- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
What Is a Pipeline Pump and How Does It Work?
In many fields such as water supply, HVAC, fire protection, petrochemical, industrial circulation, etc., pipeline pump is a very common and important fluid conveying equipment. It is widely used in various conveying systems because of its convenient installation, compact structure and stable operation. Whether it is the water supply system of high-rise buildings or the liquid circulation system of complex factories, pipeline pumps play an irreplaceable role.
1. What is a pipeline pump?
Pipeline pump, also known as vertical pipeline centrifugal pump or inline pump, is a pump equipment designed to install the pump body coaxially with the pipeline axis. Its biggest feature is that the inlet and outlet diameters of the pump are the same and on the same axis. It can be incorporated into the pipeline system like ordinary pipelines without occupying additional space and foundation.
Features summary:
The pump body is installed coaxially with the pipeline, with a compact structure
Small footprint, easy installation and maintenance
Can be used in series to increase pressure
Applicable to a variety of media such as clean water, hot water, and lightly corrosive liquids
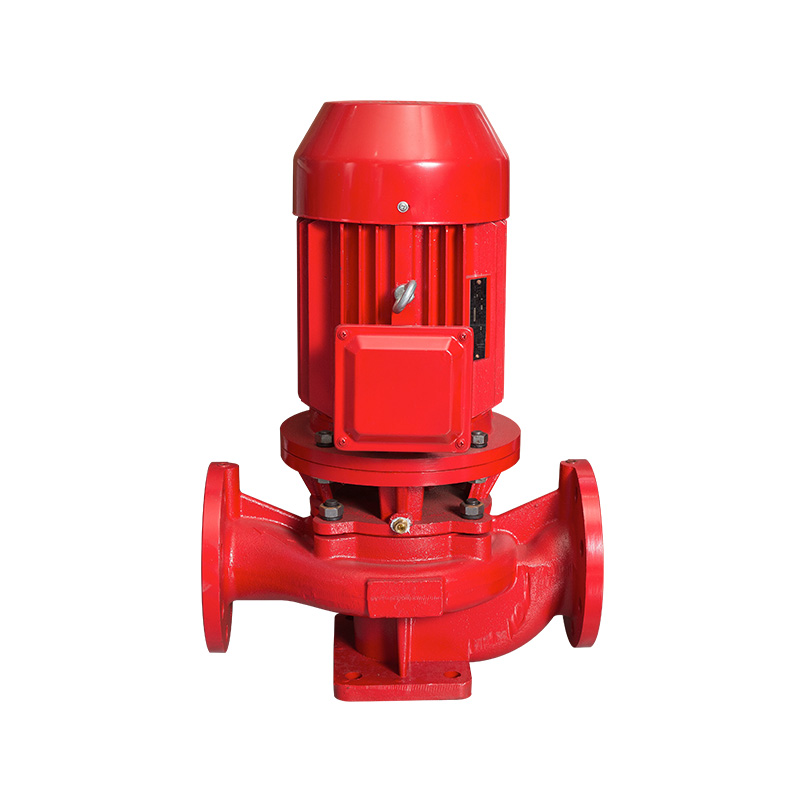

2. Working principle of pipeline pump
Basic principle:
The pipeline pump is a type of centrifugal pump (Centrifugal Pump), and its core principle is:
Use the centrifugal force generated by the high-speed rotation of the impeller to suck the liquid into the pump body and throw it out, thereby realizing the process of transporting the fluid from a low place to a high place.
The detailed workflow is as follows:
Start the motor: the drive shaft drives the impeller to rotate;
The liquid enters the center of the impeller (inlet);
The impeller rotates to generate centrifugal force: the liquid moves from the center to the outside along the blades;
The liquid is thrown out of the outer edge of the pump casing (outlet), and the kinetic energy is converted into pressure energy;
The liquid is transported to the target system along the pipeline.
