- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Web Menu
- Home
- About Us
- Products
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Powering the Modern World: The Essential Role of Electric Motors
From household appliances to industrial machinery, electric motors are among the most important inventions in modern engineering. These devices convert electrical energy into mechanical motion and are at the heart of countless machines that power our daily lives.
Despite their widespread use and significance, many people take electric motors for granted — rarely considering how they work or just how many of them surround us every day. In this article, we’ll explore what electric motors are, how they function, and why they remain a cornerstone of technology across both residential and commercial applications.
This simple yet powerful principle allows electric motors to drive everything from small handheld tools to massive factory equipment.
The basic operation of an electric motor relies on the interaction between magnetic fields and electric current:
Electromagnetism : A coil wrapped around a metal core becomes an electromagnet when electricity passes through it.
Repulsion and Attraction : The magnetic poles created by the electromagnet interact with permanent magnets or other electromagnets in the motor.
Rotation : This continuous push-and-pull causes the rotor to spin.
Commutator and Brushes (in DC motors): These components reverse the direction of current periodically to maintain continuous motion.
In AC motors, the alternating current naturally changes direction, eliminating the need for a commutator and enabling smooth, long-lasting operation.
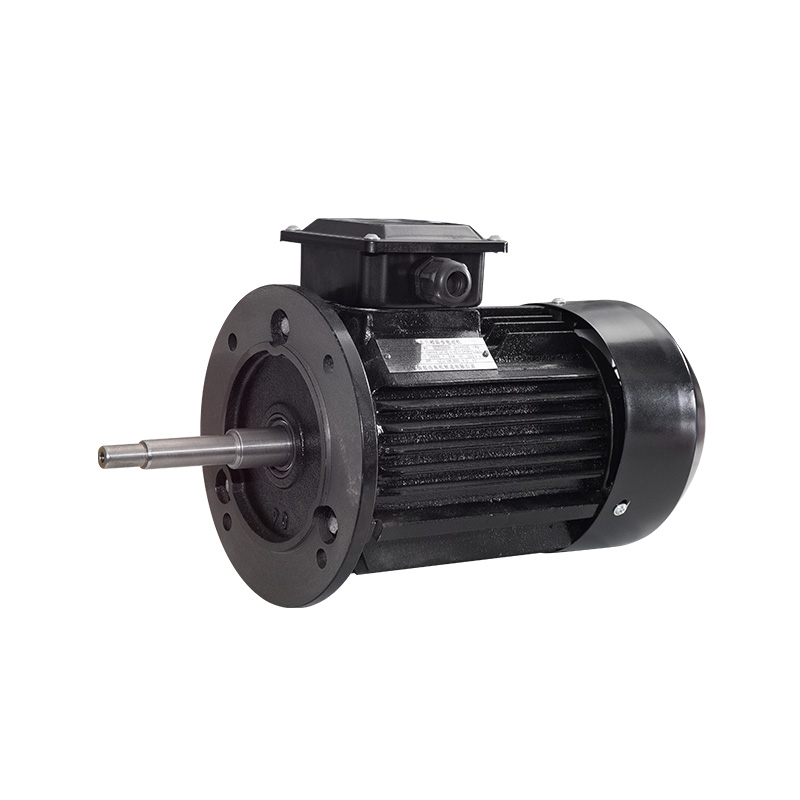

