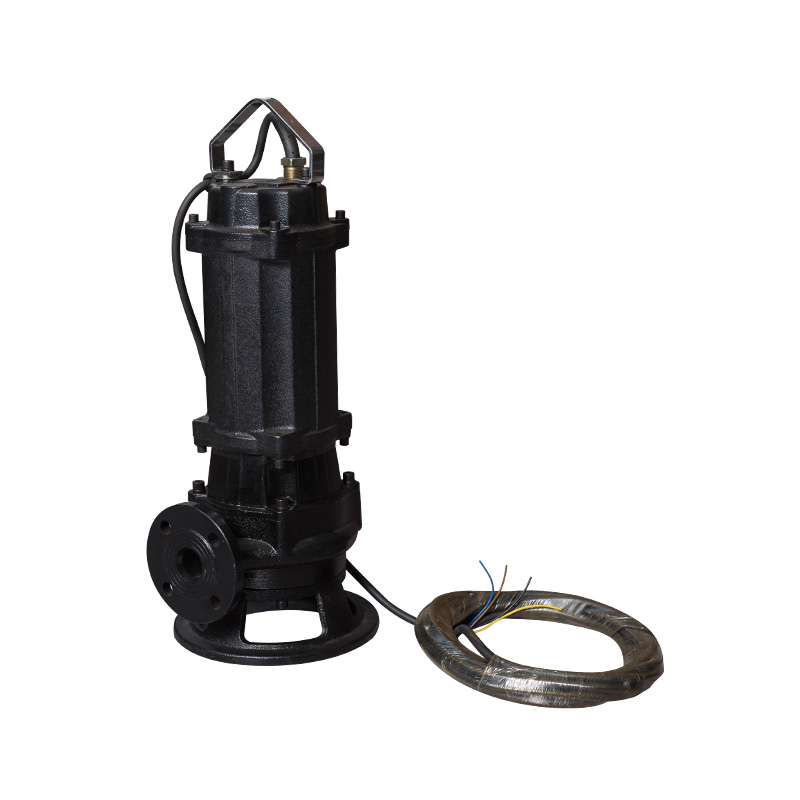

Ordinary sewage pump
Cat:Sewage Pump
1. Our WQ-type general sewage pump adopts a large flow channel anti-cl...
See Details -
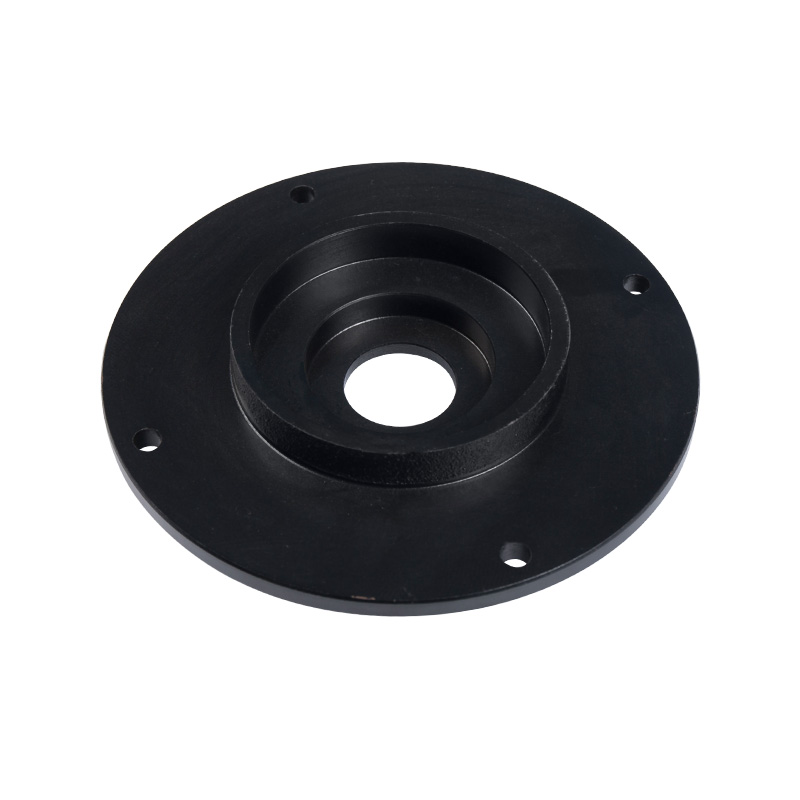