Since the inlet and outlet are located on the same straight line, the liquid flows more smoothly and the energy loss is small, which is particularly suitable for medium and short distance and high-frequency transportation tasks.
3. Main structural components of pipeline pumps
Motor part: drives the pump shaft to rotate, usually a vertical motor;
Pump housing: encapsulates the impeller and guide part, usually made of cast iron or stainless steel;
Impeller: core component, determines flow and head;
Bearing and sealing system: ensures smooth operation of the shaft and prevents leakage;
Base/bracket: some models are equipped with an adjustable base for stable installation;
Cooling system (optional): used in high temperature conditions.
4. Common types of pipeline pumps
According to different uses and structures, pipeline pumps can be divided into the following types:
1. ISG pipeline centrifugal pump (single-stage clean water pump)
For clean water or liquids with physical and chemical properties similar to water
Applied to water supply, fire protection, and domestic water systems
2. IRG hot water pipeline pump
Suitable for high-temperature hot water circulation
Commonly used in boilers, water heating systems, and air conditioning systems
3. IHG chemical pipeline pump
Corrosion-resistant material, can transport corrosive liquids such as weak acids and alkalis
Used in chemical, pharmaceutical, and food industries
4. YG oil pump
Can transport diesel, gasoline, lubricating oil, etc.
Applicable to oil transportation systems
5. Advantages of pipeline pumps
Space saving Integrated installation with pipelines, suitable for small spaces or equipment-intensive areas
Easy installation No need to build a foundation, quickly connect to the original pipeline
Easy maintenance Some models support the "disassembly-free motor replacement" design
Low noise Most use vertical structure with low vibration
A variety of materials are available Stainless steel, cast iron, alloy steel, suitable for different media
Can be pressurized in series Multiple units in series can increase the head and meet the water supply needs of high-rise buildings
6. the key points of pipeline pump selection
When choosing a suitable pipeline pump, the following parameters should be considered:
Flow rate (m³/h): the required delivery volume of the system;
Head (m): the height or system pressure loss to be overcome;
Medium type and temperature: determine whether it is corrosion-resistant and high-temperature;
Pressure level: the maximum working pressure of the pipeline system;
Inlet and outlet diameter: match the existing pipeline system;
Control method: whether a frequency converter, constant pressure control, etc. are required;
Material requirements: whether all stainless steel, rubber lining, 316L, etc. are required;
Installation position: determine whether it can be installed vertically or horizontally.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can pipeline pumps be installed horizontally?
A: Most pipeline pumps are designed for vertical installation, but some models (such as horizontal pipeline pumps) can be installed horizontally, and the manufacturer's specifications need to be consulted.
Q2: Can it convey liquids with particles or high viscosity?
A: It is generally not recommended to transport liquids containing solid particles, otherwise the impeller is easily worn. You can consider self-priming pumps or mud pumps.
Q3: How to extend the service life of pipeline pumps?
A: Regularly check the shaft seal and bearing lubrication to ensure that no air enters the system to avoid dry operation.
As one of the core equipment in modern fluid transportation systems, pipeline pumps play an indispensable role in urban buildings, industrial systems and public infrastructure with their compact structure, stable operation and convenient installation. Through reasonable selection, correct installation and scientific maintenance, pipeline pumps can not only effectively improve system efficiency, but also save a lot of operating costs.