Types of Electric Motors
There are several types of electric motors, each suited for specific applications:
AC Motors : Ideal for constant-speed applications like pumps, fans, compressors, and industrial machinery.
DC Motors : Used where speed control is essential, such as electric vehicles, robotics, and precision tools.
Brushless DC Motors (BLDC) : More efficient and durable than brushed versions, commonly found in drones, electric cars, and hard drives.
Stepper Motors : Provide precise positioning, used in 3D printers, CNC machines, and automated manufacturing systems.
Servo Motors : Combine a motor with a feedback system for high accuracy, widely used in automation and robotics.
Common Applications of Electric Motors
Electric motors are everywhere — often hidden in plain sight:
Home Appliances : Washing machines, refrigerators, air conditioners, vacuum cleaners
Transportation : Electric vehicles, trains, elevators, conveyors
Industry : Pumps, compressors, conveyor belts, assembly lines
Consumer Electronics : Smartphones, laptops, drones, toys
Renewable Energy Systems : Wind turbines, solar tracking systems
Their versatility makes them indispensable in modern society.
Electric motors may not always be visible, but their influence is undeniable. They power the technologies we rely on, improve efficiency in manufacturing, reduce energy consumption, and enable innovation in areas like automation and renewable energy.
As the world moves toward electrification and smarter systems, the importance of electric motors will only continue to grow. Whether you're an engineer, student, or simply curious about how things work, understanding the basics of electric motors opens the door to appreciating the technology that drives our modern world.
Related Products
-
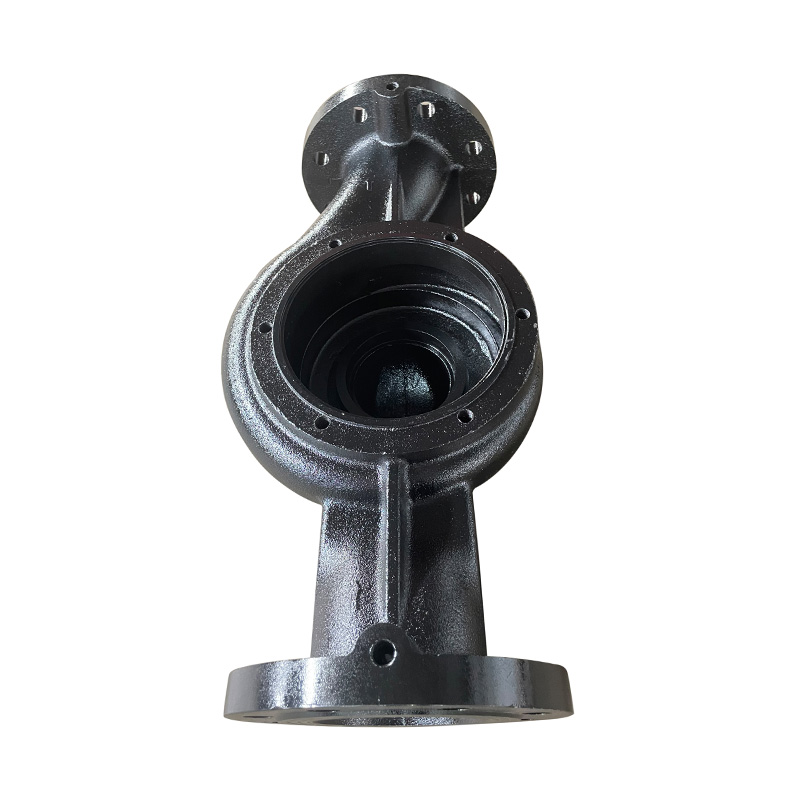

Vertical TD high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump body
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
Vertical TD Energy Efficient Circulating Pump Pump Body is the shell o...
See Details -

Pipeline pump B14 pump cover
Cat:Pipeline Pump Accessories
The pipeline pump B14 pump cover is a specific type of pump cover for ...
See Details -
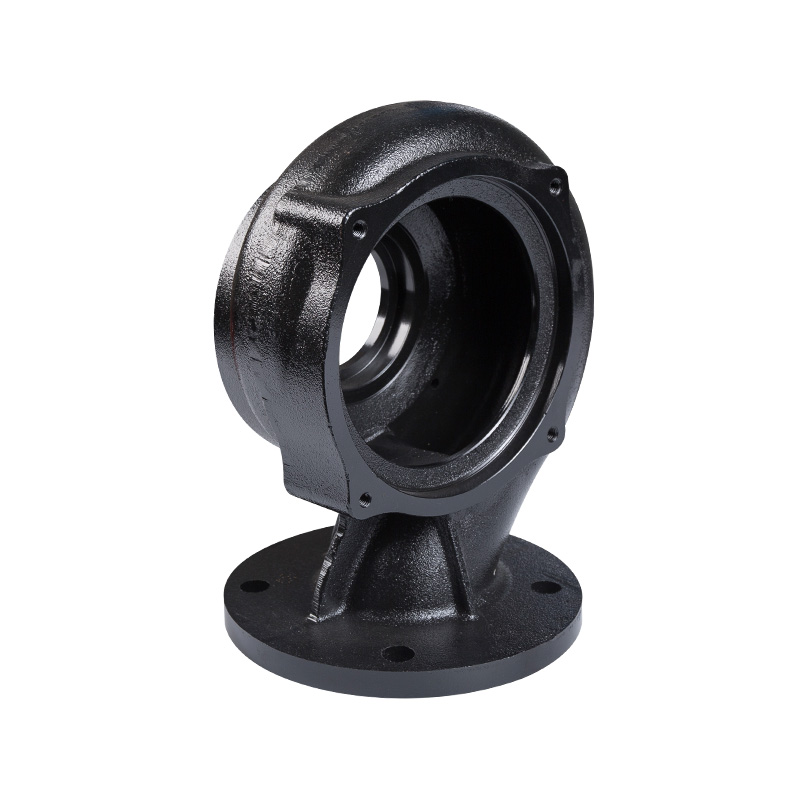