Sewage pump cover
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Installed on the top of the sewage pump unit, it is used to enclose th...
See Details -
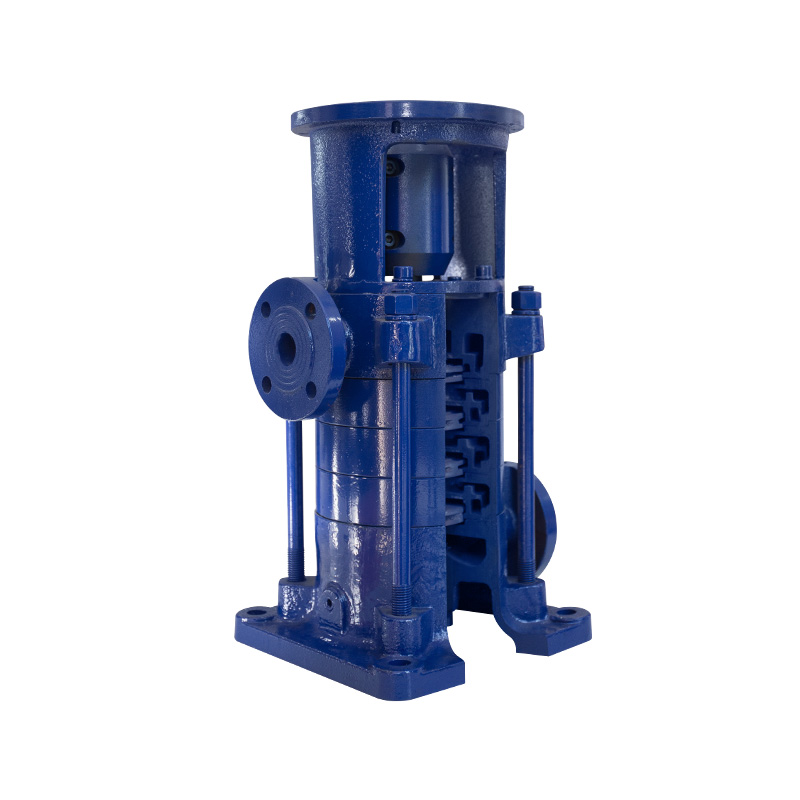

LG multistage pump 100 series
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump
Product features 1. Compact structure, small volume, small footprint. ...
See Details -
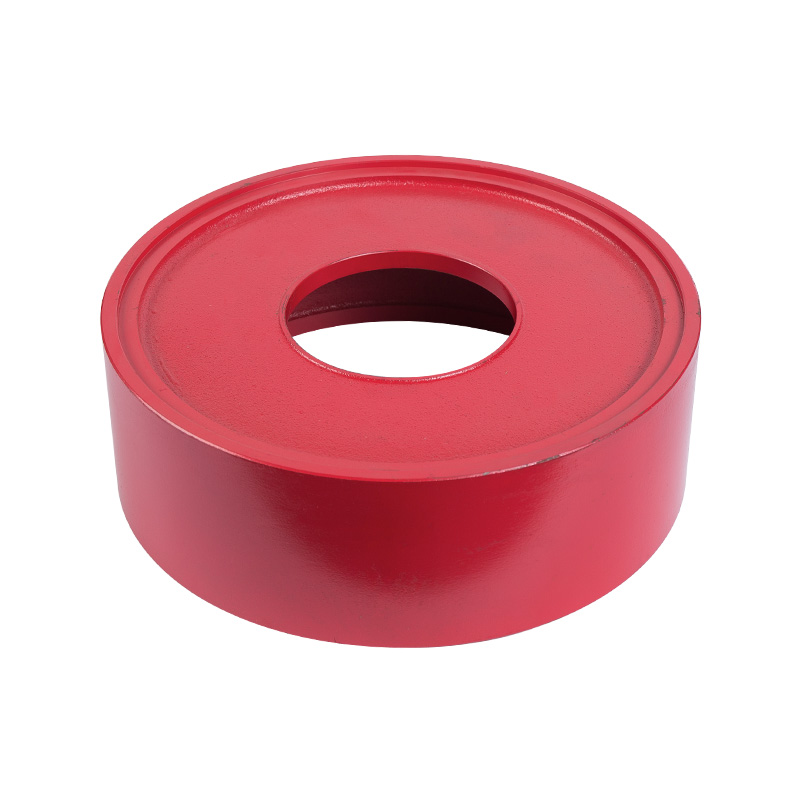