Related Products
-
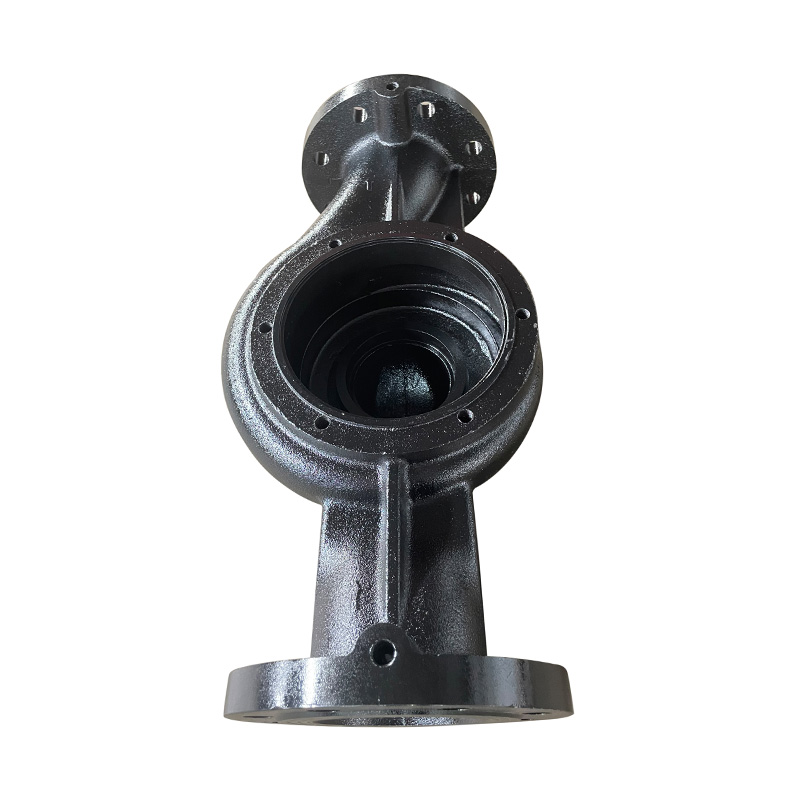

Vertical TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump body
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
Vertical TD Energy Efficient Circulating Pump Pump Body is the shell o...
See Details -
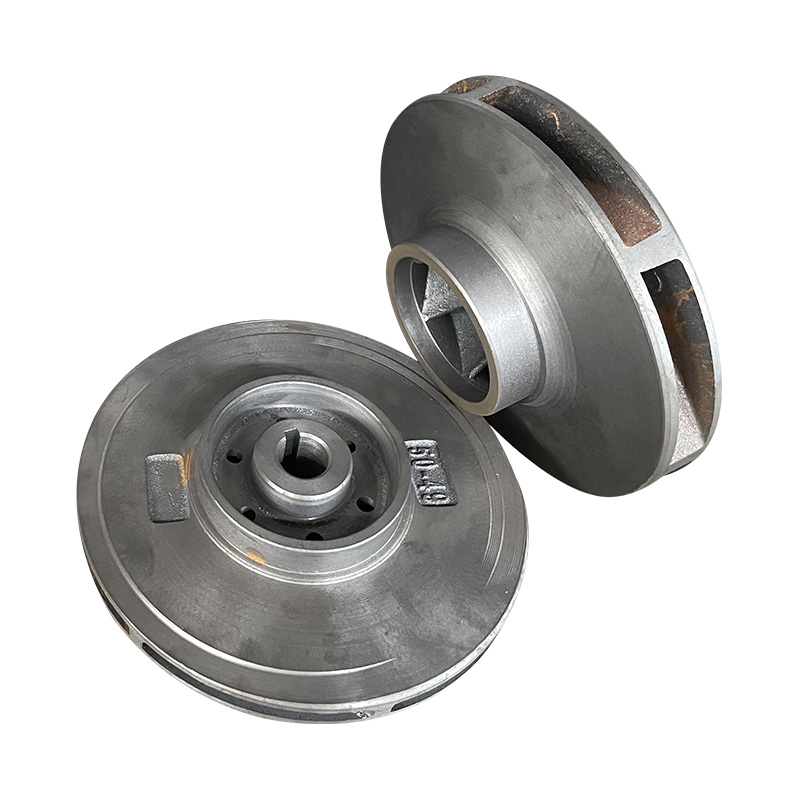

TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulating pump cast iron impeller
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
TD Energy Efficient Circulation Pump Cast Iron Impeller is an importan...
See Details -

TD high efficiency and energy saving circulating pump pump shaft
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
The pump shaft is the component that connects the motor to the impelle...