Sewage pump body
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
The pump body is the outer shell of the sewage pump, with the function...
See Details -
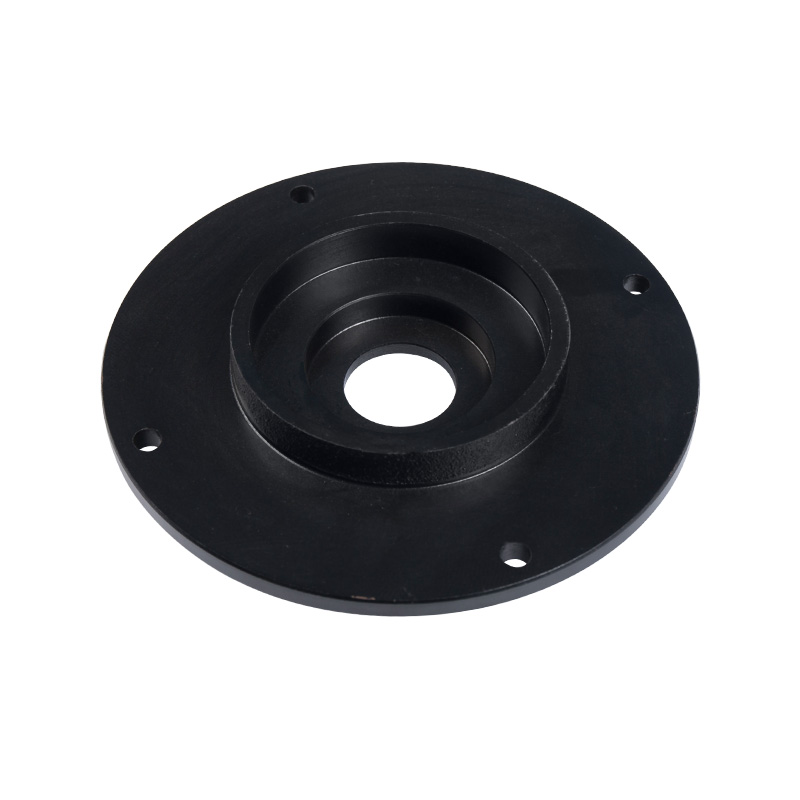

Sewage pump cover
Cat:Sewage Pump Accessories
Installed on the top of the sewage pump unit, it is used to enclose th...
See Details -
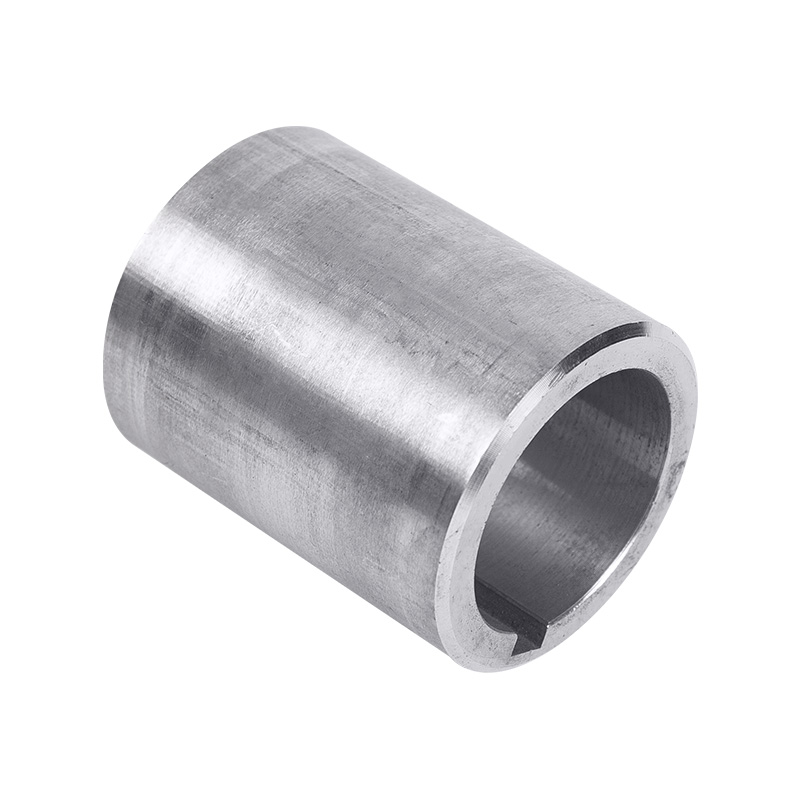