LG multi-stage pump middle section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The middle section is the main part of the pump body, responsible for ...
See Details -
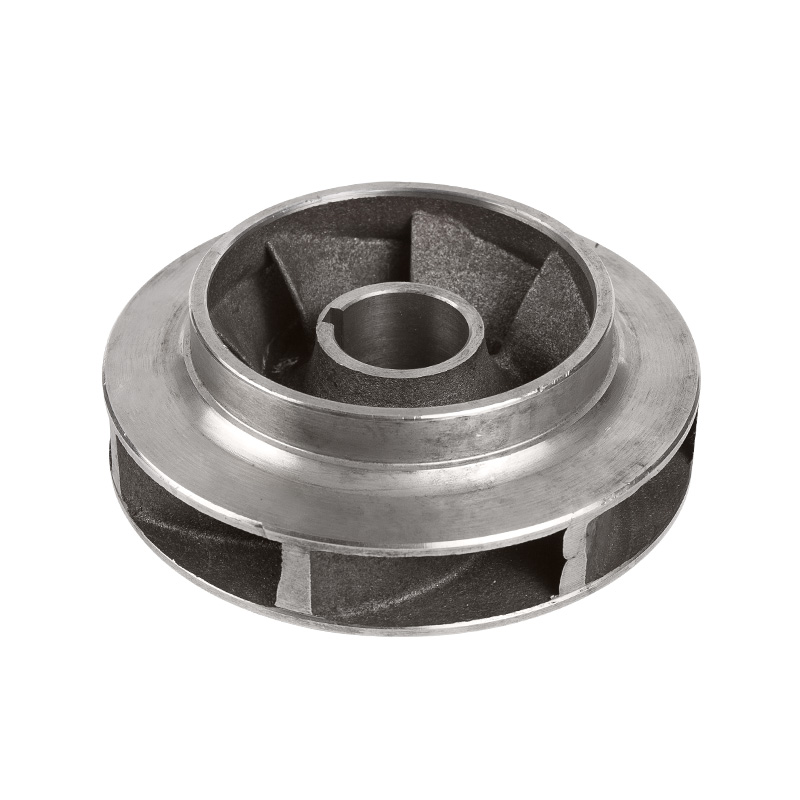

LG multi-stage pump stainless steel impeller
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Stainless steel impellers are impellers made of stainless steel materi...
See Details -
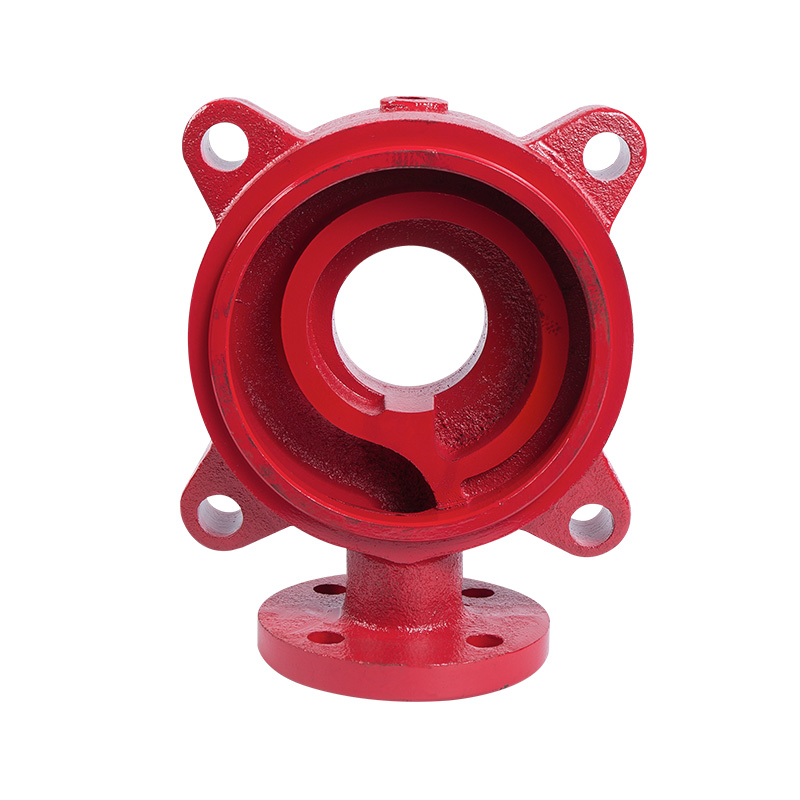