See Details -
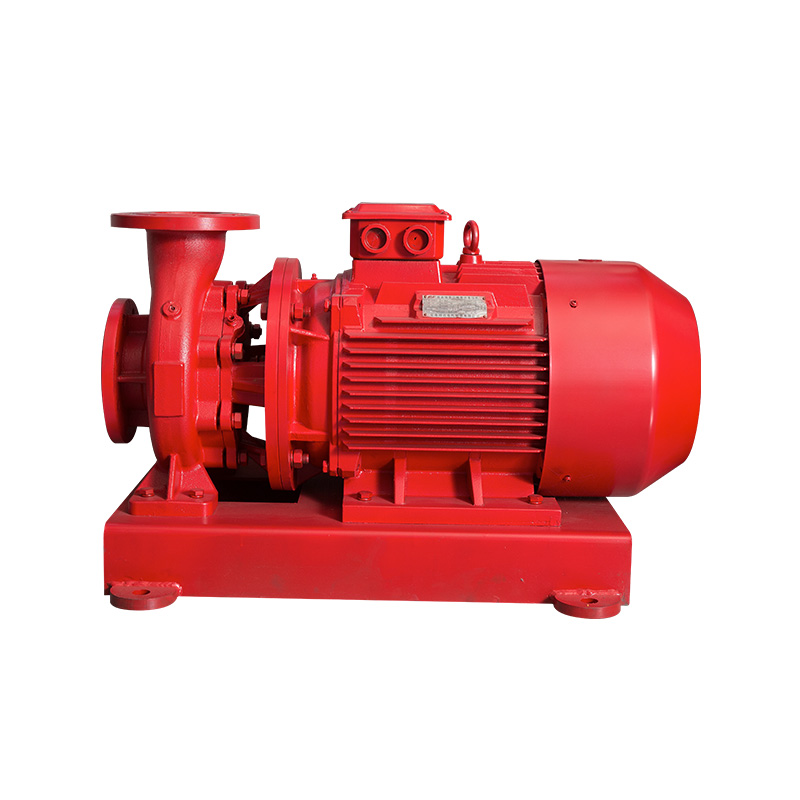

Horizontal pipeline pump
Cat:Pipeline Pump
ISW series single-stage single-suction horizontal centrifugal pumps ar...
See Details -
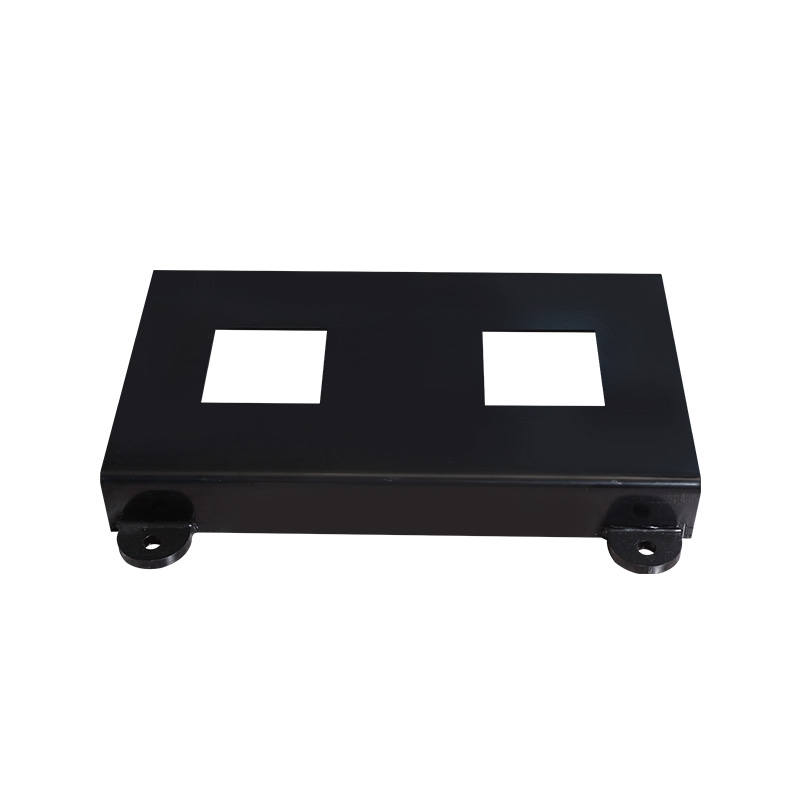

Pipe pump horizontal base
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pump base serves to support and secure the pump casing. Horizontal...