LG multi-stage pump spacer sleeve
Cat:LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
Spacer sleeve is a ring-shaped part installed between the impellers of...
See Details -
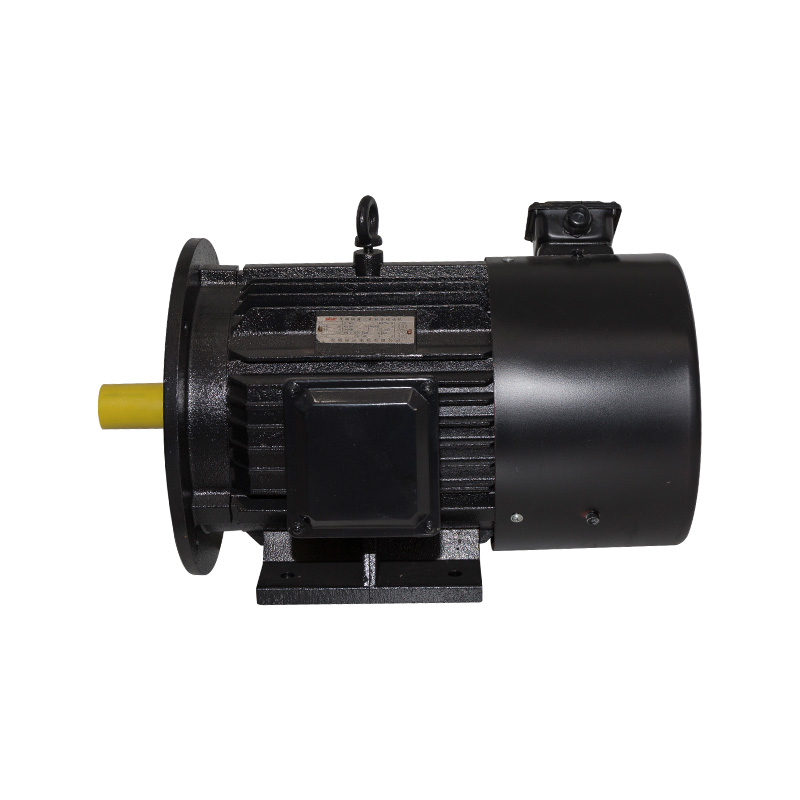