LG multi-stage pump water outlet section
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
The outlet section is the outlet part of the pump, which is responsibl...
See Details -
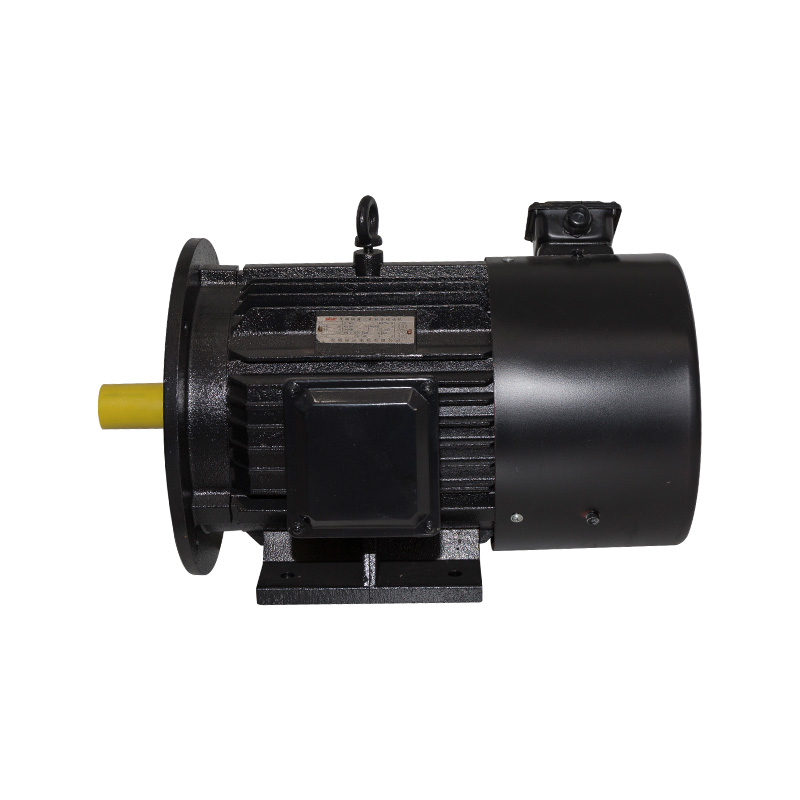

B3/B35 Horizontal inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -
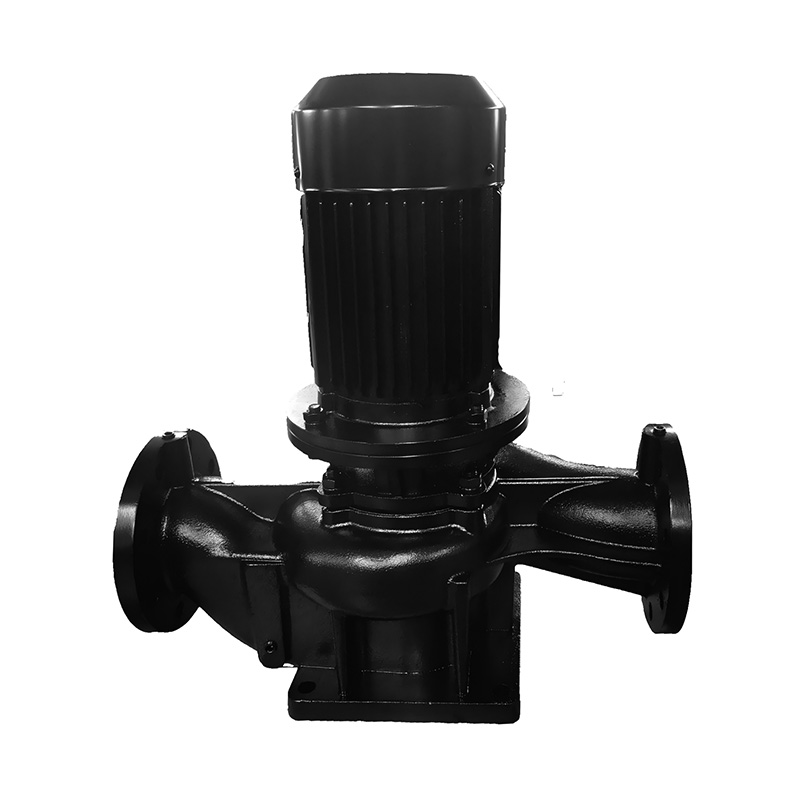

Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