See Details -
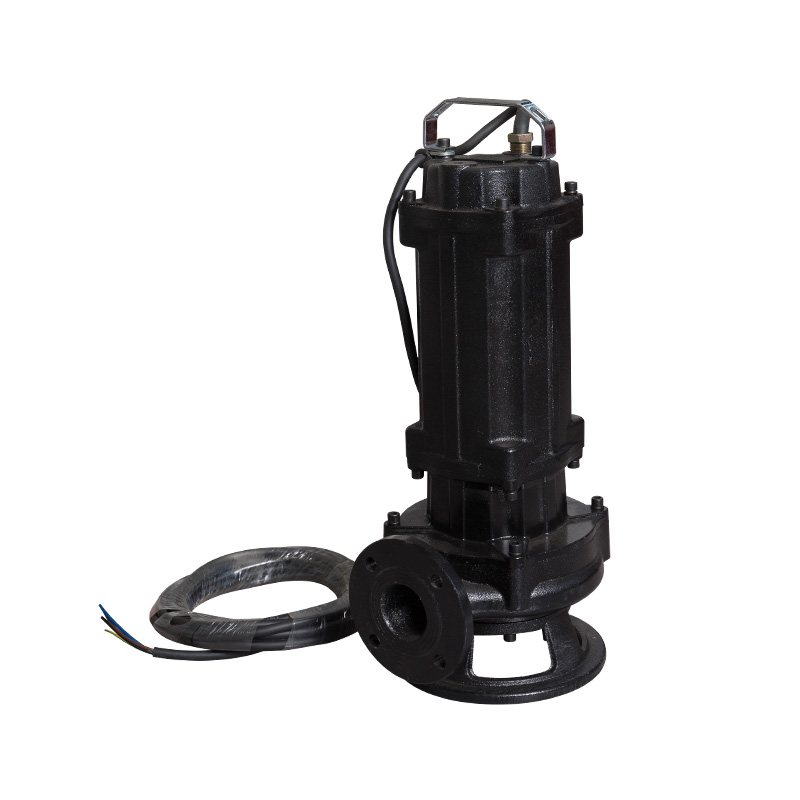

Cutting sewage pump
Cat:Sewage Pump
Cutting sewage pump is a kind of sewage pump, also called cutting pump...