B3/B35 Horizontal inverter motor
Cat:Inverter Electric Motor
Also known as base mounting, the motor is connected to the mounting da...
See Details -
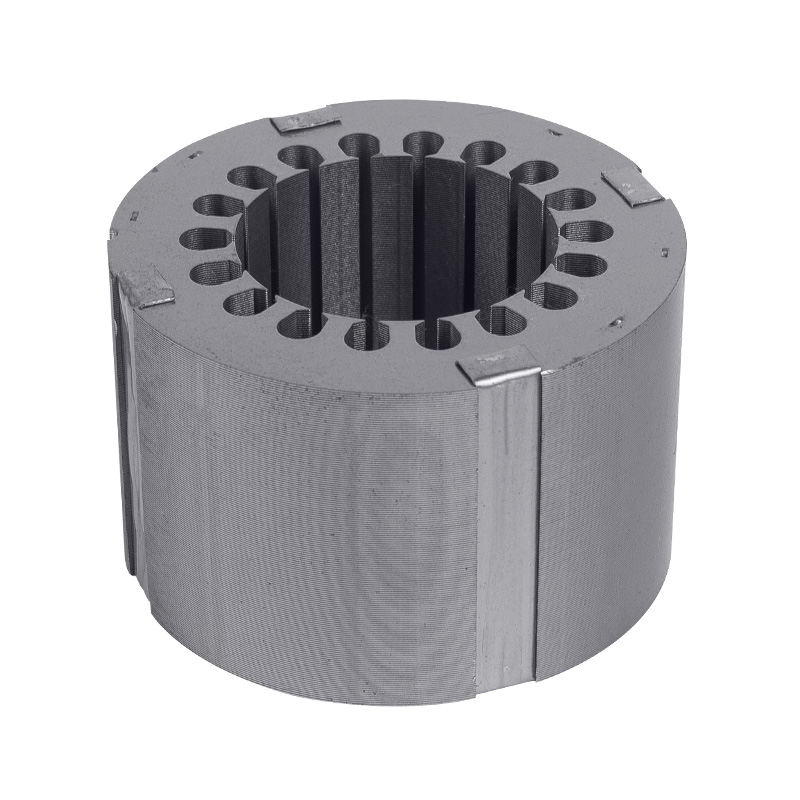

Motor core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A common motor structure, the stator is fixed by the iron core structu...
See Details -
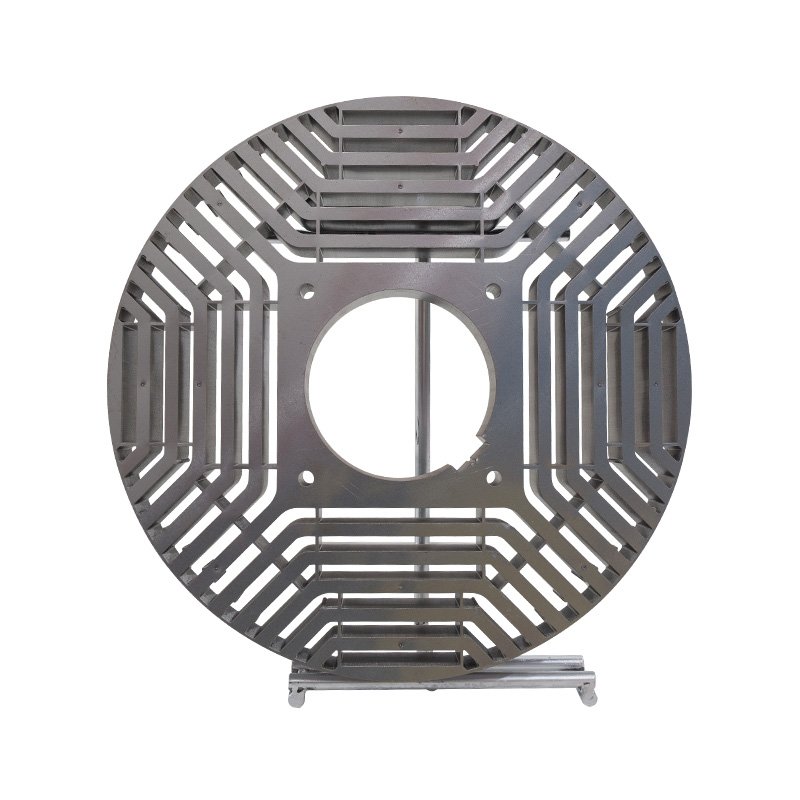