See Details -
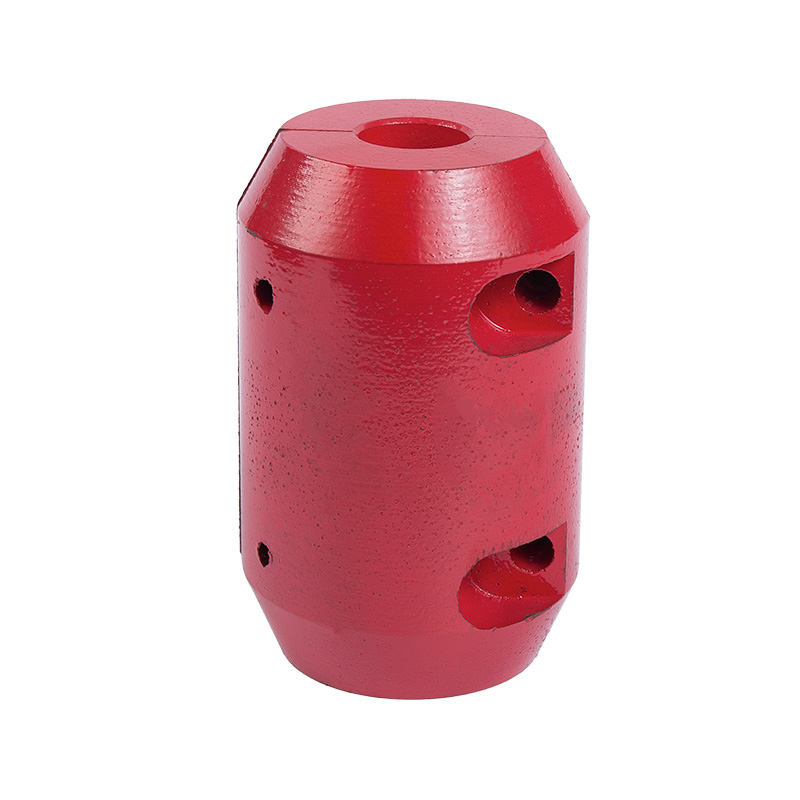

LG multi-stage pump coupling
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Couplings are used to connect the pump shaft to the motor shaft for en...
See Details -
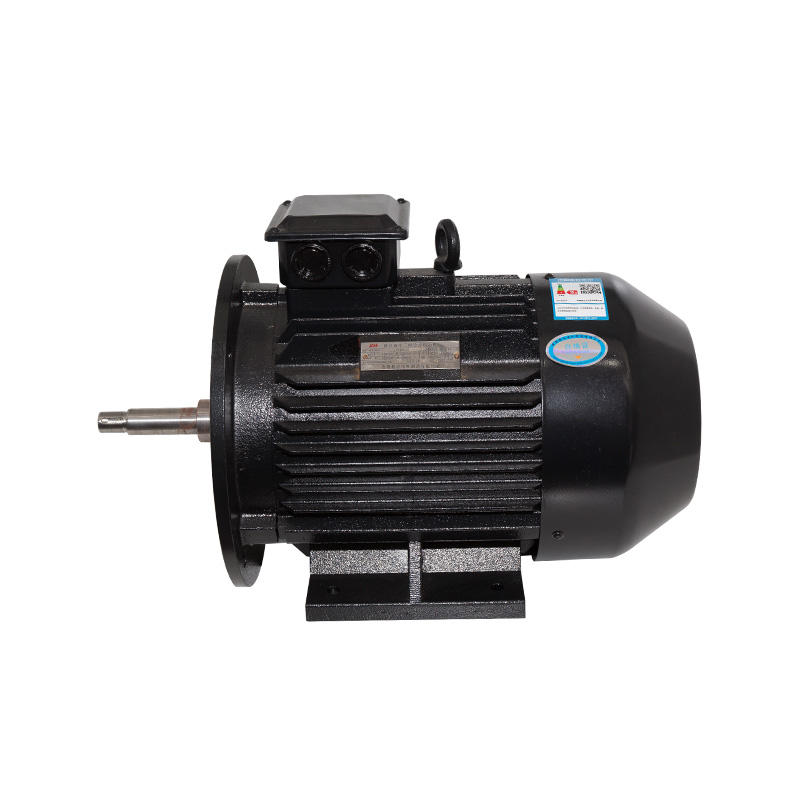

Horizontal motors
Cat:Ordinary Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -
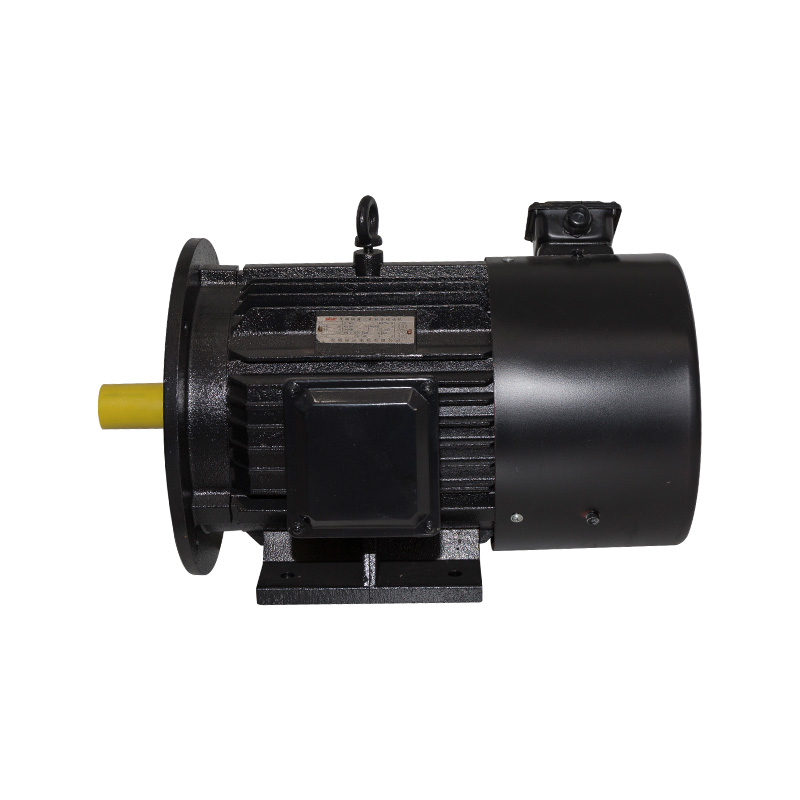