Permanent magnet core stator and rotor
Cat:Electric Motor Accessories
A type of rotor core that uses a permanent magnet material to achieve ...
See Details -
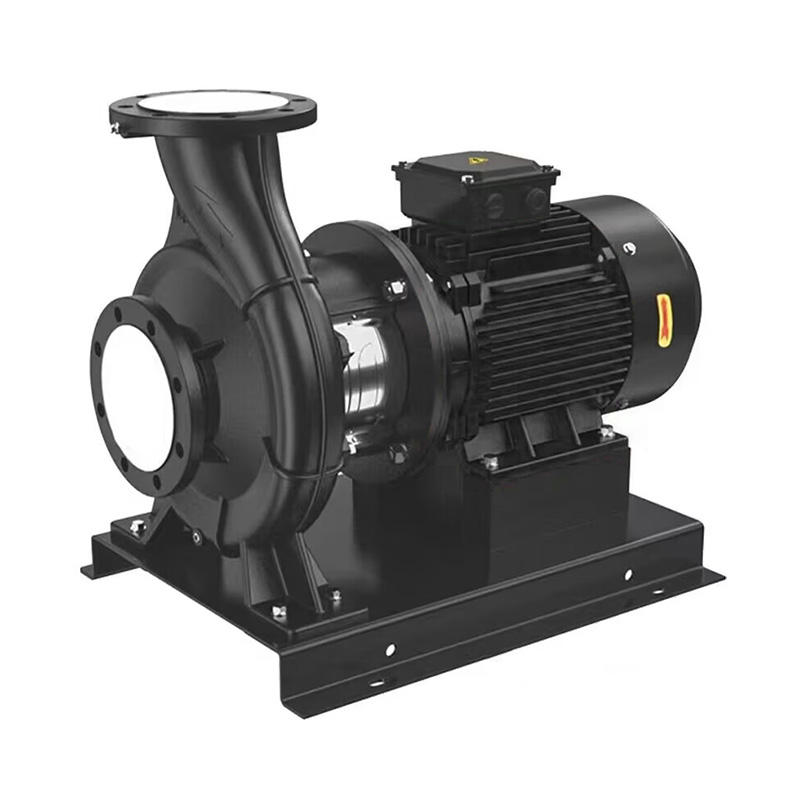

TD horizontal high-efficiency energy-saving circulation pump
Cat:TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
1.TD horizontal high-efficiency and energy-saving circulation pump is ...
See Details -
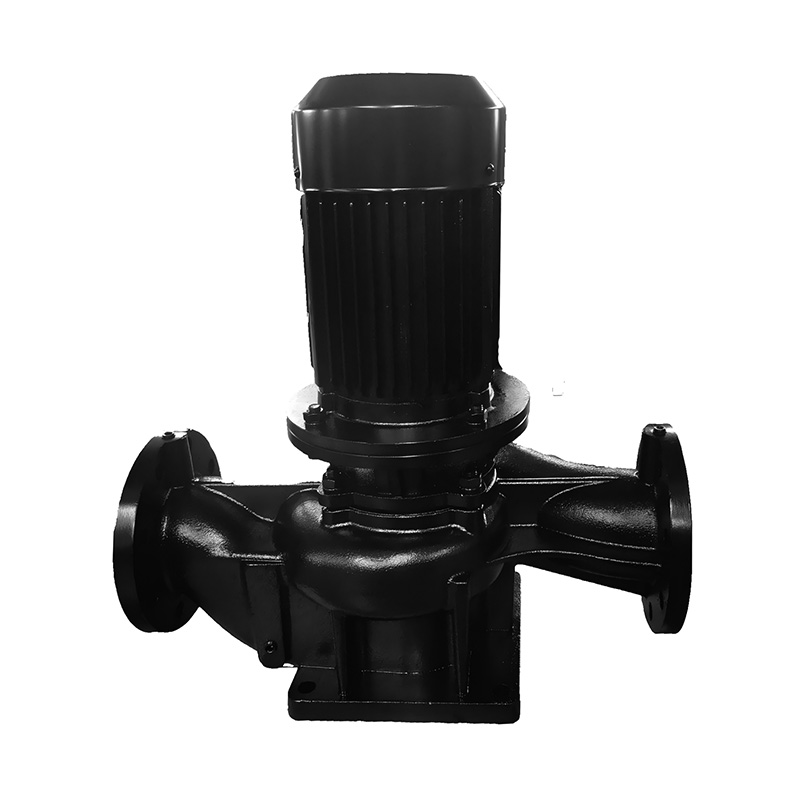

Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
Cat:Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
The cooling tower circulation pump is key equipment in the cooling tow...
See Details
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump
- TD High-efficiency And Energy-saving Circulating Pump Accessories
- Pipeline Pump
- Pipeline Pump Accessories
- Sewage Pump
- Sewage Pump Accessories
- LG Multi-stage Pump
- LG Multi-stage Pump Accessories
- Cooling Tower Circulation Pump
- Electric Motor
- Electric Motor Accessories
-

+86-0563-2251312
-
+86-0563-2251311
-

+86-139 6620 0379
-
-

No.43 Guohua Road, Guangde Economic Development Zone, Xuancheng City, Anhui Province, China