B3/B35 Horizontal inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -
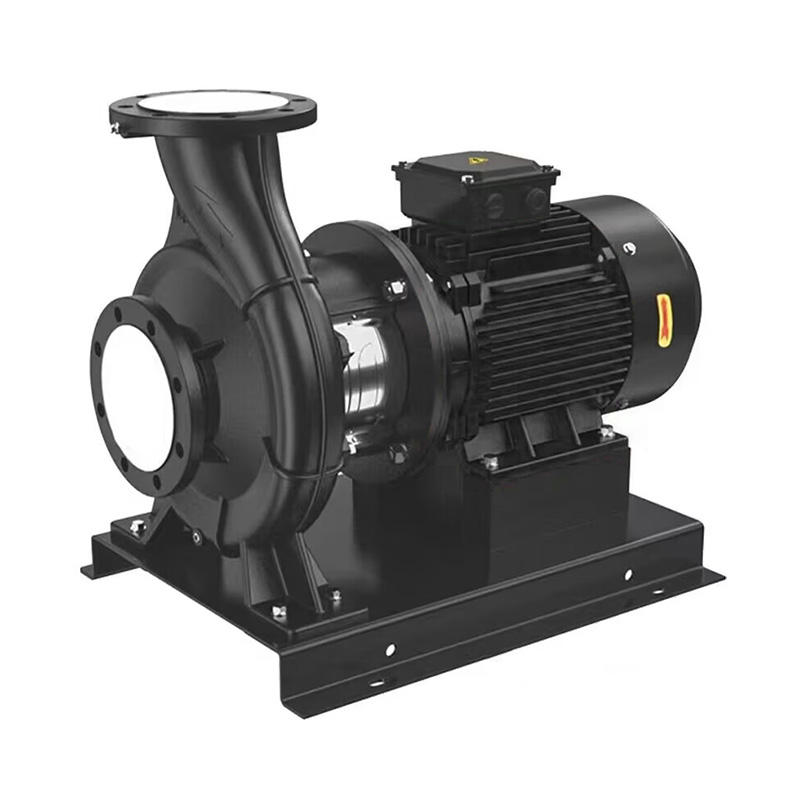

TD horizontal high-efficiency energy-saving circulation pump
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
1.TD horizontal high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump is ...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

